Related Research Articles

Serum is the fluid and solute component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum includes all proteins not used in blood clotting; all electrolytes, antibodies, antigens, hormones; and any exogenous substances. Serum does not contain white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes), platelets, or clotting factors.

Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes in living organisms. It deals with the structure and function of cellular components such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and other biomolecules.

Bovine somatotropin or bovine somatotrophin, or bovine growth hormone (BGH), is a peptide hormone produced by cows' pituitary glands.
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood proteins act as enzymes, complement components, protease inhibitors or kinin precursors. Contrary to popular belief, haemoglobin is not a blood protein, as it is carried within red blood cells, rather than in the blood serum.
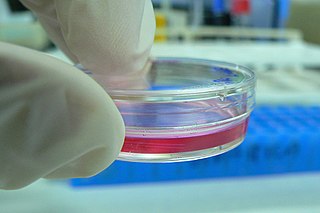
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This technique is also called micropropagation. After the cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions. They need to be kept at body temperature (37 °C) in an incubator. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or rich medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases (CO2, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment (pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate to form an adherent culture as a monolayer (one single-cell thick), whereas others can be grown free floating in a medium as a suspension culture. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, with the more specific term plant tissue culture being used for plants. The lifespan of most cells is genetically determined, but some cell-culturing cells have been “transformed” into immortal cells which will reproduce indefinitely if the optimal conditions are provided.
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are antibodies that are secreted by different B cell lineages within the body. They are a collection of immunoglobulin molecules that react against a specific antigen, each identifying a different epitope.
Serum albumin, often referred to simply as blood albumin, is an albumin found in vertebrate blood. Human serum albumin is encoded by the ALB gene. Other mammalian forms, such as bovine serum albumin, are chemically similar.

Whey protein is a mixture of proteins isolated from whey, the liquid material created as a by-product of cheese production. The proteins consist of α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin, serum albumin and immunoglobulins. Glycomacropeptide also makes up the third largest component but is not a protein. Whey protein is commonly marketed as a protein supplement, and various health claims have been attributed to it. A review published in 2010 in the European Food Safety Authority Journal concluded that the provided literature did not adequately support the proposed claims. For muscle growth, whey protein has been shown to be slightly better compared to other types of protein, such as casein or soy.

A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss Physcomitrella patens. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells.

Fetal bovine serum (FBS) is derived from the blood drawn from a bovine fetus via a closed system of collection at the slaughterhouse. Fetal bovine serum is the most widely used serum-supplement for the in vitro cell culture of eukaryotic cells. This is due to it having a very low level of antibodies and containing more growth factors, allowing for versatility in many different cell culture applications.
Bovine serum albumin is a serum albumin protein derived from cows. It is often used as a protein concentration standard in lab experiments.

Human serum albumin is the serum albumin found in human blood. It is the most abundant protein in human blood plasma; it constitutes about half of serum protein. It is produced in the liver. It is soluble in water, and it is monomeric.
Merriam-Webster defines chemotaxonomy as the method of biological classification based on similarities and dissimilarity in the structure of certain compounds among the organisms being classified. Advocates argue that, as proteins are more closely controlled by genes and less subjected to natural selection than the anatomical features, they are more reliable indicators of genetic relationships. The compounds studied most are proteins, amino acids, nucleic acids, peptides etc.

Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called albuminoids.

α-Parinaric acid is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid. Discovered by Tsujimoto and Koyanagi in 1933, it contains 18 carbon atoms and 4 conjugated double bonds. The repeating single bond-double bond structure of α-parinaric acid distinguishes it structurally and chemically from the usual "methylene-interrupted" arrangement of polyunsaturated fatty acids that have double-bonds and single bonds separated by a methylene unit (−CH2−). Because of the fluorescent properties conferred by the alternating double bonds, α-parinaric acid is commonly used as a molecular probe in the study of biomembranes.
The liver plays the major role in producing proteins that are secreted into the blood, including major plasma proteins, factors in hemostasis and fibrinolysis, carrier proteins, hormones, prohormones and apolipoprotein:
Human platelet lysate is a substitute supplement for fetal bovine serum (FBS) in experimental and clinical cell culture. It is a turbid, light-yellow liquid that is obtained from human blood platelets after freeze/thaw cycle(s). The freeze/thaw cycle causes the platelets to lyse, releasing a large quantity of growth factors necessary for cell expansion. hPL has the highest concentration of growth factors of any serum suppliments. FBS-free cell culture media, e.g. with platelet lysate or chemically defined/ animal component free, are used for cell therapy or regenerative medicine. They are commercially available in GMP -quality which is generally basis for regulatory approval.
A Hollow fiber bioreactor is a 3 dimensional cell culturing system based on hollow fibers, which are small, semi-permeable capillary membranes arranged in parallel array with a typical molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) range of 10-30 kDa. These hollow fiber membranes are often bundled and housed within tubular polycarbonate shells to create hollow fiber bioreactor cartridges. Within the cartridges, which are also fitted with inlet and outlet ports, are two compartments: the intracapillary (IC) space within the hollow fibers, and the extracapillary (EC) space surrounding the hollow fibers.
Entomoculture is the subfield of cellular agriculture which specifically deals with the production of insect tissue in vitro. It draws on principles more generally used in tissue engineering and has scientific similarities to Baculovirus Expression Vectors or soft robotics. The field has mainly been proposed because of its potential technical advantages over mammalian cells in generating cultivated meat. The name of the field was coined by Natalie Rubio at Tufts University.
Peptide therapeutics are peptides or polypeptides which are used to for the treatment of diseases. Naturally occurring peptides may serve as hormones, growth factors, neurotransmitters, ion channel ligands, and anti-infectives; peptide therapeutics mimic such functions. Peptide Therapeutics are seen as relatively safe and well-tolerated as peptides can be metabolized by the body.
References
Jayme DW, Smith SR (2000). "Media formulation options and manufacturing process controls to safeguard against introduction of animal origin contaminants in animal cell culture". Cytotechnology. 33 (1–3): 27–36. doi:10.1023/A:1008133717035. PMC 3466725 . PMID 19002808.
Yao S, Chen S, Clark J, Hao E, Beattie GM, Hayek A, Ding S (2006). "Long-term self-renewal and directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells in chemically defined conditions". PNAS. 103 (18): 6907–6912. Bibcode:2006PNAS..103.6907Y. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602280103 . PMC 1458992 . PMID 16632596.
Chen, Y.; Stevens, B.; Chang, J.; Milbrandt, J.; Barres, B. A.; Hell, J. W. (2008). "NS21: re-defined and modified supplement B27 for neuronal cultures". J. Neurosci. Methods. 171 (2): 239–247. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.03.013. PMC 2678682 . PMID 18471889.
Summers, M.C.; Biggers, J. (2003). "Chemically defined media and the culture of mammalian preimplantation embryos: historical perspective and current issues". Human Reproduction Update. 9 (6): 557–582. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmg039 . PMID 14714592.