History
Collective wisdom, which may be said to have a more distinctly human quality than collective intelligence, is contained in such early works as The Torah, The Bible, The Koran, the works of Plato, Confucius and Buddha, Bhagavad Gita, and the many myths and legends from all cultures. Drawing from the idea of universal truth, the point of collective wisdom is to make life easier/more enjoyable through understanding human behavior, whereas the point of collective intelligence is to make life easier/more enjoyable through the application of acquired knowledge. While collective intelligence may be said to have more mathematical and scientific bases, collective wisdom also accounts for the spiritual realm of human behaviors and consciousness. Thomas Jefferson referred to the concept of collective wisdom when he made his statement, "A Nation's best defense is an educated citizenry". Ιn effect, the ideal of a democracy is that government functions best when everyone participates. British philosopher Thomas Hobbes uses his Leviathan to illustrate how mankind's collective consciousness grows to create collective wisdom. Émile Durkheim argues in The Elementary Forms of Religious Life (1912) that society by definition constitutes a higher intelligence because it transcends the individual over space and time, thereby achieving collective wisdom. 19th-century Prussian physicist Gustav Fechner argued for a collective consciousness of mankind, and cited Durkheim as the most credible scholar in the field of "collective consciousness". Fechner also referred to the work of Jesuit Priest Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, whose concept of the noosphere was a precursor to the term collective intelligence. H.G. Wells's concept of "world brain", as described in his book of essays with the same title, has more recently been examined in depth by Pierre Lévy in his book, The Universe-Machine: Creation, Cognition and Computer Culture . Howard Bloom's treatise "The Global Brain: The Evolution of Mass Mind from the Big Bang to the 21st Century" examines similarities in organizational patterns in nature, human brain function, society, and the cosmos. He also posits the theory that group selection directs evolutionary change through collective information processing. Alexander Flor related the world brain concept with current developments in global knowledge networking spawned by new information and communication technologies in an online paper, A Global Knowledge Network. [1] He also discussed the collective mind within the context of social movements in Asia in a book Development Communication Praxis. [2]
Dave Pollard's restatement of Collective wisdom:
"Many cognitive, coordination and cooperation problems are best solved by canvassing groups (the larger the better) of reasonably informed, unbiased, engaged people. The group's answer is almost invariably much better than any individual expert's answer, even better than the best answer of the experts in the group."
Contemporary definition and research
Harnessing the collective wisdom of people is an area of intense contemporary interest and cutting-edge research. The application of the term to methodologies that are designed to harness collective wisdom is credited to the work of Alexander Christakis and his group, [3] [4] As the challenges society faces today are of extreme complexities, the only solution is to develop technologies capable of harnessing the Collective Intelligence and collective wisdom of many people, or even crowds. The Institute for 21st Century Agoras founded in 2002 by Alexander Christakis, the Wisdom Research Network of the University of Chicago [5] launched in 2010 and the MIT Center for Collective Intelligence founded by Thomas W. Malone in 2007 are some examples.
Collective Wisdom Initiative
The Collective Wisdom Initiative was formed in 2000 with the support of the Fetzer Institute for the purpose of gathering material on the research, theory, and practice of collective wisdom. It was a collaboration of practitioners and academics in areas such as business, health care, mental health, education, criminal justice, and conflict resolution. [6] Several of the founding members subsequently co-authored The Power of Collective Wisdom. In this, six stances or principles, which support the power of collective wisdom are presented: deep listening, suspension of certainty, seeing whole systems/seeking diverse perspectives, respect for other/group discernment, welcoming all that is arising, and trust in the transcendent. [7]
Two strands of thought relating to collective wisdom follow very different paths. The first suggests that aggregates of people and information will succeed in advancing wisdom, that wisdom is built on the accumulation of data and knowledge, without a need for judgement or qualification. Some have faulted this belief for failing to take into account the importance of 'adaptive assessment'. [8] The second argues that wisdom is only possible in reflective states of mind, including metacognition. According to Alan Briskin, wisdom requires systematic reflection on the inner self and the outer states of social order. Mark Baurelein has made the case that the hypercommunication of knowledge has hobbled rather than promoted intellectual development. [9]

The sociology of knowledge is the study of the relationship between human thought, the social context within which it arises, and the effects that prevailing ideas have on societies. It is not a specialized area of sociology. Instead, it deals with broad fundamental questions about the extent and limits of social influences on individuals' lives and the social-cultural basis of our knowledge about the world. The sociology of knowledge has a subclass and a complement. Its subclass is sociology of scientific knowledge. Its complement is the sociology of ignorance.

John Rogers Searle is an American philosopher widely noted for contributions to the philosophy of language, philosophy of mind, and social philosophy. He began teaching at UC Berkeley in 1959, and was Willis S. and Marion Slusser Professor Emeritus of the Philosophy of Mind and Language and Professor of the Graduate School at the University of California, Berkeley, until June 2019, when his status as professor emeritus was revoked because he was found to have violated the university's sexual harassment policies.

Mind uploading is a speculative process of whole brain emulation in which a brain scan is used to completely emulate the mental state of the individual in a digital computer. The computer would then run a simulation of the brain's information processing, such that it would respond in essentially the same way as the original brain and experience having a sentient conscious mind.
Collaborative intelligence characterizes multi-agent, distributed systems where each agent, human or machine, is autonomously contributing to a problem solving network. Collaborative autonomy of organisms in their ecosystems makes evolution possible. Natural ecosystems, where each organism's unique signature is derived from its genetics, circumstances, behavior and position in its ecosystem, offer principles for design of next generation social networks to support collaborative intelligence, crowdsourcing individual expertise, preferences, and unique contributions in a problem solving process.
Collective consciousness, collective conscience, or collective conscious is the set of shared beliefs, ideas, and moral attitudes which operate as a unifying force within society. In general, it does not refer to the specifically moral conscience, but to a shared understanding of social norms.
Herd mentality is the tendency for people’s behavior or beliefs to conform to those of the group they belong to. The concept of herd mentality has been studied and analyzed from different perspectives, including biology, psychology and sociology. This psychological phenomenon can have profound impacts on human behavior.

The Wisdom of Crowds: Why the Many Are Smarter Than the Few and How Collective Wisdom Shapes Business, Economies, Societies and Nations, published in 2004, is a book written by James Surowiecki about the aggregation of information in groups, resulting in decisions that, he argues, are often better than could have been made by any single member of the group. The book presents numerous case studies and anecdotes to illustrate its argument, and touches on several fields, primarily economics and psychology.

Intelligence amplification (IA) is the use of information technology in augmenting human intelligence. The idea was first proposed in the 1950s and 1960s by cybernetics and early computer pioneers.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to thought (thinking):

Alexander "Aleco" Christakis is a Greek American social scientist, systems scientist and cyberneticist, former faculty member of several Universities, organizational consultant and member of the Club of Rome, known for his "study and design of social systems".
The wisdom of the crowd is the collective opinion of a diverse and independent group of individuals rather than that of a single expert. This process, while not new to the Information Age, has been pushed into the mainstream spotlight by social information sites such as Quora, Reddit, Stack Exchange, Wikipedia, Yahoo! Answers, and other web resources which rely on collective human knowledge. An explanation for this phenomenon is that there is idiosyncratic noise associated with each individual judgment, and taking the average over a large number of responses will go some way toward canceling the effect of this noise.

The global brain is a neuroscience-inspired and futurological vision of the planetary information and communications technology network that interconnects all humans and their technological artifacts. As this network stores ever more information, takes over ever more functions of coordination and communication from traditional organizations, and becomes increasingly intelligent, it increasingly plays the role of a brain for the planet Earth. In the philosophy of mind, global brain finds an analog in Averroes's theory of the unity of the intellect.
Decentralized decision-making is any process where the decision-making authority is distributed throughout a larger group. It also connotes a higher authority given to lower level functionaries, executives, and workers. This can be in any organization of any size; it may be present in a governmental authority to a corporation. However, the context in which the term is used is generally that of larger organizations. This distribution of power, in effect, has far-reaching implications in the fields of management, organizational behavior, and government.
The Elementary Forms of Religious Life, published by the French sociologist Émile Durkheim in 1912, is a book that analyzes religion as a social phenomenon. Durkheim attributes the development of religion to the emotional security attained through communal living. His study of totemic societies in Australia led to a conclusion that the animal or plant that each clan worshipped as a sacred power was in fact that society itself. Halfway through the text, Durkheim asks, "So if [the totem animal] is at once the symbol of the god and of the society, is that not because the god and the society are only one?"

The evolutionary origin of religion and religious behavior is a field of study related to evolutionary psychology, the origin of language and mythology, and cross-cultural comparison of the anthropology of religion. Some subjects of interest include Neolithic religion, evidence for spirituality or cultic behavior in the Upper Paleolithic, and similarities in great ape behavior.
A group mind, group ego, mind coalescence, or gestalt intelligence in science fiction is a plot device in which multiple minds, or consciousnesses, are linked into a single collective consciousness or intelligence.
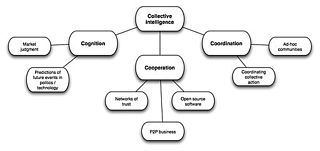
Collective intelligence (CI) is shared or group intelligence (GI) that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of many individuals and appears in consensus decision making. The term appears in sociobiology, political science and in context of mass peer review and crowdsourcing applications. It may involve consensus, social capital and formalisms such as voting systems, social media and other means of quantifying mass activity. Collective IQ is a measure of collective intelligence, although it is often used interchangeably with the term collective intelligence. Collective intelligence has also been attributed to bacteria and animals.

Reinventing Discovery: The New Era of Networked Science is a book written by Michael Nielsen and released in October 2011. It argues for the benefits of applying the philosophy of open science to research.
The concept of conscious evolution refers to the theoretical ability of human beings to become conscious participants in the evolution of their cultures, or even of the entirety of human society, based on a relatively recent combination of factors, including increasing awareness of cultural and social patterns, reaction against perceived problems with existing patterns, injustices, inequities, and other factors.
Virtual collective consciousness (VCC) is a term rebooted and promoted by two behavioral scientists, Yousri Marzouki and Olivier Oullier in their 2012 Huffington Post article titled: "Revolutionizing Revolutions: Virtual Collective Consciousness and the Arab Spring", after its first appearance in 1999-2000. VCC is now defined as an internal knowledge catalyzed by social media platforms and shared by a plurality of individuals driven by the spontaneity, the homogeneity, and the synchronicity of their online actions. VCC occurs when a large group of persons, brought together by a social media platform think and act with one mind and share collective emotions. Thus, they are able to coordinate their efforts efficiently, and could rapidly spread their word to a worldwide audience. When interviewed about the concept of VCC that appeared in the book - Hyperconnectivity and the Future of Internet Communication - he edited, Professor of Pervasive Computing, Adrian David Cheok mentioned the following: "The idea of a global (collective) virtual consciousness is a bottom-up process and a rather emergent property resulting from a momentum of complex interactions taking place in social networks. This kind of collective behaviour results from a collision between a physical world and a virtual world and can have a real impact in our life by driving collective action."










