Related Research Articles

The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:

Anotia describes a rare congenital deformity that involves the complete absence of the auricle, the outer projected portion of the ear, and narrowing or absence of the ear canal. This contrasts with microtia, in which a small part of the auricle is present. Anotia and microtia may occur unilaterally or bilaterally. This deformity results in conductive hearing loss, deafness.

The olfactory epithelium is a specialized epithelial tissue inside the nasal cavity that is involved in smell. In humans, it measures 5 cm2 (0.78 sq in) and lies on the roof of the nasal cavity about 7 cm (2.8 in) above and behind the nostrils. The olfactory epithelium is the part of the olfactory system directly responsible for detecting odors.

An ear is the organ that enables hearing and body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear in most animals, the word "ear" often refers to the external part alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing. The ear is a self cleaning organ through its relationship with earwax and the ear canals. The ears of vertebrates are placed somewhat symmetrically on either side of the head, an arrangement that aids sound localization.
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans produce two or three primary germ layers. Some animals, like cnidarians, produce two germ layers making them diploblastic. Other animals such as bilaterians produce a third layer between these two layers, making them triploblastic. Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal's tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis.
A neurogenic placode is an area of thickening of the epithelium in the embryonic head ectoderm layer that gives rise to neurons and other structures of the sensory nervous system.
The vestibular ganglion is a collection of cell bodies belonging to first order sensory neurons of the vestibular nerve. It is located within the internal auditory canal.
Otic means pertaining to the ear. It can refer to:
In embryology, Carnegie stages are a standardized system of 23 stages used to provide a unified developmental chronology of the vertebrate embryo.
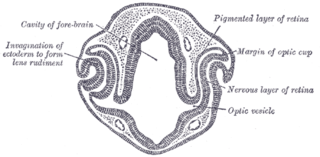
Eye formation in the human embryo begins at approximately three weeks into embryonic development and continues through the tenth week. Cells from both the mesodermal and the ectodermal tissues contribute to the formation of the eye. Specifically, the eye is derived from the neuroepithelium, surface ectoderm, and the extracellular mesenchyme which consists of both the neural crest and mesoderm.
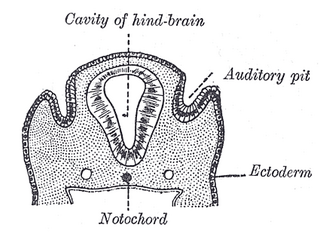
The auditory pit, also known as the otic pit, is the first rudiment of the internal ear. It appears shortly after that of the eye, in the form of a patch of thickened ectoderm, the auditory plate, over the region of the hind-brain. The auditory plate becomes depressed and converted into the auditory pit.

Otic vesicle, or auditory vesicle, consists of either of the two sac-like invaginations formed and subsequently closed off during embryonic development. It is part of the neural ectoderm, which will develop into the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. This labyrinth is a continuous epithelium, giving rise to the vestibular system and auditory components of the inner ear. During the earlier stages of embryogenesis, the otic placode invaginates to produce the otic cup. Thereafter, the otic cup closes off, creating the otic vesicle. Once formed, the otic vesicle will reside next to the neural tube medially, and on the lateral side will be paraxial mesoderm. Neural crest cells will migrate rostral and caudal to the placode.

The frontonasal process, or frontonasal prominence is one of the five swellings that develop to form the face. The frontonasal process is unpaired, and the others are the paired maxillary prominences, and the paired mandibular prominences. During the fourth week of embryonic development, an area of thickened ectoderm develops, on each side of the frontonasal process called the nasal placodes or olfactory placodes, and appear immediately under the forebrain.

Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Embryonic development in the human, covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. The eight weeks has 23 stages.

The lens placode is a thickened portion of ectoderm that serves as the precursor to the lens.
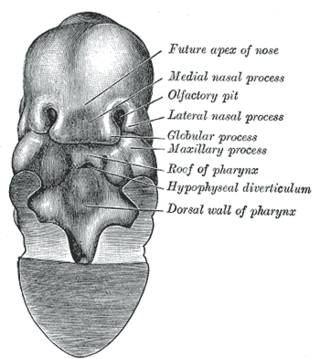
The nasal placode gives rise to the olfactory epithelium of the nose. Two nasal placodes arise as thickened ectoderm from the frontonasal process. They give rise to the nose, the philtrum of the upper lip, and the primary palate.
The cranial neural crest is one of the four regions of the neural crest.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.

The following diagram is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human nervous system:
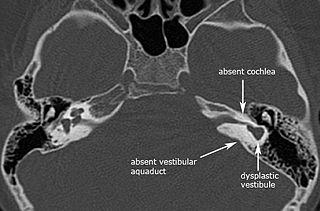
Michel aplasia, also known as complete labyrinthine aplasia (CLA), is a congenital abnormality of the inner ear. It is characterized by the bilateral absence of differentiated inner ear structures and results in complete deafness (anacusis). Michel aplasia should not be confused with michel dysplasia. It may affect one or both ears.