
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.

AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass.
Algae eater or algivore is a common name for any bottom-dwelling or filter-feeding aquatic animal species that specialize in feeding on algae and phytoplanktons. Algae eaters are important for the fishkeeping hobby and many are commonly kept by aquarium hobbyists to improve water quality. They are also important primary consumers that relay the biomass and energy from photosynthetic autotrophes up into the food web, as well as protecting the aquatic ecosystem against algae blooms.

The Jamaican slider, also known as the Cat Island slider, is a species of fresh water turtle in the family Emydidae. It is found in the Bahamas and Jamaica. As it is not currently found on any of the other surrounding islands in the region, it is assumed that the Jamaican slider was introduced from one of these countries to the other. Even though the popular theory was that these turtles originated from Jamaica, current geological evidence may suggest that they were in the Bahamas long before the native Taíno first went to the Bahamian islands. There is also evidence from archeological sites on San Salvador that the Taíno ate these turtles and transplanted them around the West Indies.

Chlorogonium is a genus of green algae in the family Haematococcaceae. This alga has a notable mutualistic relationship with the American toad, allowing the tadpoles to develop faster when covered with Chlorogonium.

Calcinus elegans, also known as the blue line hermit crab, is a small, tropical hermit crab.

Chlorococcum amblystomatis, synonym Oophila amblystomatis, commonly known as chlamydomonad algae or salamander algae, is a species of single-celled green algae. When placed in the genus Oophila, it was the only species. The Latin specific name amblystomatis means "loves salamander eggs". It does not occur anywhere in nature other than in the eggs of the spotted salamander, Ambystoma maculatum. The alga can invade and grow in the amphibian's egg capsule. Once inside, it metabolizes the carbon dioxide produced by the embryo and provides it with oxygen and sugar as a result of photosynthesis. This is an example of symbiosis, and the only known example of an intracellular endosymbiont microbe in vertebrates.

Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.

Chaetophora elegans is the type species in the algae genus Chaetophora.

Crossocheilus, also known as the fringe barbs, flying foxes, or "algae eaters", is a genus of fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is distributed in China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand in Asia. These fish occur in several types of habitat, often fast-flowing rivers with rocky bottoms.
Cyanonephron elegans is a freshwater species of cyanobacteria in the family Synechococcaceae. It is described in the Netherlands, Siberia, Russia and Queensland, Australia.
Characiopsis elegans is a species of freshwater yellow-green algae in the family Characiopsidaceae. It is described from Arkansas, North America and Brazil, South America.
Chrysococcus elegans is a species of golden algae in the family Dinobryaceae. It is a freshwater species found in North America, specifically the Northwest Territories in Canada.
Chromulina elegans is a species of golden algae in the family Chromulinaceae. It is found in freshwater, in Europe, South America and Asia.
Chlamydomonas elegans is a species of freshwater green algae. It is commonly found in rainwater pools and other small, temporary bodies of water.
Surirella elegans is a species of freshwater diatoms in the family Surirellaceae.
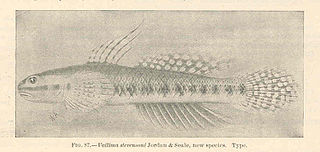
Stiphodon elegans is a species of freshwater goby. It is found in Polynesia, from Wallis and Futuna, Samoa, Cook Islands and French Polynesia. It occurs in clear, fast flowing streams in rainforest near the coast and it feeds on algae.
Navicula elegans is a marine and freshwater species of algae of the genus of Navicula.

Feeder shrimp, ghost shrimp, glass shrimp, grass shrimp, river shrimp or feeder prawns are generic names applied to inexpensive small, typically with a length of 1 to 3 cm, semi-transparent crustaceans commonly sold and fed as live prey to larger more aggressive fishes kept in aquariums.
Hilda Mabel Canter-Lund was an English mycologist, protozoologist, and photographer. She worked as a mycologist and then as a senior principal scientific officer at the laboratories of the Freshwater Biological Association. Canter took photographs and several of them were exhibited in multiple publications and published more than 74 papers of which 25 were in collaboration with colleagues. She received a fellowship from the Royal Photographic Society, the Benefactor's Medal from the British Mycological Society (BMS) and was elected an centennial fellow of the BMS. A photographic award in Canter's honour was established by the British Phycological Society.











