Related Research Articles

Prostate cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system just below the bladder. Early prostate cancer usually causes no symptoms. As the cancer develops, one or more tumors can damage nearby organs causing erectile dysfunction, blood in the urine or semen, and trouble urinating. For some patients, the cancer eventually spread to other areas of the body, particularly the bones and lymph nodes. There, tumors cause severe bone pain, leg weakness or paralysis, and eventually death.

Prostate-specific antigen (PSA), also known as gamma-seminoprotein or kallikrein-3 (KLK3), P-30 antigen, is a glycoprotein enzyme encoded in humans by the KLK3 gene. PSA is a member of the kallikrein-related peptidase family and is secreted by the epithelial cells of the prostate gland.

Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat pattern hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat excessive hair growth in women. It is usually taken orally but there are topical formulations for patients with hair loss, designed to minimize systemic exposure by acting specifically on hair follicles.

Leuprorelin, also known as leuprolide, is a manufactured version of a hormone used to treat prostate cancer, breast cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, as part of transgender hormone therapy, for early puberty, or to perform chemical castration of violent sex offenders. It is given by injection into a muscle or under the skin.
Samuel Ray Denmeade is a Professor of Oncology, Urology and Pharmacology and Molecular Sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. Over 10 of his published papers have each been cited over 100 times.

Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP), also prostatic specific acid phosphatase (PSAP), is an enzyme produced by the prostate. It may be found in increased amounts in men who have prostate cancer or other diseases.

Flutamide, sold under the brand name Eulexin among others, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which is used primarily to treat prostate cancer. It is also used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions like acne, excessive hair growth, and high androgen levels in women. It is taken by mouth, usually three times per day.
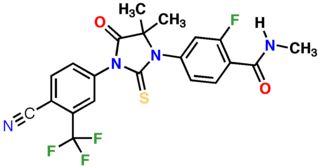
Enzalutamide, sold under the brand name Xtandi, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is indicated for use in conjunction with castration in the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC). It is taken by mouth.
Cancer screening aims to detect cancer before symptoms appear. This may involve blood tests, urine tests, DNA tests, other tests, or medical imaging. The benefits of screening in terms of cancer prevention, early detection and subsequent treatment must be weighed against any harms.

Olaparib, sold under the brand name Lynparza, is a medication for the maintenance treatment of BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer in adults. It is a PARP inhibitor, inhibiting poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP), an enzyme involved in DNA repair. It acts against cancers in people with hereditary BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, which include some ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers.

Charles L. Sawyers is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) investigator who holds the Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis Chair of the Human Oncology and Pathogenesis Program (HOPP) at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK). HOPP is a program created in 2006 that comprises researchers from many disciplines to bridge clinical and laboratory discoveries.

ZERO - The End of Prostate Cancer is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization dedicated to prostate cancer education, testing, patient support, research and advocacy.
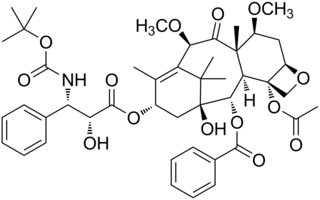
Cabazitaxel, sold under the brand name Jevtana, is a semi-synthetic derivative of a natural taxoid. It is a microtubule inhibitor, and the fourth taxane to be approved as a cancer therapy.

Anthony Peter Lowe AP is a British-Australian mathematical physicist and actuary. He previously served as chief executive officer of the Prostate Cancer Foundation of Australia, and is a frequent media commentator on prostate cancer and prostate specific antigen (PSA) testing.

Apalutamide, sold under the brand name Erleada among others, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is specifically indicated for use in conjunction with castration in the treatment of non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (NM-CRPC). It is taken by mouth.
Kevin M. Slawin is an American physician and the founder of Bellicum Pharmaceuticals and the Vanguard Urologic Institute at Memorial Hermann Medical Group. He was also the Director of Urology at Memorial Hermann Hospital. Slawin specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of urologic cancers and robotic surgery. He is also possesses patents related to the advancement of prostate cancer diagnosis, staging and treatment and to the cellular immunotherapy of cancer.

Ethinylestradiol sulfonate (EES), sold under the brand names Deposiston and Turisteron among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in birth control pills for women and in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It has also been investigated in the treatment of breast cancer in women. The medication was combined with norethisterone acetate in birth control pills. EES is taken by mouth once per week.
Rajveer Purohit is an Indian-born American physician, Director of Reconstructive Urology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City, and associate professor in its Department of Urology.
Declan G. Murphy, FRACS, FRCS, is a urologist, director of the unit for genitourinary oncology and robotic surgery at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia, professor at the Sir Peter MacCallum Department of Oncology at the University of Melbourne, and associate editor of the British Journal of Urology International. In 2010 he introduced robotic surgery for urology to the public sector health services in Victoria, Australia.
Amina Zoubeidi is a Canadian research scientist and prostate cancer researcher. She's a scientist at the Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute and an associate professor in the Department of Urologic Sciences at the University of British Columbia. During her tenure at UBC, Zoubeidi and her research team developed the first drug that targets and blocks BRN2, thus stopping Neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) tumours and creating a possible treatment for the previously thought incurable disease.
References
- ↑ Kovacs, G.; Akhtar, M.; Beckwith, BJ.; Bugert, P.; Cooper, CS.; Delahunt, B.; Eble, JN.; Fleming, S.; et al. (Oct 1997). "The Heidelberg classification of renal cell tumours". J Pathol. 183 (2): 131–3. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199710)183:2<131::AID-PATH931>3.0.CO;2-G . PMID 9390023. S2CID 34796951.
- ↑ "Thousands of prostate cancer sufferers could be spared disabling treatment thanks to new test". Daily Mirror . March 2017. Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- ↑ "Scientists praised by champion jockey after developing test to stop cancer patients get unnecessary treatment which can cause impotence". Eastern Daily Press . Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- ↑ Sample, Ian (19 April 2022). "Discovery of bacteria linked to prostate cancer hailed as potential breakthrough". The Guardian . Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Colin Cooper". Google Scholar . Retrieved 13 November 2023.