
HMAS Newcastle, named for the city of Newcastle, New South Wales, the largest provincial city in Australia, was an Adelaide-class guided-missile frigate. The last ship of the class to be constructed, Newcastle entered service with the Royal Australian Navy in 1993. During her career, the frigate has operated as part of the INTERFET peacekeeping taskforce, served in the Persian Gulf, and responded to the 2006 Fijian coup d'état. The frigate was decommissioned on 30 June 2019 and transferred to the Chilean Navy on 15 April 2020 and renamed as Capitán Prat.

HMS Ocelot (S17) is an Oberon-class diesel-electric submarine which was operated by the Royal Navy.

The Oberon class was a ship class of 27 British-designed submarines operated by five nations. They were designed as a follow-on from the Porpoise class; physical dimensions were the same but stronger materials were used in hull construction and improved equipment was fitted.

HMS Onslaught was a British Oberon-class attack submarine operated by the Royal Navy.

HMS Oberon was the lead ship of the Oberon-class submarines, operated by the Royal Navy.

HMAS Melbourne was an Adelaide-class guided-missile frigate of the Royal Australian Navy, which entered service in 1992. Melbourne has been deployed to the Persian Gulf on several occasions, and served as part of the INTERFET peacekeeping taskforce in 2000. On 26 October 2019, Melbourne was decommissioned from the RAN, subsequently being transferred to Chile. The ship was commissioned into the Chilean Navy as Almirante Latorre on 15 April 2020.

HMS Odin was a British Oberon-class submarine operated by the Royal Navy.

HMS Sealion (S07) was a Porpoise-class submarine.

HMS Opportune (S20) was an Oberon-class submarine of the Royal Navy.

HMS Otus was a Royal Navy Oberon-class submarine launched in 1962. She was decommissioned in the early 1990s and is now a museum ship in Germany.

HMAS Otway was an Oberon-class submarine of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). One of the first four Oberon-class boats ordered for the RAN, Otway was built in Scotland during the mid-1960s, and commissioned into naval service in 1968. The submarine was decommissioned in 1994. The submarine's upper casing, fin, and stern are preserved at Holbrook, New South Wales.

HMS Osiris (S13) was an Oberon-class submarine that served in the Royal Navy.
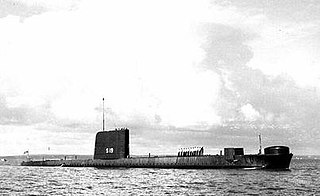
HMS Opossum (S19) was an Oberon-class submarine in service with the Royal Navy from 1964 to 1993.

HMS Oracle was an Oberon-class submarine of the Royal Navy.

HMS Orpheus was an Oberon-class submarine of the Royal Navy.
Brazilian submarine Humaitá (S20) was an Oberon-class submarine in the Brazilian Navy.

Tonelero (S21) was an Oberon-class submarine in the Brazilian Navy.

Riachuelo (S22) was an Oberon-class submarine in the Brazilian Navy.

The Chilean submarine Hyatt (S23) was an Oberon-class submarine in the Chilean Navy, originally launched under the name Condell.




















