Related Research Articles

A cereal is any grass cultivated for its edible grain, which is composed of an endosperm, a germ, and a bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food energy worldwide than any other type of crop and are therefore staple crops. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize. Edible grains from other plant families, such as buckwheat, quinoa, and chia, are referred to as pseudocereals.

Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid that acts as a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. As an extract, it is mainly used recreationally, and often illegally for its euphoric and rewarding effects. It is also used in medicine by Indigenous South Americans for various purposes and rarely, but more formally, as a local anaesthetic by medical practitioners in more developed countries. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South America: Erythroxylum coca and E. novogranatense. After extraction from the plant, and further processing into cocaine hydrochloride, the drug is administered by being either snorted, applied topically to the mouth, or dissolved and injected into a vein. It can also then be turned into free base form, in which it can be heated until sublimated and then the vapours can be inhaled.

Herbal teas, also known as herbal infusions and less commonly called tisanes, are beverages made from the infusion or decoction of herbs, spices, or other plant material in hot water. Oftentimes herb tea, or the plain term tea, is used as a reference to all sorts of herbal teas. Many herbs are used in herbal medicine. Some herbal blends contain actual tea.

Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine.

The kola nut is the seed of certain species of plant of the genus Cola, placed formerly in the cocoa family Sterculiaceae and now usually subsumed in the mallow family Malvaceae. These cola species are trees native to the tropical rainforests of Africa. Their caffeine-containing seeds are about 5 centimetres (2.0 in) across and are used as flavoring ingredients in beverages applied to various carbonated soft drinks, from which the name cola originates.

Cornmeal is a meal ground from dried corn (maize). It is a common staple food, and is ground to coarse, medium, and fine consistencies, but not as fine as wheat flour can be. In Mexico, very finely ground cornmeal is referred to as corn flour. When fine cornmeal is made from maize that has been soaked in an alkaline solution, e.g., limewater, it is called masa harina, which is used for making arepas, tamales and tortillas. Boiled cornmeal is called polenta in Italy and is also a traditional dish and bread substitute in Romania.

Ginseng is the root of plants in the genus Panax, such as Korean ginseng, South China ginseng, and American ginseng, characterized by the presence of ginsenosides and gintonin. Ginseng is common in the cuisines and medicines of China and Korea.

White bread typically refers to breads made from wheat flour from which the bran and the germ layers have been removed from the whole wheatberry as part of the flour grinding or milling process, producing a light-colored flour.

The curry tree or Bergera koenigii, is a tropical and sub-tropical tree in the family Rutaceae, native to Asia. The plant is also sometimes called sweet neem, though M. koenigii is in a different family to neem, Azadirachta indica, which is in the related family Meliaceae.

Methylecgonine cinnamate is a natural tropane alkaloid found within the coca plant. Its more common name, cinnamoylcocaine, reflects its close structural similarity to cocaine. It is pharmacologically inactive, but some studies funded by anti-drug agencies imply that it is active when smoked. Furthermore, the discovery of differing impurity products yielding methylecgonine cinnamate in confiscated cocaine have led enforcing agencies to postulate that illicit manufacturers have changed their oxidation procedures when refining cocaine from a crude form. Methylecgonine cinnamate can dimerize to the truxillic acid derivative truxilline. It is notable that methylecgonine cinnamate is given in patents of active cocaine analogue structures.

Erythroxylum coca is one of two species of cultivated coca.

Erythroxylum (Erythroxylon) is a genus of tropical flowering plants in the family Erythroxylaceae. Many of the approximately 200 species contain the tropane alkaloid cocaine, and two of the species within this genus, Erythroxylum coca and Erythroxylum novogranatense, both native to South America, are the main commercial source of cocaine and of the mild stimulant coca tea. Another species, Erythroxylum vaccinifolium is used as an aphrodisiac in Brazilian drinks and herbal medicine.

Coca tea, also called mate de coca, is an herbal tea (infusion) made using the raw or dried leaves of the coca plant, which is native to South America. It is made either by submerging the coca leaf or dipping a tea bag in hot water. The tea is most commonly consumed in the Andes mountain range, particularly Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador and especially in Peru, where it is consumed all around the country. It is greenish yellow in color and has a mild bitter flavor similar to green tea with a more organic sweetness.

Ypadú or ypadu is an unrefined, unconcentrated powder made from toasted coca leaves and the ash of various other plants. It is traditionally prepared and consumed by indigenous tribes in the Northwest Amazon. Like coca teas consumed in Peru to adapt to sickness induced by high elevation, it has a long ethnobotanical history and cultural associations.
Stepan Company is a manufacturer of specialty chemicals headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois. The company was founded in 1932 by Alfred C. Stepan, Jr., and has approximately 2,000 employees. It is currently run by his grandson, F. Quinn Stepan, Jr. The company describes itself as the largest global merchant manufacturer of anionic surfactants, which are used to enhance the foaming and cleaning capabilities of detergents, shampoos, toothpastes, and cosmetics.
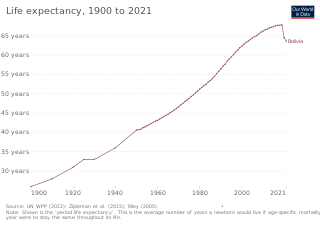
In terms of key indicators, health in Bolivia ranks nearly last among the Western Hemisphere countries. Only Haiti scores consistently lower. Bolivia's child mortality rate of 69 per 1,000 live births is the worst in South America. Proper nourishment is a constant struggle for many Bolivians. Experts estimate that 7 percent of Bolivian children under the age of five and 23 percent of the entire population suffer from malnutrition. Another health factor in Bolivia is sanitation.
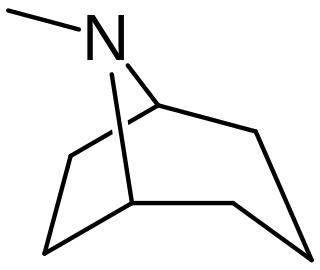
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic [3.2.1] alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants.

Agwa de Bolivia, often shortened to AGWA, is a herbal liqueur made with Bolivian coca leaves and 37 other natural herbs and botanicals including green tea, ginseng, and guarana, distilled and produced in Amsterdam by BABCO Europe Limited. The coca leaf content of the drink, like that in Coca-Cola, has the cocaine alkaloids removed during production, and does not contain the drug.

Erythroxylum novogranatense is a neotropical species of Erythroxylum (Erythroxylaceae). Cocaine is produced from the leaves.
Timothy Charles Plowman was an ethnobotanist best known for his intensive work over the course of 15 years on the genus Erythroxylum in general, and the cultivated coca species in particular. He collected more than 700 specimens from South America, housed in the collection of the Field Museum of Natural History. The standard author abbreviation Plowman is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.
References
- ↑ Plowman T. "Botanical Perspectives on Coca." Journal of Psychedelic Drugs. 1979. 11(1-2): 103-117.
- ↑ Bauer, Irmgard (2019-11-26). "Travel medicine, coca and cocaine: demystifying and rehabilitating Erythroxylum – a comprehensive review". Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines. 5 (1): 20. doi: 10.1186/s40794-019-0095-7 . ISSN 2055-0936. PMC 6880514 . PMID 31798934.
- ↑ "Coca leaf: Myths and Reality". Transnational Institute. 2014-08-05. Retrieved 2022-04-07.
- ↑ Viaño, Beatriz (2021-10-11). "La gastronomía colombiana reivindica el uso de la hoja de coca" (in Spanish). Retrieved 2022-04-07.
- ↑ "They must fight the demand and stop stigmatizing the coca countries." ABI (Agencia Boliviana de Informacion) 26 April 2012.
- ↑ James, A., Aulick, D., Plowman, T., 1975 “Nutritional Value of Coca”, Botanical Museum Leaflets, Harvard University 24 (6): 113-119.