
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa, with an area of 28,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi). Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name evokes its location near both the Equator and the Gulf of Guinea. As of 2021, the country had a population of 1,468,777.
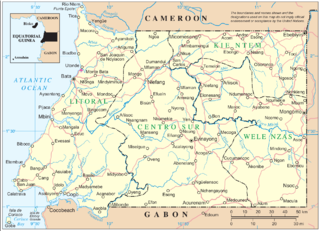
Río Muni is the Continental Region of Equatorial Guinea, and comprises the mainland geographical region, covering 26,017 square kilometres (10,045 sq mi). The name is derived from the Muni River, along which the early Europeans had built the Muni River Settlements.

Annobón, and formerly as Anno Bom and Annabona, is a province of Equatorial Guinea consisting of the island of Annobón, formerly also Pigalu and Pagalu, and its associated islets in the Gulf of Guinea. According to the 2015 census, Annobón had 5,314 inhabitants, a small population increase from the 5,008 registered by the 2001 census. The official language is Spanish but most of the inhabitants speak a creole form of Portuguese. The island's main industries are fishing and forestry.

Bioko Sur is a province of Equatorial Guinea. Its capital is Luba. It occupies the southern part of the island of Bioko, the remainder of which is part of Bioko Norte.

Kié-Ntem is a province of Equatorial Guinea. Its capital is Ebebiyín.

Litoral is the most populous province of Equatorial Guinea, recording a population of 367,348 in the 2015 national census. Its capital is Bata; the other two cities are Mbini and Kogo.
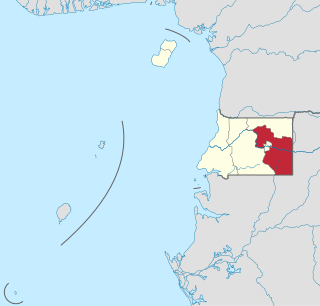
Wele-Nzas Province is a province in the eastern portion of continental Equatorial Guinea. Its capital is Mongomo. It borders the Equatoguinean provinces of Centro Sur to the west and Kié-Ntem to the north, with Gabon's Woleu-Ntem Province to the east and south. As of 2015, the population of Wele-Nzas was 192,017. It derives its name from the Benito River and the Piedra Nzas mountain range.
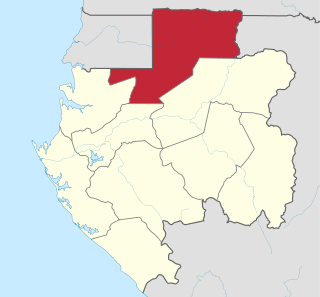
Woleu-Ntem is the northernmost of Gabon's nine provinces. It covers an area of 38,465 km2 and named after Woleu and Ntem rivers that cross it. The provincial capital is Oyem, which had a total of 60,685 inhabitants in 2013.

The Catholic Church in Equatorial Guinea is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome.

Articles related to Equatorial Guinea include:
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Ebibeyín is a diocese in the Ecclesiastical province of Malabo, yet depends on the missionary Roman Congregation for the Evangelization of Peoples.

Ntem is a department of Woleu-Ntem Province in northern Gabon. The capital lies at Bitam. It borders Equatorial Guinea and Cameroon. It had a population of 49,712 in 2013.
According to Article 3 of the Constitution of Equatorial Guinea, the country is divided for administrative and economic purposes into regions, provinces, districts, and municipalities. In practice, the provinces serve as the first-level administrative divisions. Municipalities are subdivided into village councils and neighbourhood communities. Many of the sub-municipal entities are grouped into urban districts, which remain subordinate to municipalities and are distinct from districts proper.

Estuaire is the most populous of Gabon's nine provinces. It covers an area of 20,740 km2. The provincial capital is Libreville, which is also Gabon's national capital. The province is named for the Gabon Estuary, which lies at the heart of the province.
The Ebebiyín Cathedral is a religious building belonging to the Catholic Church and is located in the province of Kié-Ntem in the northeast of the mainland of Equatorial Guinea near its border with Cameroon and Gabon.

The Navy of Equatorial Guinea is the maritime component of the Armed Forces of Equatorial Guinea. Its main functions are anti-piracy operations in the Gulf of Guinea and protecting the offshore oil and gas assets of the nation. The Navy has around 200 personnel.
The Diocese of Evinayong is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or diocese of the Catholic Church in Equatorial Guinea. It is a suffragan diocese in the ecclesiastical province of the metropolitan Archdiocese of Malabo, yet depends on the missionary Roman Congregation for the Evangelization of Peoples.
The vehicle registration plates of Equatorial Guinea is a legal form requiring the citizens of Equatorial Guinea to have the car registered.
Cecilia Akeng Ñengono or Cecilia Akeng Nguema is an Equatorial Guinean footballer who plays as a defender for Deportivo Evinayong and the Equatorial Guinea women's national team.

Equatorial Guinea–Venezuela relations refers to international relations between Equatorial Guinea and Venezuela. In both countries the official language is Spanish and they have an important economic activity based on oil extraction.















