In biology, tissue is an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Tissues occupy a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. Accordingly, organs are formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.

The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.

Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with little extracellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves.

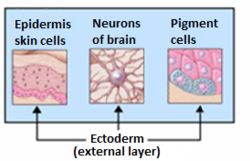
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm and endoderm. It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the Greek ektos meaning "outside", and derma meaning "skin".

The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract.

The olfactory epithelium is a specialized epithelial tissue inside the nasal cavity that is involved in smell. In humans, it measures 5 cm2 (0.78 sq in) and lies on the roof of the nasal cavity about 7 cm (2.8 in) above and behind the nostrils. The olfactory epithelium is the part of the olfactory system directly responsible for detecting odors.
The olfactory mucosa is the neuroepithelialial mucosa lining the roof and upper parts of the septum and lateral wall of the nasal cavity which contains bipolar neurons of the primary receptor neurons of the olfactory pathway, as well as supporting cells. The neurons' dendrites project towards the nasal cavity while their axons ascend through the cribriform plate as the olfactory nerves.
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans produce two or three primary germ layers. Some animals, like cnidarians, produce two germ layers making them diploblastic. Other animals such as bilaterians produce a third layer between these two layers, making them triploblastic. Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal's tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis.
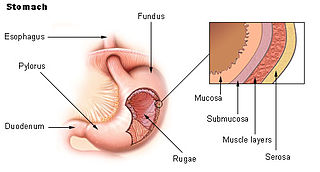
The serous membrane is a smooth tissue membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces. The serous membrane that covers internal organs is called visceral, while the one that covers the cavity wall is called parietal. For instance the parietal peritoneum is attached to the abdominal wall and the pelvic walls. The visceral peritoneum is wrapped around the visceral organs. For the heart, the layers of the serous membrane are called parietal and visceral pericardium. For the lungs they are called parietal and visceral pleura. The visceral serosa of the uterus is called the perimetrium. The potential space between two opposing serosal surfaces is mostly empty except for the small amount of serous fluid.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved.

Neuroectoderm consists of cells derived from the ectoderm. Formation of the neuroectoderm is the first step in the development of the nervous system. The neuroectoderm receives bone morphogenetic protein-inhibiting signals from proteins such as noggin, which leads to the development of the nervous system from this tissue. Histologically, these cells are classified as pseudostratified columnar cells.
This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.
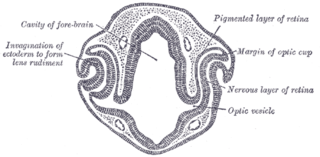
Eye formation in the human embryo begins at approximately three weeks into embryonic development and continues through the tenth week. Cells from both the mesodermal and the ectodermal tissues contribute to the formation of the eye. Specifically, the eye is derived from the neuroepithelium, surface ectoderm, and the extracellular mesenchyme which consists of both the neural crest and mesoderm.

The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

The submandibular lymph nodes, are some 3-6 lymph nodes situated at the inferior border of the ramus of mandible.

A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes through the pharynx, shared with the digestive system, and then into the rest of the respiratory system. In humans, the nose is located centrally on the face and serves as an alternative respiratory passage especially during suckling for infants. The protruding nose that is completely separate from the mouth part is a characteristic found only in therian mammals. It has been theorized that this unique mammalian nose evolved from the anterior part of the upper jaw of the reptilian-like ancestors (synapsids).

Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Embryonic development in the human, covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. The eight weeks have 23 stages.
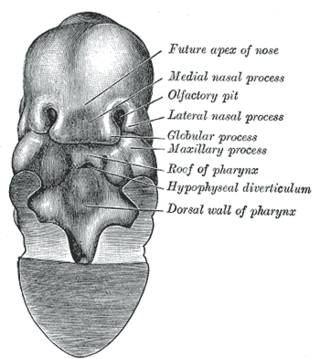
The nasal placode gives rise to the olfactory epithelium of the nose. Two nasal placodes arise as thickened ectoderm from the frontonasal process. They give rise to the nose, the philtrum of the upper lip, and the primary palate.
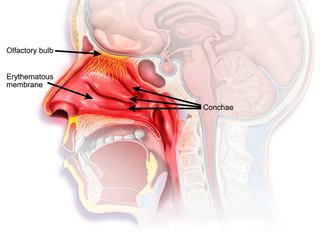
The nasal mucosa lines the nasal cavity. It is part of the respiratory mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract. The nasal mucosa is intimately adherent to the periosteum or perichondrium of the nasal conchae. It is continuous with the skin through the nostrils, and with the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx through the choanae. From the nasal cavity its continuity with the conjunctiva may be traced, through the nasolacrimal and lacrimal ducts; and with the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, through the several openings in the nasal meatuses. The mucous membrane is thickest, and most vascular, over the nasal conchae. It is also thick over the nasal septum where increased numbers of goblet cells produce a greater amount of nasal mucus. It is very thin in the meatuses on the floor of the nasal cavities, and in the various sinuses. It is one of the most commonly infected tissues in adults and children. Inflammation of this tissue may cause significant impairment of daily activities, with symptoms such as stuffy nose, headache, mouth breathing, etc.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.