 | |
China | Grenada |
|---|---|
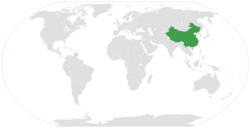
Diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and Grenada were established on 1 October 1985. [1] Prime Minister Herbert Blaize established diplomatic relations with the Republic of China in 1989, prompting Beijing to sever diplomatic ties to Grenada. This position was later reversed under Prime Minister Keith Mitchell. [1]
The current Chinese ambassador to St. George's is Mme. Ou Boqian, [2] while the current Grenadian ambassador to Beijing is Mrs. F. Marcelle Gairy. [3] The People's Republic of China and Grenada resumed diplomatic relations on 20 January 2005. [4]