Related Research Articles
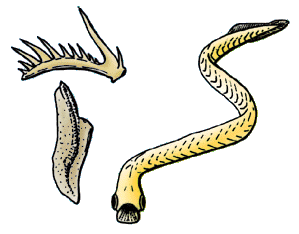
Conodonts are extinct agnathan chordates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from tooth-like microfossils found in isolation and now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. The animals are also called Conodontophora to avoid ambiguity.
Hindeodus is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Anchignathodontidae. The generic name Hindeodus is a tribute to George Jennings Hinde.
Taphrognathus is an extinct genus of conodonts from the Dinantian.
Vinceria is an extinct genus of kannemeyeriiform dicynodont in the family Shansiodontidae.
The Norian is a division of the Triassic geological period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). The Norian lasted from ~227 to 208.5 million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian.
Ozarkodina is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Spathognathodontidae.
Parapachycladina is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Ellisoniidae, from the Early Triassic of the Beisi Formation in Guangxi Province, China.
Jerzy Dzik is a Polish paleontologist.
Clarkina is an extinct genus of conodonts. It is considered to be an offshore, outer shelf or basinal, deep-water taxon.
Neogondolellla is an extinct genus of conodonts. Neogondolela regalis was re-evaluated in 2018 by Martyn Lee Golding.
Heinz Walter Kozur was a German paleontologist and stratigrapher.
Metapolygnathus is an extinct genus of platform conodonts.
Carnepigondolella is an extinct genus of conodonts of the Late Triassic of Italy or Canada.
Kraussodontus is an extinct genus of gondolellid ozarkodinid conodonts of the Late Triassic in the Pardonet Formation of Canada.
Epigondolella is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Gondolellidae.
Conodonts are an extinct class of animals whose feeding apparatuses called teeth or elements are common microfossils found in strata dating from the Stage 10 of the Furongian, the fourth and final series of the Cambrian, to the Rhaetian stage of the Late Triassic. These elements can be used alternatively to or in correlation with other types of fossils in the subfield of the stratigraphy named biostratigraphy.
Neospathodus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Cypridodella is an extinct genus of conodonts.
References
- ↑ Kozur, Cour Forschungsinst Senckenb, 1990, volume 117, page 414
- ↑ The elusive origin of Chiosella timorensis (Conodont Triassic). N Goudemand, MJ Orchard, H Bucher andJ Jenks, Geobios, Volume 45, Issue 2, March–April 2012, Pages 199–207, doi : 10.1016/j.geobios.2011.06.001

