Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology.
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of ether bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
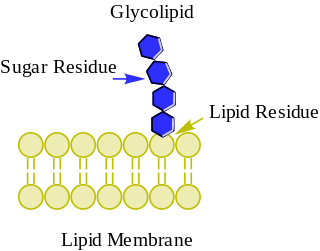
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.
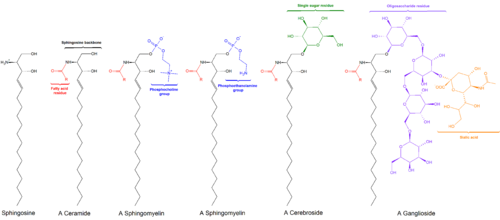
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, which are a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. These compounds play important roles in signal transduction and cell recognition. Sphingolipidoses, or disorders of sphingolipid metabolism, have particular impact on neural tissue. A sphingolipid with a terminal hydroxyl group is a ceramide. Other common groups bonded to the terminal oxygen atom include phosphocholine, yielding a sphingomyelin, and various sugar monomers or dimers, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively. Cerebrosides and globosides are collectively known as glycosphingolipids.

Sphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphocholine and ceramide, or a phosphoethanolamine head group; therefore, sphingomyelins can also be classified as sphingophospholipids. In humans, SPH represents ~85% of all sphingolipids, and typically make up 10–20 mol % of plasma membrane lipids.
Glycosphingolipids are a subtype of glycolipids containing the amino alcohol sphingosine. They may be considered as sphingolipids with an attached carbohydrate. Glycosphingolipids are a group of lipids and are a part of the cell membrane. They consist of a hydrophobic ceramide part and a glycosidically bound carbohydrate part. This oligosaccharide content remains on the outside of the cell membrane where it is important for biological processes such as cell adhesion or cell–cell interactions. Glycosphingolipids play also important role in oncogenesis and ontogenesis.

A ganglioside is a molecule composed of a glycosphingolipid with one or more sialic acids linked on the sugar chain. NeuNAc, an acetylated derivative of the carbohydrate sialic acid, makes the head groups of gangliosides anionic at pH 7, which distinguishes them from globosides.

Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of sphingosine and a fatty acid joined by an amide bond. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells.

β-Glucocerebrosidase is an enzyme with glucosylceramidase activity that cleaves by hydrolysis the β-glycosidic linkage of the chemical glucocerebroside, an intermediate in glycolipid metabolism that is abundant in cell membranes. It is localized in the lysosome, where it remains associated with the lysosomal membrane. β-Glucocerebrosidase is 497 amino acids in length and has a molecular mass of 59,700 Da.

Glucocerebroside is any of the cerebrosides in which the monosaccharide head group is glucose.

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological cell signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes. One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized "on demand" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.
Sulfatide, also known as 3-O-sulfogalactosylceramide, SM4, or sulfated galactocerebroside, is a class of sulfolipids, specifically a class of sulfoglycolipids, which are glycolipids that contain a sulfate group. Sulfatide is synthesized primarily starting in the endoplasmic reticulum and ending in the Golgi apparatus where ceramide is converted to galactocerebroside and later sulfated to make sulfatide. Of all of the galactolipids that are found in the myelin sheath, one fifth of them are sulfatide. Sulfatide is primarily found on the extracellular leaflet of the myelin plasma membrane produced by the oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and in the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. However, sulfatide is also present on the extracellular leaflet of the plasma membrane of many cells in eukaryotic organisms.
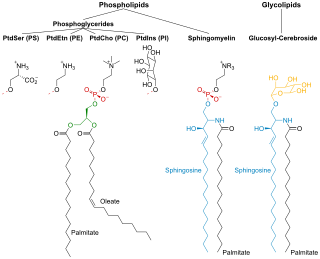
Membrane lipids are a group of compounds which form the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The three major classes of membrane lipids are phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol. Lipids are amphiphilic: they have one end that is soluble in water ('polar') and an ending that is soluble in fat ('nonpolar'). By forming a double layer with the polar ends pointing outwards and the nonpolar ends pointing inwards membrane lipids can form a 'lipid bilayer' which keeps the watery interior of the cell separate from the watery exterior. The arrangements of lipids and various proteins, acting as receptors and channel pores in the membrane, control the entry and exit of other molecules and ions as part of the cell's metabolism. In order to perform physiological functions, membrane proteins are facilitated to rotate and diffuse laterally in two dimensional expanse of lipid bilayer by the presence of a shell of lipids closely attached to protein surface, called annular lipid shell.

A galactosylceramide, or galactocerebroside is a type of cerebroside consisting of a ceramide with a galactose residue at the 1-hydroxyl moiety.
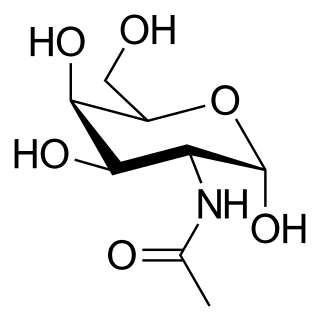
Globosides are a sub-class of the lipid class glycosphingolipid with three to nine sugar molecules as the side chain of ceramide. The sugars are usually a combination of N-acetylgalactosamine, D-glucose or D-galactose. One characteristic of globosides is that the "core" sugars consists of Glucose-Galactose-Galactose (Ceramide-βGlc4-1βGal4-1αGal), like in the case of the most basic globoside, globotriaosylceramide (Gb3), also known as pk-antigen. Another important characteristic of globosides is that they are neutral at pH 7, because they usually do not contain neuraminic acid, a sugar with an acidic carboxy-group. However, some globosides with the core structure Cer-Glc-Gal-Gal do contain neuraminic acid, e.g. the globo-series glycosphingolipid "SSEA-4-antigen".
Myelinogenesis is the formation and development of myelin sheaths in the nervous system, typically initiated in late prenatal neurodevelopment and continuing throughout postnatal development. Myelinogenesis continues throughout the lifespan to support learning and memory via neural circuit plasticity as well as remyelination following injury. Successful myelination of axons increases action potential speed by enabling saltatory conduction, which is essential for timely signal conduction between spatially separate brain regions, as well as provides metabolic support to neurons.
In enzymology, a 2-hydroxyacylsphingosine 1-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Ceramide glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UGCG gene.

2-hydroxyacylsphingosine 1-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UGT8 gene.

The Lactosylceramides, also known as LacCer, are a class of glycosphingolipids composed of a variable hydrophobic ceramide lipid and a hydrophilic sugar moiety. Lactosylceramides are found in microdomains on the plasma layers of numerous cells. Moreover, they are a type of ceramide including lactose, which is an example of a globoside.