
In telecommunications, RS-232 or Recommended Standard 232 is a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal or PC, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997.

Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization.
In telecommunications, a customer-premises equipment or customer-provided equipment (CPE) is any terminal and associated equipment located at a subscriber's premises and connected with a carrier's telecommunication circuit at the demarcation point ("demarc"). The demarc is a point established in a building or complex to separate customer equipment from the equipment located in either the distribution infrastructure or central office of the communications service provider.
A data service unit, sometimes called a digital service unit, is a piece of telecommunications circuit terminating equipment that transforms digital data between telephone company lines and local equipment. The device converts bipolar digital signals coming ultimately from a digital circuit and directly from a Channel service unit (CSU), into a format compatible with the piece of data terminal equipment (DTE) to which the data is sent. The DSU also performs a similar process in reverse for data heading from the DTE toward the circuit. The telecommunications service a DSU supports can be a point-to-point or multipoint operation in a digital data network.
Digital subscriber line is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), the most commonly installed DSL technology, for Internet access.

In telecommunications, a network interface device is a device that serves as the demarcation point between the carrier's local loop and the customer's premises wiring. Outdoor telephone NIDs also provide the subscriber with access to the station wiring and serve as a convenient test point for verification of loop integrity and of the subscriber's inside wiring.

The T-carrier is a member of the series of carrier systems developed by AT&T Bell Laboratories for digital transmission of multiplexed telephone calls.
Loopback is the routing of electronic signals or digital data streams back to their source without intentional processing or modification. It is primarily a means of testing the communications infrastructure.

A digital subscriber line access multiplexer is a network device, often located in telephone exchanges, that connects multiple customer digital subscriber line (DSL) interfaces to a high-speed digital communications channel using multiplexing techniques. Its cable internet (DOCSIS) counterpart is the cable modem termination system.

In telephony, the demarcation point is the point at which the public switched telephone network ends and connects with the customer's on-premises wiring. It is the dividing line which determines who is responsible for installation and maintenance of wiring and equipment—customer/subscriber, or telephone company/provider. The demarcation point varies between countries and has changed over time.
A leased line is a private telecommunications circuit between two or more locations provided according to a commercial contract. It is sometimes also known as a private circuit, and as a data line in the UK. Typically, leased lines are used by businesses to connect geographically distant offices.
Digital Signal 1 is a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs. DS1 is the primary digital telephone standard used in the United States, Canada and Japan and is able to transmit up to 24 multiplexed voice and data calls over telephone lines. E-carrier is used in place of T-carrier outside the United States, Canada, Japan, and South Korea. DS1 is the logical bit pattern used over a physical T1 line; in practice, the terms DS1 and T1 are often used interchangeably.
A CSU/DSU is a digital-interface device used to connect data terminal equipment (DTE), such as a router, to a digital circuit, such as a Digital Signal 1 (DS1) T1 line. The CSU/DSU implements two different functions. The channel service unit (CSU) is responsible for the connection to the telecommunication network, while the data service unit (DSU) is responsible for managing the interface with the DTE. A CSU/DSU can have an external connection point or it can be integrated into a modular card installed in a router.
Direct inward dialing (DID), also called direct dial-in (DDI) in Europe and Oceania, is a telecommunication service offered by telephone companies to subscribers who operate private branch exchange (PBX) systems. The feature provides service for multiple telephone numbers over one or more analog or digital physical circuits to the PBX, and transmits the dialed telephone number to the PBX so that a PBX extension is directly accessible for an outside caller, possibly by-passing an auto-attendant.
IEEE 802.1ag is an amendment to the IEEE 802.1Q networking standard which introduces Connectivity Fault Management (CFM). This defines protocols and practices for the operations, administration, and maintenance (OAM) of paths through 802.1 bridges and local area networks (LANs). The final version was approved by the IEEE in 2007.
A digital cross-connect system is a piece of circuit-switched network equipment, used in telecommunications networks, that allows lower-level TDM bit streams, such as DS0 bit streams, to be rearranged and interconnected among higher-level TDM signals, such as DS1 bit streams. DCS units are available that operate on both older T-carrier/E-carrier bit streams, as well as newer SONET/SDH bit streams.
Operations, administration, and management or operations, administration, and maintenance are the processes, activities, tools, and standards involved with operating, administering, managing and maintaining any system. This commonly applies to telecommunication, computer networks, and computer hardware.
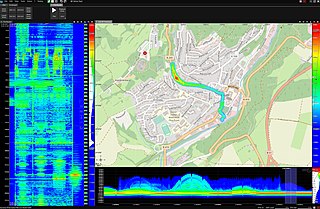
RF Drive testing is a method of measuring and assessing the coverage, capacity and Quality of Service (QoS) of a mobile radio network.
The GTD-5 EAX is the Class 5 telephone switch developed by GTE Automatic Electric Laboratories. This digital central office telephone circuit switching system is used in the former GTE service areas and by many smaller telecommunications service providers.
Carrier Ethernet is a marketing term for extensions to Ethernet for communications service providers that utilize Ethernet technology in their networks.






