
Helsinki is the capital, largest and most populous city in Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the Uusimaa region in southern Finland and has a population of 673,011. The city's urban area has a population of 1,268,296, making it by far the most populous urban area in Finland and the country's most important centre for politics, education, finance, culture and research. Helsinki is located 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of Tallinn, Estonia, 400 km (250 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden, and 300 km (190 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has close historical links with these three cities.

Vantaa is a city and municipality in the region of Uusimaa in Finland. Vantaa has a population of 246,023, making it the fourth most populous city in Finland. Vantaa is part of the Helsinki Metropolitan Area, which has over 1.5 million inhabitants. The administrative centre of Vantaa is located in the Tikkurila district. Vantaa lies in Southern Finland and shares borders with Helsinki, the Finnish capital, to the south, Espoo to the southwest, Nurmijärvi to the northwest, Kerava and Tuusula to the north, and Sipoo to the east. The city covers a total area of 240.35 square kilometres (92.80 sq mi)), of which 1.97 km2 (0.76 sq mi) is water.

Kauniainen is a small town and a municipality of 10,184 inhabitants in the Helsinki Metropolitan Area in Uusimaa, Finland. It is surrounded and enclaved by the City of Espoo, in the Capital Region of Greater Helsinki. Kauniainen was founded by a corporation in 1906, AB Grankulla, that parcelled land and created a suburb for villas; Kauniainen received the status of a market town in 1920, the Finnish name in 1949 and the title of kaupunki in 1972.

Porvoo is a city and a municipality in the Uusimaa region of Finland, situated on the southern coast about 35 kilometres (22 mi) east of the city border of Helsinki and about 50 kilometres (30 mi) from the city centre. Porvoo was one of the six medieval towns of Finland, along with Turku, Ulvila, Rauma, Naantali and Vyborg. It is first mentioned as a city in texts from the 14th century. Porvoo is the seat of the Swedish-speaking Diocese of Borgå of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Finland. Porvoo was briefly the capital of the former Eastern Uusimaa region.

Southern Finland was a province of Finland from 1997 to 2009. It bordered the provinces of Western Finland and Eastern Finland. It also bordered the Gulf of Finland and Russia.

Sipoo is a municipality of Finland. It is part of the Helsinki metropolitan area. The municipality has a population of 22,570 (30 September 2023) and covers an area of 698.60 square kilometres (269.73 sq mi) of which 358.97 km2 (138.60 sq mi) is water. The population density is 66.45 inhabitants per square kilometre (172.1/sq mi). The administrative center of the municipality is Nikkilä, which is located 34 kilometres (21 mi) northeast of the center of Helsinki. Another significant urban area is Söderkulla, located in the southern part of the municipality.

Kotka is a city in the southern part of the Kymenlaakso province on the Gulf of Finland. Kotka is a major port and industrial city and also a diverse school and cultural city, which was formerly part of the old Kymi parish; later, Kymi with the Haapasaari island and Karhula, the latter of which once separate from Kymi as the market town, were incorporated into Kotka. The neighboring municipalities of Kotka are Hamina, Kouvola and Pyhtää. Kotka belongs to the Kotka-Hamina subdivision, and with Kouvola, Kotka is one of the capital center of the Kymenlaakso region. It is the 19th largest city in terms of population as a single city, but the 12th largest city of Finland in terms of population as an urban area.
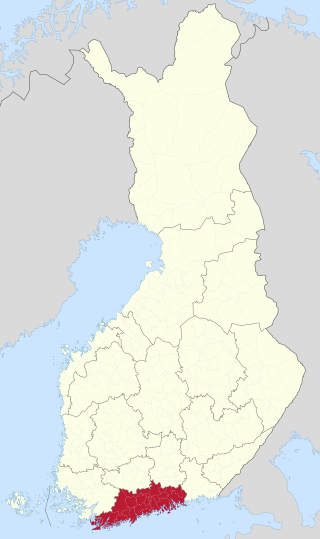
Uusimaa is a region of Finland. It borders the regions of Southwest Finland, Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme), Päijänne Tavastia (Päijät-Häme), and Kymenlaakso. Finland's capital and largest city, Helsinki, along with the surrounding Greater Helsinki area, are both contained in the region, and Uusimaa is Finland's most populous region. The population of Uusimaa is 1,734,000.

Päijät-Häme is a region in Southern Finland south of the lake Päijänne. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Kanta-Häme, Pirkanmaa, Central Finland, South Savo and Kymenlaakso. The biggest city in the region is Lahti.

Tuusula is a municipality of Finland. It belongs to the Helsinki sub-region of the Uusimaa region. The municipality has a population of 40,944 (30 September 2023) and is by far the third largest municipality in Finland after Nurmijärvi and Kirkkonummi that does not use the town or city title by itself.

Helsinki Cathedral is the Finnish Evangelical Lutheran cathedral of the Diocese of Helsinki, located in the neighborhood of Kruununhaka in the centre of Helsinki, Finland, at the Senate Square. The church was originally built from 1830 to 1852 as a tribute to the Grand Duke of Finland, Tsar Nicholas I of Russia. It was also known as St Nicholas's Church until the independence of Finland in 1917. It is a major landmark of the city, and possibly the most famous structure in Finland as a whole when viewed globally.

The coat of arms of Finland is a crowned lion on a red field, the right foreleg replaced with an armoured human arm brandishing a sword, trampling on a sabre with the hindpaws. The coat of arms was originally created around the year 1580.

Korkeasaari is an island in Helsinki. The literal meaning of Korkeasaari is "Tall Island/Islet". It is part of the Mustikkamaa–Korkeasaari district. Korkeasaari Zoo is located on the island and named after it.

The Order of the White Rose of Finland is one of three official orders in Finland, along with the Order of the Cross of Liberty, and the Order of the Lion of Finland. The President of Finland is the Grand Master of all three orders. The orders are administered by boards consisting of a chancellor, a vice-chancellor and at least four members. The orders of the White Rose of Finland and the Lion of Finland have a joint board.

Trams in Helsinki form part of the public transport system organised by Helsinki Regional Transport Authority and operated by Metropolitan Area Transport Ltd in Finland's capital city of Helsinki. The trams are the main means of transport in the city centre, and 56.8 million trips were made on the system in 2019. In addition to the older tram network, there is a single light rail line that was opened in October 2023. Although technically compatible with the tram network, the light rail line is separate from the tram network.

Jätkäsaari is a peninsula and a quarter in Helsinki, the capital city of Finland. It is part to the Kampinmalmi district and Länsisatama neighbourhood. It was the site of the main container harbour in Helsinki until late 2008, when the harbour moved to the new facilities in Vuosaari. The terminals for passenger ferries to Tallinn and Saint Petersburg remain in Jätkäsaari at the West Harbour.

Heinolan maalaiskunta is a former municipality in Päijänne Tavastia, Finland. It was established in 1848. It surrounded Heinola town and was united to Heinola in 1997. Most of its surface area was forest. Population was about 8000 before uniting to Heinola.
The Helsinki City Theatre is a theatre located in Helsinki, Finland. Owned by the Helsinki Theatre Foundation, it calls itself a "modern popular bilingual repertoire theatre."

Kolmikulma, also known as the Diana Park, is a small, rectangular triangular-shaped park located in the Kaartinkaupunki district in the city center of Helsinki, Finland. It is limited by the Yrjönkatu, Uudenmaankatu and Erottajankatu streets. The park was renovated in 2006 and 2007.

Alexander II is a monumental statue located at the Senate Square in central Helsinki, Finland.



















