
Schleswig-Holstein is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg.
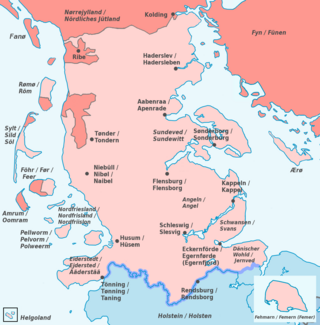
The Duchy of Schleswig was a duchy in Southern Jutland covering the area between about 60 km north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English.
Schleswig-Flensburg is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Rendsburg-Eckernförde, Dithmarschen and Nordfriesland, the Region Syddanmark in Denmark, the city of Flensburg and the Baltic Sea.
Rendsburg-Eckernförde is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by the city of Kiel, the district of Plön, the city of Neumünster, the districts of Segeberg, Steinburg, Dithmarschen and Schleswig-Flensburg, and the Baltic Sea.

Herzogtum Lauenburg is the southernmost Kreis, or district, officially called Kreis Herzogtum Lauenburg, of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bordered by the district of Stormarn, the city of Lübeck, the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, the state of Lower Saxony, and the city state of Hamburg. The district of Herzogtum Lauenburg is named after the former Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg.

South Jutland County is a former county on the south-central portion of the Jutland Peninsula in southern Denmark.

District Harburg is a district (Landkreis) in Hamburg and Lower Saxony, Germany. It takes its name from the town of Harburg upon Elbe, which used to be the capital of the district but is now part of Hamburg. It is bounded by the districts of Lüneburg, Heidekreis, Rotenburg (Wümme) and Stade, by the City of Hamburg and the State of Schleswig-Holstein.
Lüneburg is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Lüchow-Dannenberg, Uelzen, Heidekreis and Harburg, and the states of Schleswig-Holstein and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.

Christian I was a Scandinavian monarch under the Kalmar Union. He was king of Denmark (1448–1481), Norway (1450–1481) and Sweden (1457–1464). From 1460 to 1481, he was also duke of Schleswig and count of Holstein. He was the first king of the House of Oldenburg.

The coat of arms of Finland is a crowned lion on a red field, the right foreleg replaced with an armoured human arm brandishing a sword, trampling on a sabre with the hindpaws. The coat of arms was originally created around the year 1580.

Adolphus XI of Schauenburg, as Adolph I Duke of Schleswig, and as Adolph VIII Count of Holstein-Rendsburg, was the mightiest vassal of the Danish realm.

The coat of arms of Norway is the arms of dominion of king Harald V of Norway, and as such represents both the monarch and the kingdom. It depicts a standing golden lion on a red background, bearing a golden crown and axe with silver blade.

The coat of arms of Denmark has a lesser and a greater version.
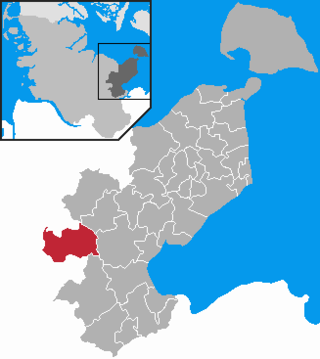
Bosau is a municipality on the Great Plön Lake the district of Ostholstein, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated approximately 13 km west of Eutin, and 30 km southeast of the state capital of Kiel.

The lion is a common charge in heraldry. It traditionally symbolises courage, nobility, royalty, strength, stateliness and valour, because historically the lion has been regarded as the "king of beasts". The lion also carries Judeo-Christian symbolism. The Lion of Judah stands in the coat of arms of Jerusalem. Similar-looking lions can be found elsewhere, such as in the coat of arms of the Swedish royal House of Bjelbo, from there in turn derived into the coat of arms of Finland, formerly belonging to Sweden.

The coat of arms of Schleswig or Southern Jutland depicts two blue lions in a golden shield. It is the heraldic symbol of the former Duchy of Schleswig, originally a Danish province but later disputed between Danes and Germans. The region has been divided between Germany and Denmark since 1920 and the symbol consequently appears in official heraldry in both countries. It is derived from the national coat of arms of Denmark and has been dated to the middle of the 13th century, first known from the arms of Erik Abelsøn, Duke of Schleswig. Throughout the ages, the design has featured both crowned and uncrowned lions, the lions have occasionally been accompanied by heraldic hearts, and usage between heraldic lions and leopards has shifted. The far most common version was to omit both crowns and hearts and this version has been used exclusively for several centuries.
The state of Prussia developed from the State of the Teutonic Order. The original flag of the Teutonic Knights had been a black cross on a white flag. Emperor Frederick II in 1229 granted them the right to use the black Eagle of the Holy Roman Empire. This "Prussian Eagle" remained the coats of arms of the successive Prussian states until 1947.

The flag of Schleswig-Holstein is a horizontal tricolour of blue, white, and red. Schleswig-Holstein is one of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig.

German heraldry is the tradition and style of heraldic achievements in Germany and the Holy Roman Empire, including national and civic arms, noble and burgher arms, ecclesiastical heraldry, heraldic displays and heraldic descriptions. German heraldic style is one of the four major broad traditions within European heraldry and stands in contrast to Gallo-British, Latin and Eastern heraldry, and strongly influenced the styles and customs of heraldry in the Nordic countries, which developed comparatively late. Together, German and Nordic heraldry are often referred to as German-Nordic heraldry.

The coat of arms of Oldenburg is the coat of arms associated with the state of Oldenburg, a county, duchy and then grand duchy that existed between 1101 and 1918. The arms are also associated with the parts of the House of Oldenburg that ruled the state.





















