
Churn Creek is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia.

Churn Creek is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia.
Churn Creek flows generally north before turning northeast on its final leg through grasslands, joining the Fraser River just south of the headquarters of the Gang Ranch and opposite the community of Dog Creek and associated creek. Most of its lower course is a heavily-eroded canyon lined by benchlands, and is protected in Churn Creek Protected Area, which also includes the ecological preserve of the Empire Valley Ranch. [1]
Its source at approximately 51°05.7′N122°36.3′W / 51.0950°N 122.6050°W is at two subalpine lakes (one of which is called Horse Lake) on the northeastern shoulder of Big Dog Mountain, the northernmost major summit of the Shulaps Range, and flowing north and northwesterly until reaching the southern skirt of Poison Mountain, a northeastern outpost of the Camelsfoot Range, where it continues northwesterly, forming a divide with a small upper tributary of the Yalakom River, the main north fork of the Bridge River which divides those two ranges. From there it proceeds northwest, falling steeply from the high plateau between those two ranges, joining at the bottom of that grade with an unnamed creek from Swartz (Fish) Lake, one a chain of lakes in the area of the Mud Lakes Pass, at the divide with the basin of Tyaughton Creek, also a tributary of the Bridge River. From there it turns north in its main trajectory, forming the northwestern flank of the northern Camelsfoot Range. It is joined in its upper reaches by its two main left tributaries, Lone Valley Creek and Dash Creek, which drain the southernmost Chilcotin Plateau just north of the edge of the Chilcotin Ranges and the Spruce Lake Protected Area (now known as the South Chilcotin Mountain Park, created in 2010, which consists of a smaller area than the original Protected Area).

The Fraser Canyon is a major landform of the Fraser River where it descends rapidly through narrow rock gorges in the Coast Mountains en route from the Interior Plateau of British Columbia to the Fraser Valley. Colloquially, the term "Fraser Canyon" is often used to include the Thompson Canyon from Lytton to Ashcroft, since they form the same highway route which most people are familiar with, although it is actually reckoned to begin above Williams Lake at Soda Creek Canyon near the town of the same name.
The Chilcotin region of British Columbia is usually known simply as "the Chilcotin", and also in speech commonly as "the Chilcotin Country" or simply Chilcotin. It is a plateau and mountain region in British Columbia on the inland lee of the Coast Mountains on the west side of the Fraser River. Chilcotin is also the name of the river draining that region. In the language of the Tsilhqot'in people, their name and the name of the river means "those of the red ochre river". The proper name of the Chilcotin Country, or Tsilhqotʼin territory, in their language is Tŝilhqotʼin Nen.

The Chilcotin River /tʃɪlˈkoʊtɪn/ located in Southern British Columbia, Canada is a 241 km (150 mi) long tributary of the Fraser River. The name Chilcotin comes from Tŝilhqot’in, meaning "ochre river people," where ochre refers to the mineral used by Tŝilhqot’in Nation and other Indigenous communities as a base for paint or dye. The Chilcotin River, Chilko River and Lake, and Taseko River and Lake make up the Chilcotin River watershed. This 19,200 km2 (7,400 sq mi) watershed drains the Chilcotin Plateau which reaches north to south from the Nechako Plateau to Bridge River county and east to west from Fraser River to the Coast Mountains. It is also one of twelve watersheds that make up the Fraser River Basin. Made up of seven major tributaries, Chilcotin River starts northeast of Itcha Mountain, flowing southeast until it joins the Fraser River south of Williams Lake, 22 km (14 mi) upstream from Gang Ranch.

The Chilcotin Ranges are a subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. They lie on the inland lea of the Pacific Ranges, abutting the Interior Plateau of British Columbia. Their northwestern end is near the head of the Klinaklini River and their southeast end is the Fraser River just north of Lillooet; their northern flank is the edge of the Plateau while their southern is the north bank of the Bridge River. In some reckonings they do not go all the way to the Fraser but end at the Yalakom River, which is the North Fork of the Bridge.
The Niut Range is 3600 km2 in area. It is a subrange of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, although in some classifications it is considered part of the Chilcotin Ranges. The Niut is located in the angle of the Homathko River and its main west fork, Mosley Creek. It is isolated, island-like, by those rivers from its neighbour ranges, as both streams have their source on the Chilcotin Plateau in behind the range. Razorback Mountain is its highest peak.

The Shulaps Range is a subrange of the Chilcotin Ranges subset of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in southwest-central British Columbia. The range is 55 km NW–SE and 15 km SW–NE and 2,970 km2 (1,150 sq mi) in area.

The Camelsfoot Range is a sub-range of the Chilcotin Ranges subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia. The Fraser River forms its eastern boundary. The range is approximately 90 km at its maximum length and less than 30 km wide at its widest.
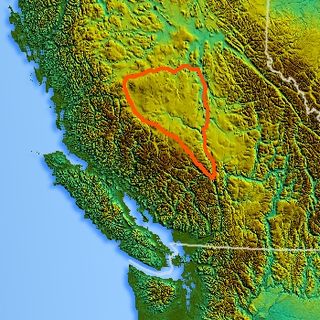
The Chilcotin Plateau is part of the Fraser Plateau, a major subdivision of the Interior Plateau of British Columbia. The Chilcotin Plateau is physically near-identical with the region of the same name, i.e. "the Chilcotin", which lies between the Fraser River and the southern Coast Mountains and is defined by the basin of the Chilcotin River and so includes montane areas beyond the plateau. East of the Chilcotin Plateau, across the Fraser River, is the Cariboo Plateau, while to the north beyond the West Road (Blackwater) River is the Nechako Plateau. West and south of the Chilcotin Plateau are various subdivisions of the Coast Mountains, including the Chilcotin Ranges which lie along the plateau's southwest.
Junction Sheep Range Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located near the confluence of the Chilcotin and Fraser Rivers on the west bank of the latter river.

The Spruce Lake Protected Area, formerly known variously as the Southern Chilcotin Mountains Provincial Park, Southern Chilcotins, and also as South Chilcotin Provincial Park, is a 71,347-hectare Protected Area in the British Columbia provincial parks system, approximately 200 km north of Vancouver. The area had been the subject of an ongoing preservationist controversy since the 1930s. In 2007, its status as a provincial park was downgraded to protected area.
Tyaughton Creek, formerly gazetted as the Tyaughton River, also historically known as Tyoax Creek, is a 50 kilometre tributary of British Columbia's Bridge River, flowing generally southeast to enter the main flow of that river about mid-way along the length of Carpenter Lake, a reservoir formed by Terzaghi Dam of the Bridge River Power Project.
Big Creek is a roughly 120-kilometre (75 mi) long tributary of British Columbia's Chilcotin River.

Gold Bridge is an unincorporated community in the Bridge River Country of British Columbia, Canada. Although numbering only around 40 inhabitants, Gold Bridge is the service and supply centre for the upper basin of the Bridge River Valley, which includes recreation-residential areas at the Gun Lakes, Tyaughton Lake, Marshall Creek, and Bralorne; and the nearby ghost towns of Brexton and Pioneer Mine.
Black Dome Mountain is the northernmost summit of the Camelsfoot Range, which lies along the west side of the Fraser River, north of Lillooet, British Columbia, Canada. It is an ancient butte-like volcano located in the formation known as the Chilcotin Group, which lie between the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains and the mid-Fraser River in British Columbia, Canada.

The Churn Creek Protected Area is a 36,747-hectare (90,800-acre) provincial protected area in British Columbia, Canada. It is a mix of dryland canyon and steppe and adjoining rangeland flanking the canyon of Churn Creek and that stream's confluence with the Fraser River at the northern apex of the Camelsfoot Range. The historic Gang Ranch is just north of the Churn Creek Protected Area. The Empire Valley Ranch ecological preserve was added to the Protected Area in an expansion.

The Bridge River Country is a historic geographic region and mining district in the Interior of British Columbia, Canada, lying between the Fraser Canyon and the valley of the Lillooet River, south of the Chilcotin Plateau and north of the Lillooet Ranges. "The Bridge River" can mean the Bridge River Country as opposed to the Bridge River itself, and is considered to be part of the Lillooet Country, but has a distinct history and identity within the larger region. As Lillooet is sometimes considered to be the southwest limit of the Cariboo, some efforts were made to refer to the Bridge River as the "West Cariboo" but this never caught on.

The Fraser Plateau is an intermontane plateau. It is one of the main subdivisions of the Interior Plateau located in the Central Interior of British Columbia.
Tyoax Pass is a mountain pass in the Chilcotin Ranges of the Pacific Ranges, the southernmost main subdivision of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. Located at the head of Tyaughton Creek, a north tributary of the Bridge River, it connects the basin of the Bridge River with that of Big Creek in the southern Chilcotin District, and is therefore at the boundary between the Spruce Lake Protected Area and Big Creek Provincial Park.
Red Mountain, 2445 m (8022 ft) prominence: 740 m, is the highest summit of the Camelsfoot Range, part of the Chilcotin Plateau located on the west bank of the Fraser River to the north of Lillooet, British Columbia, Canada. Located at the headwaters of the Yalakom River, which is the main north fork of the Bridge River, it has been the site of copper prospects but no major mining activity has so far taken place.
Dash Creek is a river in the Canadian province of British Columbia which flows easterly to join Churn Creek, a tributary of the Fraser River. Dash Creek rises on the northern slopes of the Dash Plateau and Dash Hill in the South Chilcotin Mountains as well as taking in several tributaries draining the south slopes of the Hungry Mountains.