
The retina is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.

In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma, is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes, it is located within the brain.

In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.

The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye. It contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye, while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0.1 mm. The choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. Along with the ciliary body and iris, the choroid forms the uveal tract.
This is a partial list of human eye diseases and disorders.

A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain.

In neuroanatomy, the optic tract is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.

Fluorescein angiography (FA), fluorescent angiography (FAG), or fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) is a technique for examining the circulation of the retina and choroid using a fluorescent dye and a specialized camera. Sodium fluorescein is added into the systemic circulation, the retina is illuminated with blue-green light at a wavelength of 490 nanometers, and an angiogram is obtained by photographing the fluorescent green light that is emitted by the dye. The fluorescein is administered intravenously in intravenous fluorescein angiography (IVFA) and orally in oral fluorescein angiography (OFA). The test is a dye tracing method.

The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye.

A coloboma is a hole in one of the structures of the eye, such as the iris, retina, choroid, or optic disc. The hole is present from birth and can be caused when a gap called the choroid fissure, which is present during early stages of prenatal development, fails to close up completely before a child is born. Ocular coloboma is relatively uncommon, affecting less than one in every 10,000 births.

The central retinal artery branches off the ophthalmic artery, running inferior to the optic nerve within its dural sheath to the eyeball.

Retinotopy is the mapping of visual input from the retina to neurons, particularly those neurons within the visual stream. For clarity, 'retinotopy' can be replaced with 'retinal mapping', and 'retinotopic' with 'retinally mapped'.
Collie eye anomaly (CEA) is a congenital, inherited, bilateral eye disease of dogs, which affects the retina, choroid, and sclera. It can be a mild disease or cause blindness. CEA is caused by a simple autosomal recessive gene defect. There is no treatment.

The optic vesicles project toward the sides of the head, and the peripheral part of each expands to form a hollow bulb, while the proximal part remains narrow and constitutes the optic stalk.

Papillorenal syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder marked by underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the kidney and colobomas of the optic nerve.
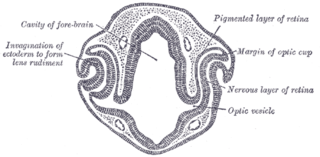
Eye formation in the human embryo begins at approximately three weeks into embryonic development and continues through the tenth week. Cells from both the mesodermal and the ectodermal tissues contribute to the formation of the eye. Specifically, the eye is derived from the neuroepithelium, surface ectoderm, and the extracellular mesenchyme which consists of both the neural crest and mesoderm.

Optic disc drusen (ODD) are globules of mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides that progressively calcify in the optic disc. They are thought to be the remnants of the axonal transport system of degenerated retinal ganglion cells. ODD have also been referred to as congenitally elevated or anomalous discs, pseudopapilledema, pseudoneuritis, buried disc drusen, and disc hyaline bodies.

Optic pit, optic nerve pit, or optic disc pit (ODP) is rare a congenital excavation (or regional depression) of the optic disc (also optic nerve head), resulting from a malformation during development of the eye. The incidence of ODP is 1 in 10,000 people with no predilection for either gender. There is currently no known risk factors for their development. Optic pits are important because they are associated with posterior vitreous detachments (PVD) and even serous retinal detachments.

Fundus photography involves photographing the rear of an eye, also known as the fundus. Specialized fundus cameras consisting of an intricate microscope attached to a flash enabled camera are used in fundus photography. The main structures that can be visualized on a fundus photo are the central and peripheral retina, optic disc and macula. Fundus photography can be performed with colored filters, or with specialized dyes including fluorescein and indocyanine green.
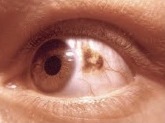
Choroidal nevus is a type of eye neoplasm that is classified under choroidal tumors as a type of benign (non-cancerous) melanocytic tumor. A choroidal nevus can be described as an unambiguous pigmented blue or green-gray choroidal lesion, found at the front of the eye, around the iris, or the rear end of the eye.
















