
Opole Voivodeship, or Opole Province, is the smallest and least populated voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Upper Silesia. A relatively large German minority, with representatives in the Sejm, lives in the voivodeship, and the German language is co-official in 28 communes.

A voivodeship is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province".
Voivode, also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode, voivoda, vojvoda or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the medieval rulers of the Romanian-inhabited states and of governors and military commanders of Ukrainian Cossacks, Hungarian, Balkan, Russian people and other Slavic-speaking populations.
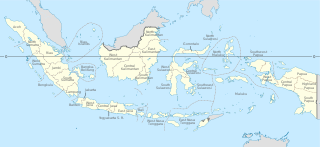
Provinces of Indonesia are the 38 administrative divisions of Indonesia and the highest tier of the local government. Provinces are further divided into regencies and cities, which are in turn subdivided into districts (kecamatan).

The Gdańsk Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Gdańsk, and it was centered on the region of Pomerelia. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the parts of the voivodeships of Gdańsk, and Bydgoszcz, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established Pomeranian Voivodeship.

The Zielona Góra Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Zielona Góra, and it was centered on the southern Lubusz Land, in west-centre part of the county. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the part of the Zielona Góra Voivodeship, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established Lubusz and Greater Poland Voivodeships.

The Warsaw Voivodeship, between 1975 and 1990 known as the Warsaw Capital Voivodeship, was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Warsaw, and it was located in the central Masovia. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the part of the Warsaw Voivodeship, and a city voivodeship of Warsaw, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established Masovian Voivodeship.

Ternopil Oblast, also referred to as Ternopilshchyna or Ternopillia, is an oblast (province) of Ukraine. Its administrative center is Ternopil, through which flows the Seret, a tributary of the Dniester. Population: 1,021,713.

Sieniawa, is a town in southeastern Poland. It had a population of 2,127 inhabitants (02.06.2009). Since 1999, Sieniawa has been part of Subcarpathian Voivodeship.

The gmina is the principal unit of the administrative division of Poland, similar to a municipality. As of 1 January 2019, there were 2,477 gminas throughout the country, encompassing over 43,000 villages. 940 gminas include cities and towns, with 302 among them constituting an independent urban gmina consisting solely of a standalone town or one of the 107 cities, the latter governed by a city mayor.

The administrative division of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The territory of Poland is divided into voivodeships (provinces); these are further divided into powiats, and these in turn are divided into gminas. Major cities normally have the status of both gmina and powiat. Poland currently has 16 voivodeships, 380 powiats, and 2,478 gminas.

Czarnolas is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Policzna, within Zwoleń County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It lies approximately 12 kilometres (7 mi) north-east of Zwoleń and 100 km (62 mi) south-east of Warsaw.

Modliszewice is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Końskie, within Końskie County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It lies approximately 4 kilometres (2 mi) west of Końskie and 40 km (25 mi) north-west of the regional capital Kielce.
Kadłubowo is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Dzierzążnia, within Płońsk County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It lies approximately 6 kilometres (4 mi) south-west of Dzierzążnia, 16 km (10 mi) west of Płońsk, and 71 km (44 mi) north-west of Warsaw.
Kolonia Gradowska is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Nowa Sucha, within Sochaczew County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland.

Poland A and B refers to the historical, political and cultural distinction between the western and the eastern part of the country, with Poland "A", west of the Vistula, being much more developed and having faster growth than Poland "B", east of the river. The General Secretary of the Polish Chamber of Commerce Marek Kłoczko, said in his 2007 interview that the divisions are more spread out and forming three separate categories, Poland "A" is the metropolitan cities, Poland "B" is the rest of the country, and Poland "C" is the plains and the landscape parks east of the Vistula, which require a different treatment.
Będzimierz is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Główczyce, within Słupsk County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately 12 kilometres (7 mi) east of Główczyce, 36 km (22 mi) east of Słupsk, and 75 km (47 mi) west of the regional capital Gdańsk.
Długi Kąt is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Biała Piska, within Pisz County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately 10 kilometres (6 mi) south of Biała Piska, 18 km (11 mi) south-east of Pisz, and 105 km (65 mi) east of the regional capital Olsztyn.

The Szczecin Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Szczecin, and it was centered on the western Farther Pomerania. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the part of the Szczecin Voivodeship, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established West Pomeranian Voivodeship.

The Koszalin Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Koszalin, and it was centered on the eastern Farther Pomerania. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the part of the Koszalin Voivodeship, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established West Pomeranian Voivodeship.
















