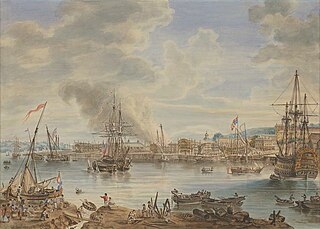Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces the French department of Pas-de-Calais across the Strait of Dover. The county town is Maidstone. It is the fifth most populous county in England, the most populous non-Metropolitan county and the most populous of the home counties.

Chatham is a town located within the Medway unitary authority in the ceremonial county of Kent, England. The town forms a conurbation with neighbouring towns Gillingham, Rochester, Strood and Rainham.

Rochester is a town in the unitary authority of Medway, in Kent, England. The town forms a conurbation with neighbouring towns Chatham, Rainham, Strood and Gillingham. It is at the lowest bridging point of the River Medway about 30 miles (50 km) from London. Rochester was a city until losing its status as one in 1998 following the forming of Medway and failing to protect its status as a city. There have been ongoing campaigns to reinstate the city status for Rochester.

Medway is a unitary authority district and conurbation in Kent, South East England. It had a population in 2019 of 278,016. The unitary authority was formed in 1998 when Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with the Borough of Gillingham to form Medway Towns. It is now a unitary authority area run by Medway Council, independent of Kent County Council but still part of the ceremonial county of Kent.

Gillingham is a large town in the unitary authority area of Medway in the ceremonial county of Kent, England. The town forms a conurbation with neighbouring towns Chatham, Rochester, Strood and Rainham. It is also the largest town in the borough of Medway.

Sheerness is a town and civil parish beside the mouth of the River Medway on the north-west corner of the Isle of Sheppey in north Kent, England. With a population of 11,938, it is the second largest town on the island after the nearby town of Minster which has a population of 21,319.
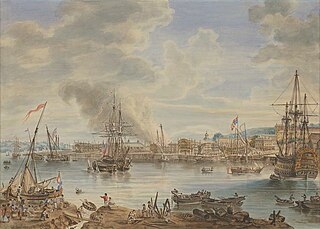
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham.

Garrison Point Fort is a former artillery fort situated at the end of the Garrison Point peninsula at Sheerness on the Isle of Sheppey in Kent. Built in the 1860s in response to concerns about a possible French invasion, it was the last in a series of artillery batteries that had existed on the site since the mid-16th century. The fort's position enabled it to guard the strategic point where the River Medway meets the Thames. It is a rare example of a two-tiered casemated fort – one of only two of that era in the country – with a design that is otherwise similar to that of several of the other forts along the lower Thames. It remained operational until 1956 and is now used by the Sheerness Docks as a port installation.

Fort Amherst, in Medway, South East England, was constructed in 1756 at the southern end of the Brompton lines of defence to protect the southeastern approaches to Chatham Dockyard and the River Medway against a French invasion. Fort Amherst is now open as a visitor attraction throughout the year with tours provided through the tunnel complex

Hoo Fort is a nineteenth-century military installation on the River Medway in Kent, England, that formed part of the defences of Chatham Naval Dockyard. Hoo Fort, like Fort Darnet 1 km (0.6 mi) downstream, was built on the recommendations of the 1859 Royal Commission. It is located on Hoo Island covering Pinup Reach, the inner navigable channel of the River Medway. Hoo Island sits to the south of the Hoo Peninsula and is within the parish of Hoo, Kent. The fort can be viewed from along the Saxon Shore Way, accessible from Vicarage Lane in Hoo.

Lower Upnor and Upper Upnor are two small villages in Medway, Kent, England. They are in the parish of Frindsbury Extra on the western bank of the River Medway. Today the two villages are mainly residential and a centre for small craft moored on the river, but Upnor Castle is a preserved monument, part of the river defences from the sixteenth century.

His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy. Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is located on the eastern shore of Portsmouth Harbour, north of the Solent and the Isle of Wight. Until the early 1970s, it was officially known as Portsmouth Royal Dockyard ; thereafter the term 'Naval Base' gained currency, acknowledging a greater focus on personnel and support elements alongside the traditional emphasis on building, repairing and maintaining ships. In 1984 Portsmouth's Royal Dockyard function was downgraded and it was formally renamed the 'Fleet Maintenance and Repair Organisation' (FMRO). The FMRO was privatized in 1998, and for a time, shipbuilding, in the form of block construction, returned. Around 2000, the designation HMS Nelson was extended to cover the entire base.

The Historic Dockyard Chatham is a maritime museum on part of the site of the former royal/naval dockyard at Chatham in Kent, South East England.

Upnor Castle is an Elizabethan artillery fort located on the west bank of the River Medway in Kent. It is in the village of Upnor, opposite and a short distance downriver from the Chatham Dockyard, at one time a key naval facility. The fort was intended to protect both the dockyard and ships of the Royal Navy anchored in the Medway. It was constructed between 1559–67 on the orders of Elizabeth I, during a period of tension with Spain and other European powers. The castle consists of a two-storeyed main building protected by a curtain wall and towers, with a triangular gun platform projecting into the river. It was garrisoned by about 80 men with a peak armament of around 20 cannon of various calibres.

St Mary's Island, is part of the Chatham Maritime development area in Medway, South East England. It is located at the northern end of Chatham, adjacent to Brompton and Gillingham. Once part of the Royal Dockyard, Chatham, the area had consisted of a mixture of sports fields and warehousing during the later years of the Royal Navy's time in occupation.

Sheerness Dockyard also known as the Sheerness Station was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the Sheerness peninsula, at the mouth of the River Medway in Kent. It was opened in the 1660s and closed in 1960.

Grain Tower is a mid-19th-century gun tower situated offshore just east of Grain, Kent, standing in the mouth of the River Medway. It was built along the same lines as the Martello towers that were constructed along the British and Irish coastlines in the early 19th century and is the last-built example of a gun tower of this type. It owed its existence to the need to protect the important dockyards at Sheerness and Chatham from a perceived French naval threat during a period of tension in the 1850s.
Fort Gillingham, also known as Gillingham Fort, was constructed in 1669 on the south bank of the River Medway in Kent, England.

The Great Lines Heritage Park is a complex network of open spaces in the Medway Towns, connecting Chatham, Gillingham, Brompton and the Historic Dockyard. The long military history of the towns has dominated the history of the site and the park. The Great Lines Heritage Park, consists of Fort Amherst, Chatham Lines, the Field of Fire, Inner Lines, Medway Park together with the Lower Lines.

The Royal Naval Barracks, Chatham also known as HMS Pembroke was a naval barracks built between the Victorian Steam Yard and Brompton Barracks between 1897 and 1902. It was built on the site of a prison built in 1853 to house over 1,000 convicts, with the intention that they would be used to build the Dockyard extension.