
The Toronto Islands are a chain of 15 small islands in Lake Ontario, south of mainland Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Comprising the only group of islands in the western part of Lake Ontario, the Toronto Islands are located just offshore from the city's downtown and provide shelter for Toronto Harbour. The islands are home to parkland, the Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport, several yacht clubs, Centreville Amusement Park, a residential area, and several beaches. The island community is considered to be the largest urban car-free community in North America, although some service vehicles are permitted. Access to the Islands is by ferry, including the City of Toronto ferries operating from Jack Layton Ferry Terminal at the foot of Bay Street, or by water taxis.

HMS Bristol was a Town-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. She was the lead ship of the five in her sub-class and was completed in late 1910. The ship spent part of her early career in reserve before she was transferred to the 4th Cruiser Squadron of the North America and West Indies Station in mid-1914. Bristol was briefly deployed to Mexico during the Mexican Revolution to protect British interests there.

The Mediterranean monk seal is a monk seal belonging to the family Phocidae. As of 2015, it is estimated that fewer than 700 individuals survive in three or four isolated subpopulations in the Mediterranean, (especially) in the Aegean Sea, the archipelago of Madeira and the Cabo Blanco area in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. It is believed to be the world's rarest pinniped species.

HMS Monmouth was the lead ship of her class of 10 armoured cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century, jointly known as the County Cruisers.

HMS Glasgow was one of five ships of the Bristol sub-class of the Town-class light cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. Completed in 1910, the ship was briefly assigned to the Home Fleet before she was assigned to patrol the coast of South America. Shortly after the start of the First World War in August 1914, Glasgow captured a German merchant ship. She spent the next several months searching for German commerce raiders. The ship was then ordered to join Rear Admiral Christopher Cradock's squadron in their search for the German East Asia Squadron. He found the German squadron on 1 November off the coast of Chile in the Battle of Coronel. They outnumbered Cradock's force and were individually more powerful, sinking Cradock's two armoured cruisers, although Glasgow was only lightly damaged.

The Isle of May is located in the north of the outer Firth of Forth, approximately 8 km (5.0 mi) off the coast of mainland Scotland. It is 1.8 kilometres long and less than half a kilometre wide. The island is owned and managed by Scottish Natural Heritage as a national nature reserve. There are now no permanent residents, but the island was the site of a St Adrian's Priory during the Middle Ages.

The Malta convoys were Allied supply convoys of the Second World War. The convoys took place during the Siege of Malta in the Mediterranean Theatre. Malta was a base from which British sea and air forces could attack ships carrying supplies from Europe to Italian Libya. Britain fought the Western Desert Campaign against Axis armies in North Africa to keep the Suez Canal and to control Middle Eastern oil. The strategic value of Malta was so great the British risked many merchant vessels and warships to supply the island and the Axis made determined efforts to neutralise the island as an offensive base.

Porlock Weir, about 1.5 miles west of the inland village of Porlock, Somerset, England, is a small settlement around a harbour. Porlock means place of the port and Porlock Weir is its harbour. Weir refers to salmon stakes and traps that were situated along the shore. It is a popular visitor attraction.

The Mediterranean U-boat Campaign lasted from about 21 September 1941 to 19 September 1944 during the Second World War. Malta was an active British base strategically located near supply routes from Europe to North Africa. Axis supply convoys across the Mediterranean Sea suffered severe losses, which in turn threatened the fighting ability of the Axis armies in North Africa. The Allies were able to keep their North African armies supplied. The Kriegsmarine tried to isolate Malta but later it concentrated its U-boat operations on disrupting Allied landing operations in southern Europe.

The military history of Gibraltar during World War II exemplifies Gibraltar's position as a British fortress since the early 18th century and as a vital factor in British military strategy, both as a foothold on the continent of Europe, and as a bastion of British sea power. During World War II, Gibraltar served a vital role in both the Atlantic Theatre and the Mediterranean Theatre, controlling virtually all naval traffic into and out of the Mediterranean Sea from the Atlantic Ocean.

HMS Falmouth was a Town-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during the 1910s. She was one of four ships of the Weymouth sub-class. The ship was initially assigned to the Atlantic Fleet upon completion in 1911, but was reduced to reserve in mid-1913. When the First World War began in 1914, Falmouth was transferred to the 1st Light Cruiser Squadron (LCS) of the Grand Fleet and then the 3rd Light Cruiser Squadron at the end of the year. The ship participated in most of the early fleet actions, including the Battles of Heligoland Bight, Dogger Bank, and Jutland, but was only seriously engaged in the latter. She was torpedoed and sunk off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire by German submarines during the Action of 19 August 1916.
German submarine U-343 was a Type VIIC U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The submarine was laid down in April 1942 at the Nordseewerke yard at Emden, launched in December and commissioned in February 1943 under the command of Leutnant zur See Wolfgang Rahn.

The First Battle of Algeciras was a naval battle fought on 6 July 1801 between a squadron of British Royal Navy ships of the line and a smaller French Navy squadron at anchor in the fortified Spanish port of Algeciras in the Strait of Gibraltar. The British outnumbered their opponents, but the French position was protected by Spanish gun batteries and the complicated shoals that obscured the entrance to Algeciras Bay. The French squadron, under Contre-Amiral Charles Linois, had stopped at Algeciras en route to the major Spanish naval base at Cadiz, where they were to form a combined French and Spanish fleet for operations against Britain and its allies in the French Revolutionary Wars. The British, under Rear-Admiral Sir James Saumarez, sought to eliminate the French squadron before it could reach Cadiz and form a force powerful enough to overwhelm Saumarez and launch attacks against British forces in the Mediterranean Sea.

United States Navy operations during World War I began on April 6, 1917, after the formal declaration of war on the German Empire. The American navy focused on countering enemy U-boats in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, while convoying men and supplies to France and Italy. Because of United States' late entry into the war, her capital ships never engaged the German fleet, and few decisive submarine actions occurred.

The Second Battle of Algeciras was a naval battle fought on the night of 12 July 1801 between a squadron of British Royal Navy ships of the line and a larger squadron of ships from the Spanish Navy and French Navy in the Gut of Gibraltar.

The South Mole is a breakwater located in the southern section of Gibraltar Harbour, in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar, at the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula. Previously known as the New Mole and New Mole Extension, the South Mole, with the rest of harbour, is just north of the east entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar.
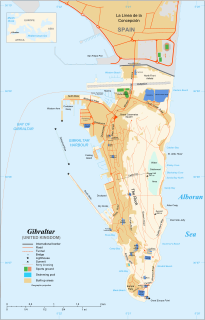
The Detached Mole is a breakwater located at the western aspect of the middle section of Gibraltar Harbour, in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar, at the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula. The Detached Mole, with the rest of harbour, is just north of the east entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar and was the site of the Detached Mole Battery. In addition to the role the breakwater plays in the defence of and access to the harbour, the Detached Mole provides berths for ships. The area adjacent to the mole is also a source of recreational and research opportunities, with dive sites at the wrecks of sunken ships.

The Royal Gibraltar Yacht Club, formerly the Gibraltar Yacht Club, was established by officers of the Royal Navy in 1829. It was one of the first yacht clubs founded outside of Britain. British monarchs and Gibraltarian governors have been patrons of the club; the first visit by a reigning monarch was in 1954. During the latter twentieth century, the naval presence waned and the membership of locals dominated. The club's sailing school was established in 2001, accredited as a teaching facility in 2004, and became a testing centre in 2010. The reclamation projects in the middle section of Gibraltar Harbour necessitated the club's move from 26 Queensway to temporary premises. A new facility is under construction.
Ragged Staff Cave is a cave bordering the harbour in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The cave was converted into Ragged Staff Magazine in 1901.



















