
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts.

Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.

Caroli disease is a rare inherited disorder characterized by cystic dilatation of the bile ducts within the liver. There are two patterns of Caroli disease: focal or simple Caroli disease consists of abnormally widened bile ducts affecting an isolated portion of liver. The second form is more diffuse, and when associated with portal hypertension and congenital hepatic fibrosis, is often referred to as "Caroli syndrome". The underlying differences between the two types are not well understood. Caroli disease is also associated with liver failure and polycystic kidney disease. The disease affects about one in 1,000,000 people, with more reported cases of Caroli syndrome than of Caroli disease.

Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8–10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice, ascites, fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy. Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severity in alcoholic hepatitis is determined several clinical prediction models such as the Maddrey's Discriminant Function and the MELD score.

Biliary atresia, also known as extrahepatic ductopenia and progressive obliterative cholangiopathy, is a childhood disease of the liver in which one or more bile ducts are abnormally narrow, blocked, or absent. It can be congenital or acquired. It has an incidence of one in 10,000–15,000 live births in the United States, and a prevalence of one in 16,700 in the British Isles. Biliary atresia is most common in East Asia, with a frequency of one in 5,000.

Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build up in the liver, a condition called cholestasis. Further slow damage to the liver tissue can lead to scarring, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis.
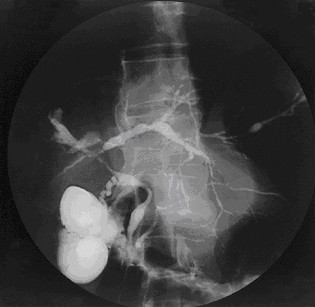
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may have no symptoms or may experience signs and symptoms of liver disease, such as yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes, itching, and abdominal pain.

Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
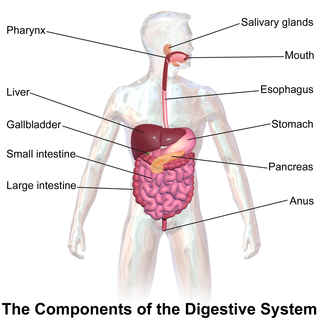
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a secondary bile acid, produced in humans and most other species from metabolism by intestinal bacteria. It is synthesized in the liver in some species, and was first identified in bile of bears of genus Ursus, from which its name derived. In purified form, it has been used to treat or prevent several diseases of the liver or bile ducts.

Cholestasis is a condition where the flow of bile from the liver to the duodenum is impaired. The two basic distinctions are:
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a group of familial cholestatic conditions caused by defects in biliary epithelial transporters. The clinical presentation usually occurs first in childhood with progressive cholestasis. This usually leads to failure to thrive, cirrhosis, and the need for liver transplantation.

The biliary tract refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and conjugated bilirubin. Some components are synthesized by hepatocytes ; the rest are extracted from the blood by the liver.

The liver is a major metabolic organ only found in vertebrate animals, which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells.

Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue can replace normal functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include itchiness, swelling in the lower legs, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, bruising easily, and the development of spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen may develop into spontaneous infections. More serious complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, and liver cancer. Stages of cirrhosis include compensated cirrhosis and decompensated cirrhosis.
Vanishing bile duct syndrome is a loose collection of diseases which leads to the injury to hepatic bile ducts and eventual ductopenia.

S-Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) is an endogenous S-nitrosothiol (SNO) that plays a critical role in nitric oxide (NO) signaling and is a source of bioavailable NO. NO coexists in cells with SNOs that serve as endogenous NO carriers and donors. SNOs spontaneously release NO at different rates and can be powerful terminators of free radical chain propagation reactions, by reacting directly with ROO• radicals, yielding nitro derivatives as end products. NO is generated intracellularly by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) family of enzymes: nNOS, eNOS and iNOS while the in vivo source of many of the SNOs is unknown. In oxygenated buffers, however, formation of SNOs is due to oxidation of NO to dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3). Some evidence suggests that both exogenous NO and endogenously derived NO from nitric oxide synthases can react with glutathione to form GSNO.
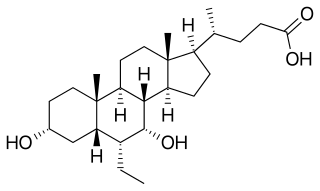
Obeticholic acid (OCA), sold under the brand name Ocaliva, is a semi-synthetic bile acid analogue which has the chemical structure 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid. It is used as a medication used to treat primary biliary cholangitis. Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. hold the worldwide rights to develop OCA outside Japan and China, where it is licensed to Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma.

Bilirubin glucuronide is a water-soluble reaction intermediate over the process of conjugation of indirect bilirubin. Bilirubin glucuronide itself belongs to the category of conjugated bilirubin along with bilirubin di-glucuronide. However, only the latter one is primarily excreted into the bile in the normal setting.
Hyperbilirubinemia is a clinical condition describing an elevation of blood bilirubin level due to the inability to properly metabolise or excrete bilirubin, a product of erythrocytes breakdown. In severe cases, it is manifested as jaundice, the yellowing of tissues like skin and the sclera when excess bilirubin deposits in them. The US records 52,500 jaundice patients annually. By definition, bilirubin concentration of greater than 3 mg/ml is considered hyperbilirubinemia, following which jaundice progressively develops and becomes apparent when plasma levels reach 20 mg/ml. Rather than a disease itself, hyperbilirubinemia is indicative of multifactorial underlying disorders that trace back to deviations from regular bilirubin metabolism. Diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemia depends on physical examination, urinalysis, serum tests, medical history and imaging to identify the cause. Genetic diseases, alcohol, pregnancy and hepatitis viruses affect the likelihood of hyperbilirubinemia. Causes of hyperbilirubinemia mainly arise from the liver. These include haemolytic anaemias, enzymatic disorders, liver damage and gallstones. Hyperbilirubinemia itself is often benign. Only in extreme cases does kernicterus, a type of brain injury, occur. Therapy for adult hyperbilirubinemia targets the underlying diseases but patients with jaundice often have poor outcomes.
















