
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.

Raytheon BBN is an American research and development company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States.

The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first computer networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the technical foundation of the Internet. The ARPANET was established by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the United States Department of Defense.

Robert Elliot Kahn is an American electrical engineer who, along with Vint Cerf, first proposed the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP), the fundamental communication protocols at the heart of the Internet.

Bailey Whitfield 'Whit' Diffie ForMemRS is an American cryptographer and mathematician and one of the pioneers of public-key cryptography along with Martin Hellman and Ralph Merkle. Diffie and Hellman's 1976 paper New Directions in Cryptography introduced a radically new method of distributing cryptographic keys, that helped solve key distribution—a fundamental problem in cryptography. Their technique became known as Diffie–Hellman key exchange. The article stimulated the almost immediate public development of a new class of encryption algorithms, the asymmetric key algorithms.
Quantum networks form an important element of quantum computing and quantum communication systems. Quantum networks facilitate the transmission of information in the form of quantum bits, also called qubits, between physically separated quantum processors. A quantum processor is a machine able to perform quantum circuits on a certain number of qubits. Quantum networks work in a similar way to classical networks. The main difference is that quantum networking, like quantum computing, is better at solving certain problems, such as modeling quantum systems.

Lawrence Gilman Roberts was an American engineer who received the Draper Prize in 2001 "for the development of the Internet", and the Principe de Asturias Award in 2002.

Jonathan Andrew Crowcroft is the Marconi Professor of Communications Systems in the Department of Computer Science and Technology, University of Cambridge, a Visiting Professor at the Department of Computing at Imperial College London, and the chair of the programme committee at the Alan Turing Institute.

Henning Schulzrinne is a German-American computer engineer who led research and development of the voice over IP network protocols.

Dipankar Raychaudhuri is the Director of Wireless Information Network Laboratory (WINLAB) and distinguished professor in the Electrical and Computer Engineering department at Rutgers University.

The Packet Radio Network (PRNET) was a set of early, experimental mobile ad hoc networks whose technologies evolved over time. It was funded by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). Major participants in the project included BBN Technologies, Hazeltine Corporation, Rockwell International's Collins division, and SRI International.
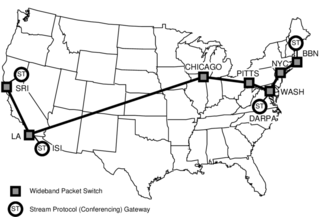
The Terrestrial Wideband Network was a DARPA-sponsored experimental network designed to support research in high-speed networking protocols and distributed multimedia applications. It was built and operated by BBN Technologies from May 1989 to about 1991; although originally planned to turn into the Defense Research Internet, it instead evolved into the Defense Simulation Internet.
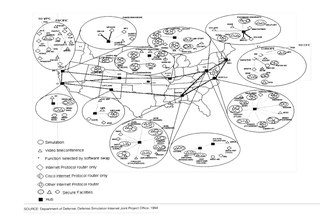
The Defense Simulation Internet (DSI) was a specialized, wide-area network created to support Distributed Interactive Simulation and videoconferences. It was sponsored by DARPA, and built and operated by BBN Technologies from about 1991-1995, after which time it was operated by the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA).

The ARPANET pioneered the creation of novel encryption devices for packet networks in the 1970s and 1980s, and as such were ancestors to today's IPsec architecture, and High Assurance Internet Protocol Encryptor (HAIPE) devices more specifically.

Craig Partridge is an American computer scientist, known for his contributions to the technical development of the Internet.

The DARPA Quantum Network (2002–2007) was the world's first quantum key distribution (QKD) network, operating 10 optical nodes across Boston and Cambridge, Massachusetts. It became fully operational on October 23, 2003 in BBN's laboratories, and in June 2004 was fielded through dark fiber under the streets of Cambridge and Boston, where it ran continuously for over 3 years. The project also created and fielded the world's first superconducting nanowire single-photon detector. It was sponsored by DARPA as part of the QuIST program, and built and operated by BBN Technologies in close collaboration with colleagues at Harvard University and the Boston University Photonics Center.
George N. Rouskas is a computer scientist, academic, and author. He is an Alumni Distinguished Graduate Professor and Director of Graduate Programs in the Department of Computer Science at North Carolina State University.














