
Gatwick Express is an express rail passenger service between London Victoria, Gatwick Airport, and Brighton in South East England. It is the brand name used by the Govia Thameslink Railway train operating company on the Gatwick Express route of the Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern franchise.

The Deutsche Bahn AG is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company (AG).

A conductor or guard is a train crew member responsible for operational and safety duties that do not involve actual operation of the train/locomotive. The conductor title is most common in North American railway operations, but the role is common worldwide under various job titles. In Commonwealth English, a conductor is also known as guard or train manager.

The Great Eastern Railway (GER) was a pre-grouping British railway company, whose main line linked London Liverpool Street to Norwich and which had other lines through East Anglia. The company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway in 1923.
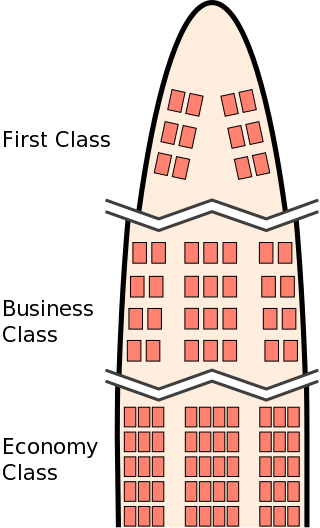
A travel class is a quality of accommodation on public transport. The accommodation could be a seat or a cabin for example. Higher travel classes are designed to be more comfortable and are typically more expensive.

The British Rail Class 458 Juniper (5-JUP) is a class of electric multiple unit passenger trains of the Alstom Coradia Juniper family, built at Washwood Heath between 1998 and 2002 for South West Trains. The order for the original fleet of 30 four-car trains was placed in 1997, and delivery of the first unit followed in October 1998. The fleet entered passenger service between 2000 and 2003 and is maintained at Wimbledon depot.
There have been two separate generations of trams in London, from 1860 to 1952 and from 2000 to the present. There were no trams at all in London between 1952 and 2000.
The Callander and Oban Railway company was established with the intention of linking the sea port of Oban to the railway network. This involved a long line from Callander through wild and thinly populated terrain, and shortage of money meant that the line was opened in stages from 1866 to 1880.

The Victorian Railways (VR), trading from 1974 as VicRail, was the state-owned operator of most rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations. Most of the lines operated by the Victorian Railways were of 5 ft 3 in. However, the railways also operated up to five 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge lines between 1898 and 1962, and a 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge line between Albury and Melbourne from 1961.

The Swansea Vale Railway (SVR) was a railway line connecting the port of Swansea in South Wales to industries and coalfields along the River Tawe on the northern margin of Swansea, by taking over a tramroad in 1846. It was extended to Brynamman in 1868. Passengers were carried from 1860, and a loop line through Morriston was built.
Rail transport in Japan is a major means of passenger transport, especially for mass and high-speed travel between major cities and for commuter transport in urban areas. It is used relatively little for freight transport, accounting for just 0.84% of goods movement. The privatised network is highly efficient, requiring few subsidies and running with extreme punctuality, though since privatisation several unprofitable but socially valuable lines have been closed by private operators.
A parliamentary train was a passenger service operated in the United Kingdom to comply with the Railway Regulation Act 1844 that required train companies to provide inexpensive and basic rail transport for less affluent passengers. The act required that at least one such service per day be run on every railway route in the UK.

A passenger is a person who travels in a vehicle, but does not bear any responsibility for the tasks required for that vehicle to arrive at its destination or otherwise operate the vehicle, and is not a steward. The vehicles may be bicycles, buses, passenger trains, airliners, ships, ferryboats, and other methods of transportation.
The North Devon Railway connected Barnstaple to the growing railway network in 1854 and as Ilfracombe developed as a watering place, it was obvious a railway connection to the town was needed. The hilly terrain was very difficult, but an Ilfracombe Railway was authorised in 1864 but failed when a major shareholder was unable to respond to a subscription call. After several false starts the Barnstaple and Ilfracombe Railway, soon taken over by the London and South Western Railway, opened in 1870.
The Cheddar Valley line was a railway line in Somerset, England, running between Yatton and Witham. It was opened in parts: the first section connecting Shepton Mallet to Witham, later extended to Wells, was built by the East Somerset Railway from 1858. Later the Bristol and Exeter Railway built their branch line from Yatton to Wells, but the two lines were prevented for a time from joining up. Eventually the gap was closed, and the line became a simple through line, operated by the Great Western Railway.
The Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway (WS&WR) was an early railway company in south-western England. It obtained Parliamentary powers in 1845 to build a railway from near Chippenham in Wiltshire, southward to Salisbury and Weymouth in Dorset. It opened the first part of the network but found it impossible to raise further money and sold its line to the Great Western Railway (GWR) in 1850.
The Harborne Railway was a short standard gauge railway line constructed for residential travel from the Harborne area into the centre of Birmingham, England. The line opened in 1874, and was worked by the London and North Western Railway. As business developed, an increasingly frequent passenger service was operated, at its peak thirty trains each way daily.

The Railway Regulation Act 1844 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom providing a minimum standard for rail passenger travel. It provided compulsory services at a price affordable to poorer people to enable them to travel to find work. It is one of the Railway Regulation Acts 1840 to 1893.
A penalty fare, standard fare, or fixed penalty notice is a special, usually higher, fare charged because a passenger using public transport did not comply with the normal ticket purchasing rules. It should not be confused with an unpaid fares notice.

The Wye Valley Railway was a standard gauge railway that ran for nearly 15 miles (24 km) along the Lower Wye Valley between the towns of Chepstow and Monmouth, crossing several times between Wales and England. Opened on 1 November 1876, it was leased to, and worked by, the Great Western Railway (GWR), before being fully absorbed by the GWR in 1905.












