Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, phase and frequency of an analog signal.

NTSC is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170.

SECAM, also written SÉCAM, is an analog color television system that was used in France, Russia and some other countries or territories of Europe and Africa. It was one of three major analog color television standards, the others being PAL and NTSC. Like PAL, a SECAM picture is also made up of 625 interlaced lines and is displayed at a rate of 25 frames per second. However, due to the way SECAM processes color information, it is not compatible with the PAL video format standard. SECAM video is composite video; the luminance and chrominance are transmitted together as one signal.
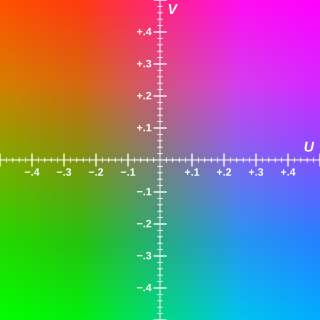
Y′UV, also written YUV, is the color model found in the PAL analogue color TV standard. A color is described as a Y′ component (luma) and two chroma components U and V. The prime symbol (') denotes that the luma is calculated from gamma-corrected RGB input and that it is different from true luminance. Today, the term YUV is commonly used in the computer industry to describe colorspaces that are encoded using YCbCr.

Composite video is an baseband analog video format that typically carries a 405, 525 or 625 line interlaced black and white or color signal, on a single channel, unlike the higher-quality S-Video and the even higher-quality YPbPr.

S-Video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate channels, achieving higher image quality than composite video which encodes all video information on one channel. It also eliminates several types of visual defects such as dot crawl which commonly occur with composite video. Although it is improved over composite video, S-Video has lower color resolution than component video, which is encoded over three channels.

Kinescope, shortened to kine, also known as telerecording in Britain, is a recording of a television program on motion picture film directly through a lens focused on the screen of a video monitor. The process was pioneered during the 1940s for the preservation, re-broadcasting, and sale of television programs before the introduction of quadruplex videotape, which from 1956 eventually superseded the use of kinescopes for all of these purposes. Kinescopes were the only practical way to preserve live television broadcasts prior to videotape.

Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.
ITU-R Recommendation BT.601, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 601 or BT.601, is a standard originally issued in 1982 by the CCIR for encoding interlaced analog video signals in digital video form. It includes methods of encoding 525-line 60 Hz and 625-line 50 Hz signals, both with an active region covering 720 luminance samples and 360 chrominance samples per line. The color encoding system is known as YCbCr 4:2:2.

Component video is an analog video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals. Component video can be contrasted with composite video in which all the video information is combined into a single signal that is used in analog television. Like composite, component cables do not carry audio and are often paired with audio cables.

SMPTE color bars are a television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in North America. The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) refers to the pattern as Engineering Guideline (EG) 1-1990. Its components are a known standard, and created by test pattern generators. Comparing it as received to the known standard gives video engineers an indication of how an NTSC video signal has been altered by recording or transmission and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce NTSC chrominance and luminance information correctly.

Dot crawl is a visual defect of color analog video standards when signals are transmitted as composite video, as in terrestrial broadcast television. It consists of moving checkerboard patterns which appear along horizontal color transitions. It results from intermodulation or crosstalk between chrominance and luminance components of the signal, which are imperfectly multiplexed in the frequency domain.

Several portions of the long-running British science-fiction television programme Doctor Who are no longer held by the BBC. Between 1967 and 1978, the BBC routinely deleted archive programmes for various practical reasons—lack of space, scarcity of materials, and a lack of rebroadcast rights. As a result, 97 of 253 episodes from the programme's first six years are currently missing, primarily from seasons 3, 4 and 5, leaving 26 serials incomplete. Many more were considered lost until recovered from various sources, mostly overseas broadcasters.
In video, luma represents the brightness in an image. Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image, while the chroma components represent the color information. Converting R′G′B′ sources into luma and chroma allows for chroma subsampling: because human vision has finer spatial sensitivity to luminance differences than chromatic differences, video systems can store and transmit chromatic information at lower resolution, optimizing perceived detail at a particular bandwidth.
MUSE, commercially known as Hi-Vision was a Japanese analog high-definition television system, with design efforts going back to 1979.
Colour recovery is a process that restores lost colour to television programmes that were originally recorded on colour videotape but for which only black-and-white copies exist. This is not the same as colourisation, a process by which colour is artificially added to source material that was always black-and-white, or used to enhance poor-quality original sources. Colour recovery is a newer process and is fundamentally different from colourisation. Most of the work has been performed on PAL programmes, but the concept is not fundamentally restricted to that system.
The color killer is an electronic stage in color TV receiver sets which acts as a cutting circuit to cut off color processing when the TV set receives a monochrome signal.
This glossary defines terms that are used in the document "Defining Video Quality Requirements: A Guide for Public Safety", developed by the Video Quality in Public Safety (VQIPS) Working Group. It contains terminology and explanations of concepts relevant to the video industry. The purpose of the glossary is to inform the reader of commonly used vocabulary terms in the video domain. This glossary was compiled from various industry sources.

The TEA1002 is a PAL video encoder chip produced by Mullard in 1982 and used on the Mattel Aquarius computer and AlphaTantel Prestel adapter. It was also used on teletext decoders and color bar generators associated with video test equipment.

The EBU colour bars are a television test card used to check if a video signal has been altered by recording or transmission, and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce chrominance and luminance information correctly. The EBU bars are most commonly shown arranged side-by-side in a vertical manner, though some broadcasters – such as TVP in Poland, and Gabon Télévision in Gabon – were known to have aired a horizontal version of the EBU bars.