Bevacizumab, sold under the brand name Avastin among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat a number of types of cancers and a specific eye disease. For cancer, it is given by slow injection into a vein (intravenous) and used for colon cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, glioblastoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and renal-cell carcinoma. In many of these diseases it is used as a first-line therapy. For age-related macular degeneration it is given by injection into the eye (intravitreal).

Cediranib is a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinases.

Lestaurtinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor structurally related to staurosporine. This semisynthetic derivative of the indolocarbazole K252a was investigated by Cephalon as a treatment for various types of cancer. It is an inhibitor of the kinases fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), tropomyosin receptor kinase (trk) A (TrkA), TrkB and TrkC.

ARIAD Pharmaceuticals, Inc. was an American oncology company, now part of Takeda Oncology, which was founded in 1991 by Harvey J. Berger, M.D. and headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. ARIAD engaged in the discovery, development, and commercialization of medicines for cancer patients.

Olaparib, sold under the brand name Lynparza, is a medication for the maintenance treatment of BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer in adults. It is a PARP inhibitor, inhibiting poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP), an enzyme involved in DNA repair. It acts against cancers in people with hereditary BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, which include some ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers.

PARP inhibitors are a group of pharmacological inhibitors of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP).

Rucaparib, sold under the brand name Rubraca, is a PARP inhibitor used as an anti-cancer agent. Rucaparib is a first-in-class pharmaceutical drug targeting the DNA repair enzyme poly-ADP ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1). It is taken by mouth.
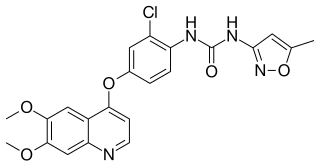
Tivozanib, sold under the brand name Fotivda, is a medication used for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. It is an oral VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
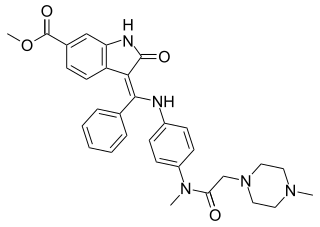
Nintedanib, sold under the brand names Ofev and Vargatef, is an oral medication used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and along with other medications for some types of non-small-cell lung cancer.

CompugenLtd. is a clinical-stage publicly traded predictive drug discovery and development company headquartered in Israel, with shares traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market and on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange. Compugen was established as computational drug discovery service provider in 1993. Compugen originally acted as service provider for pharma companies, supplying its software and computational services to predict different types of biological phenomena. It had arrangements with big companies such as Novartis AG, Abbot Laboratories and Pfizer Inc. Subsequently, Compugen made a decision to become a drug development company with its own internal pipeline, and in 2010, decided to a focus on oncology and immunology. OncoMed Pharmaceuticals and Five Prime Therapeutics are among Compugen's competitors.

Binimetinib, sold under the brand name Mektovi, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat various cancers. Binimetinib is a selective inhibitor of MEK, a central kinase in the tumor-promoting MAPK pathway. Inappropriate activation of the pathway has been shown to occur in many cancers. In June 2018 it was approved by the FDA in combination with encorafenib for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive melanoma. In October 2023, it was approved by the FDA for treatment of NSCLC with a BRAF V600E mutation in combination with encorafenib. It was developed by Array Biopharma.

Atezolizumab, sold under the brand name Tecentriq among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat urothelial carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), hepatocellular carcinoma and alveolar soft part sarcoma, but discontinued for use in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). It is a fully humanized, engineered monoclonal antibody of IgG1 isotype against the protein programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1).
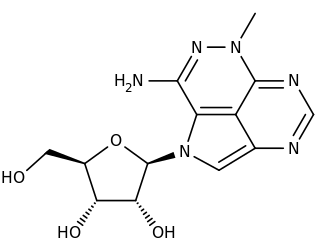
Triciribine is a cancer drug which was first synthesized in the 1970s and studied clinically in the 1980s and 1990s without success. Following the discovery in the early 2000s that the drug would be effective against tumours with hyperactivated Akt, it is now again under consideration in a variety of cancers. As PTX-200, the drug is currently in two early stage clinical trials in breast cancer and ovarian cancer being conducted by the small molecule drug development company Prescient Therapeutics.

Talazoparib, sold under the brand name Talzenna, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is an orally available poly ADP ribose polymerase PARP inhibitor marketed by Pfizer for the treatment of advanced breast cancer with germline BRCA mutations. Talazoparib is similar to the first in class PARP inhibitor, olaparib.

Niraparib, sold under the brand name Zejula, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer. It is taken by mouth. It is a PARP inhibitor.

Capmatinib, sold under the brand name Tabrecta, is an anticancer medication used for the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors have a mutation that leads to the exon 14 skipping of the MET gene, which codes for the membrane receptor HGFR.
Verastem, Inc., doing business as Verastem Oncology, is an American pharmaceutical company that develops medicines to treat certain cancers. Headquartered and founded in Boston, Massachusetts, the firm is a member of NASDAQ Biotechnology Index.
Elizabeth Ruth Plummer is a Professor of Experimental Cancer Medicine at Newcastle University and an oncologist specialising in treating patients with melanoma. Based in Newcastle, she directs the Sir Bobby Robson Cancer Trials Research Centre, set up by the Sir Bobby Robson Foundation to run early-stage clinical trials.v Plummer and the Newcastle team won a 2010 Translational Cancer Research Prize from Cancer Research UK for work using rucaparib to treat ovarian cancer. Plummer was elected as a fellow of the UK's Academy of Medical Sciences in 2018.
Faron Pharmaceuticals is a Finnish drug discovery and development company based in Turku, Finland.

G1 Therapeutics, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. The company specializes in developing and commercializing small molecule therapeutics for the treatment of patients with cancer.
















