
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood or with pus.

A callus is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.

Irritation, in biology and physiology, is a state of inflammation or painful reaction to allergy or cell-lining damage. A stimulus or agent which induces the state of irritation is an irritant. Irritants are typically thought of as chemical agents but mechanical, thermal (heat), and radiative stimuli can also be irritants. Irritation also has non-clinical usages referring to bothersome physical or psychological pain or discomfort.

Tinea cruris, also known as jock itch, is a common type of contagious, superficial fungal infection of the groin and buttocks region, which occurs predominantly but not exclusively in men and in hot-humid climates.
Heat exhaustion is a heat-related illness characterized by the body's inability to effectively cool itself, typically occurring in high ambient temperatures or during intense physical exertion. In heat exhaustion, core body temperature ranges from 37 °C to 40 °C. Symptoms include profuse sweating, weakness, dizziness, headache, nausea, and lowered blood pressure, resulting from dehydration and serum electrolyte depletion. Heat-related illnesses lie on a spectrum of severity, where heat exhaustion is considered less severe than heat stroke but more severe than heat cramps and heat syncope.

Miliaria, commonly known as heat rash, sweat rash, or prickly heat, is a skin disease marked by small, itchy rashes due to sweat trapped under the skin by clogged sweat-gland ducts. Miliaria is a common ailment in hot and humid conditions, such as in the tropics and during the summer. Although it affects people of all ages, it is especially common in children and infants due to their underdeveloped sweat glands.

A rash guard, also known as rash vest or rashie, is an athletic shirt made of spandex and nylon or polyester. The name rash guard reflects the fact that the shirt protects the wearer against rashes caused by abrasion, or by sunburn from extended exposure to the sun, as sun protective clothing.

Pasties are patches that cover a person's nipples and areolae, typically self-adhesive or affixed with adhesive. They are usually worn in pairs. They originated as part of burlesque shows, allowing dancers to perform fully topless without exposing the nipples in order to provide a commercial form of bare-breasted entertainment. Pasties are also, at times, used while sunbathing, worn by strippers and showgirls, or as a form of protest during women's rights events such as Go Topless Day. In some cases this is to avoid potential prosecution under indecency laws.

Cycling shorts are short, skin-tight garments designed to improve comfort and efficiency while cycling.
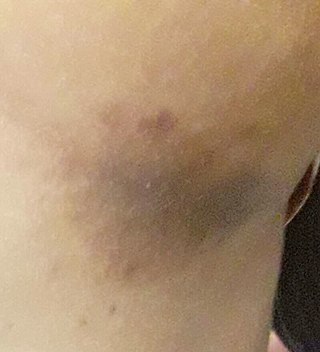
Erythrasma is a superficial skin infection that causes brown, scaly skin patches. It is caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum bacteria, a normal part of skin flora.

Outdoor recreation, such as hiking, camping, canoeing, cycling, or skiing, entails risks, even if participants do not recklessly place themselves in harm's way. In some circumstances, such as being in remote locations or in extreme weather conditions, even a minor accident may create a dangerous situation that requires survival skills. However, with correct precautions, even fairly adventurous outdoor recreation can be enjoyable and safe.

Sportswear or activewear is athletic clothing, including footwear, worn for sports activity or physical exercise. Sport-specific clothing is worn for most sports and physical exercise, for practical, comfort or safety reasons.
Pruritus ani is the irritation of the skin at the exit of the rectum, known as the anus, causing the desire to scratch. The intensity of anal itching increases from moisture, pressure, and rubbing caused by clothing and sitting. At worst, anal itching causes intolerable discomfort that often is accompanied by burning and soreness. It is estimated that up to 5% of the population of the United States experiences this type of discomfort daily.

A friction burn is a form of abrasion caused by the friction of skin rubbing against a surface. A friction burn may also be referred to as skinning, chafing, or a term named for the surface causing the burn such as rope burn, carpet burn or rug burn. Because friction generates heat, extreme cases of chafing may result in genuine thermal burning of the outer layers of skin.

Heat illness is a spectrum of disorders due to increased body temperature. It can be caused by either environmental conditions or by exertion. It includes minor conditions such as heat cramps, heat syncope, and heat exhaustion as well as the more severe condition known as heat stroke. It can affect any or all anatomical systems. Heat illnesses include: heat stroke, heat exhaustion, heat syncope, heat edema, heat cramps, heat rash, heat tetany.
Keratolysis exfoliativa is a sometimes harmless, sometimes painful skin condition that can affect the focal surface of the fingers and/or the palm or soles of the feet. It is often misdiagnosed as chronic contact dermatitis or psoriasis. It is characterized by dry skin and superficial, air-filled blisters. These blisters can be peeled off very easily and will leave reddish, tender areas. The loss of this corneal layer of the skin, which protects the underlying layers, leaves the skin more vulnerable to dryness and cracking.
Acne mechanica is an acneiform eruption that has been observed after repetitive physical trauma to the skin such as rubbing, occurring from clothing or sports equipment. In addition to those mechanisms, the skin not getting enough exposure to air also contributes to the formation of acne mechanica. It is often mistaken as a rash that forms on sweaty skin that is constantly being rubbed, but in reality, it is a breakout of acne mechanica. The term "acne" itself describes the occurrence in which hair follicles in the skin get clogged by oil, dead skin cells, dirt and bacteria, or cosmetic products and create a pimple. Pimples can vary in type, size, and shape, but the sole basis of them occurring is the same - the oil gland in the pore becomes clogged and sometimes infected, which creates pus in order to fight the infection and subsequently causes the development of swollen, red lesions on the skin.

Irritant folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle. It characteristically presents with small red bumps in the skin at sites of occlusion, pressure, friction, or hair removal; typically around the beard area in males, pubic area and lower legs of females, or generally the inner thighs and bottom. An associated itch may or may not be present. Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a type of irritant folliculitis in the beard area.
Cracked nipple is a condition that can occur in breastfeeding women as a result of a number of possible causes. Developing a cracked nipple can result in soreness, dryness or irritation to, or bleeding of, one or both nipples during breastfeeding. The mother with a cracked nipple can have severe nipple pain when the baby is nursing. This severe pain is a disincentive for continued breastfeeding. The crack can appear as a cut across the tip of the nipple and may extend to its base. Cracked nipple can develop after the birth of the infant and is managed with pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatment.














