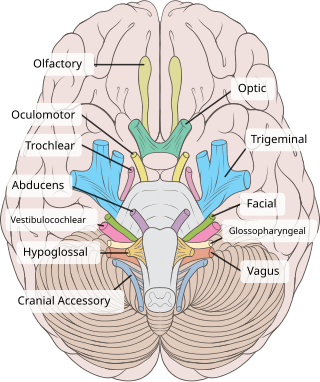
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain, of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing.

In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma, is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes, it is located within the brain.

In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation. The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement.
The vitreous body is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor, from Latin meaning liquid, or simply "the vitreous". Vitreous fluid or "liquid vitreous" is the liquid component of the vitreous gel, found after a vitreous detachment. It is not to be confused with the aqueous humor, the other fluid in the eye that is found between the cornea and lens.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.
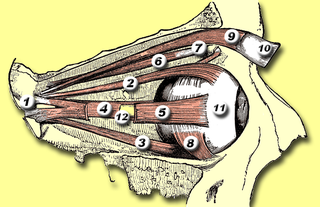
The superior oblique muscle or obliquus oculi superior is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular muscle innervated by the trochlear nerve.

In the human brain, the diencephalon is a division of the forebrain. It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain. The diencephalon has also been known as the tweenbrain in older literature. It consists of structures that are on either side of the third ventricle, including the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the epithalamus and the subthalamus.

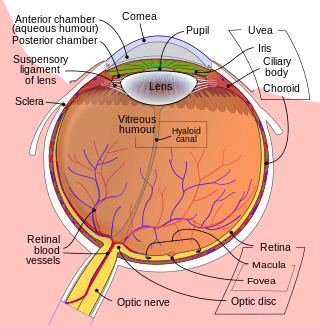
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye.

The central retinal artery branches off the ophthalmic artery, running inferior to the optic nerve within its dural sheath to the eyeball.

The zonule of Zinn is a ring of fibrous strands forming a zonule that connects the ciliary body with the crystalline lens of the eye. These fibers are sometimes collectively referred to as the suspensory ligaments of the lens, as they act like suspensory ligaments.

The optic foramen is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.

The short ciliary nerves are nerves of the orbit around the eye. They are branches of the ciliary ganglion. They supply parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve fibers to the ciliary muscle, iris, and cornea. Damage to the short ciliary nerve may result in loss of the pupillary light reflex, or mydriasis.

The ciliary arteries are divisible into three groups, the long posterior, short posterior, and the anterior.

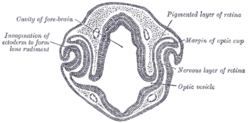
The optic vesicles project toward the sides of the head, and the peripheral part of each expands to form a hollow bulb, while the proximal part remains narrow and constitutes the optic stalk.
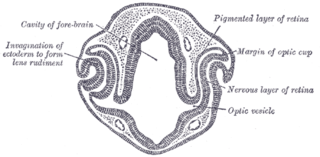
The eyes begin to develop as a pair of diverticula (pouches) from the lateral aspects of the forebrain. These diverticula make their appearance before the closure of the anterior end of the neural tube; after the closure of the tube around the 4th week of development, they are known as the optic vesicles. Previous studies of optic vesicles suggest that the surrounding extraocular tissues – the surface ectoderm and extraocular mesenchyme – are necessary for normal eye growth and differentiation.

The long posterior ciliary arteries are arteries of the orbit. There are long posterior ciliary arteries two on each side of the body. They are branches of the ophthalmic artery. They pass forward within the eye to reach the ciliary body where they ramify and anastomose with the anterior ciliary arteries, thus forming the major arterial circle of the iris.The long posterior ciliary arteries contribute arterial supply to the choroid, ciliary body, and iris.

The short posterior ciliary arteries are a number of branches of the ophthalmic artery. They pass forward with the optic nerve to reach the eyeball, piercing the sclera around the entry of the optic nerve into the eyeball.
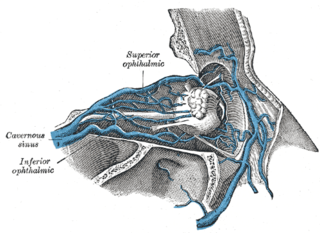
The central retinal vein is a vein that drains the retina of the eye. It travels backwards through the centre of the optic nerve accompanied by the central retinal artery before exiting the optic nerve together with the central retinal artery to drain into either the superior ophthalmic vein or the cavernous sinus.

The globe of the eye, or bulbus oculi, is the frontmost sensory organ of the human ocular system, going from the cornea at the front, to the anterior part of the optic nerve at the back. More simply, the eyeball itself, as well as the ganglion cells in the retina that eventually transmit visual signals through the optic nerve. A hollow structure, the bulbus oculi is composed of a wall enclosing a cavity filled with fluid with three coats: the sclera, choroid, and the retina. Normally, the bulbus oculi is bulb-like structure. However, the bulbus oculi is not completely spherical. Its anterior surface, transparent and more curved, is known as the cornea of the bulbus oculi.