Related Research Articles
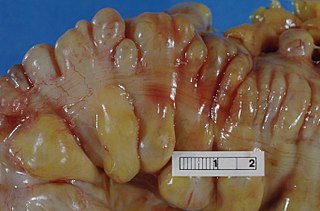
Diverticulitis, also called colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—diverticula—that can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdominal pain of sudden onset, but the onset may also occur over a few days. There may also be nausea, diarrhea or constipation. Fever or blood in the stool suggests a complication. People may experience a single attack, repeated attacks, or ongoing "smouldering" diverticulitis.

Colorectal surgery is a field in medicine dealing with disorders of the rectum, anus, and colon. The field is also known as proctology, but this term is now used infrequently within medicine and is most often employed to identify practices relating to the anus and rectum in particular. The word proctology is derived from the Greek words πρωκτός proktos, meaning "anus" or "hindparts", and -λογία -logia, meaning "science" or "study".

A colostomy is an opening (stoma) in the large intestine (colon), or the surgical procedure that creates one. The opening is formed by drawing the healthy end of the colon through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and suturing it into place. This opening, often in conjunction with an attached ostomy system, provides an alternative channel for feces to leave the body. Thus if the natural anus is unavailable for that function, an artificial anus takes over. It may be reversible or irreversible, depending on the circumstances.
In anatomy, a stoma is any opening in the body. For example, a mouth, a nose, and an anus are natural stomata. Any hollow organ can be manipulated into an artificial stoma as necessary. This includes the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, ileum, colon, pleural cavity, ureters, urinary bladder, and renal pelvis. Such a stoma may be permanent or temporary.
An abdomino perineal resection, formally known as abdominoperineal resection of the rectum and abdominoperineal excision of the rectum is a surgery for rectal cancer or anal cancer. It is frequently abbreviated as AP resection, APR and APER.

Ileostomy is a stoma constructed by bringing the end or loop of small intestine out onto the surface of the skin, or the surgical procedure which creates this opening. Intestinal waste passes out of the ileostomy and is collected in an external ostomy system which is placed next to the opening. Ileostomies are usually sited above the groin on the right hand side of the abdomen.
In medicine, the ileal pouch–anal anastomosis (IPAA), also known as restorative proctocolectomy (RPC), ileal-anal reservoir (IAR), an ileo-anal pouch, ileal-anal pullthrough, or sometimes referred to as a J-pouch, S-pouch, W-pouch, or a pelvic pouch, is an anastomosis of a reservoir pouch made from ileum to the anus, bypassing the former site of the colon in cases where the colon and rectum have been removed. The pouch retains and restores functionality of the anus, with stools passed under voluntary control of the person, preventing fecal incontinence and serving as an alternative to a total proctocolectomy with ileostomy.
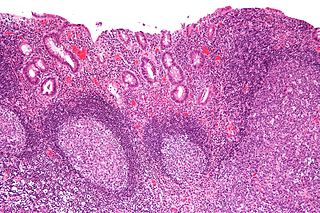
Diversion colitis is an inflammation of the colon which can occur as a complication of ileostomy or colostomy, where symptoms may occur between one month and three years following surgery. It also occurs frequently in a neovagina created by colovaginoplasty, with varying delay after the original procedure. Despite the presence of a variable degree of inflammation the most suggestive histological feature remains the prominent lymphoid aggregates.
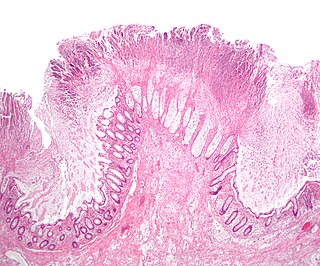
Colectomy is bowel resection of the large bowel (colon). It consists of the surgical removal of any extent of the colon, usually segmental resection. In extreme cases where the entire large intestine is removed, it is called total colectomy, and proctocolectomy denotes that the rectum is included.

An imperforate anus or anorectal malformations (ARMs) are birth defects in which the rectum is malformed. ARMs are a spectrum of different congenital anomalies which vary from fairly minor lesions to complex anomalies. The cause of ARMs is unknown; the genetic basis of these anomalies is very complex because of their anatomical variability. In 8% of patients, genetic factors are clearly associated with ARMs. Anorectal malformation in Currarino syndrome represents the only association for which the gene HLXB9 has been identified.
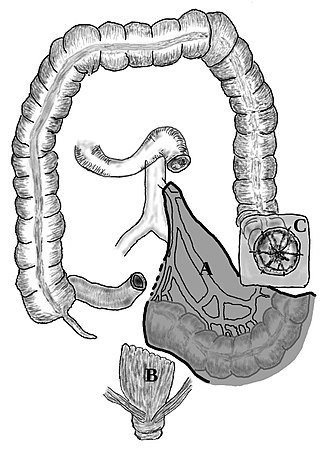
A proctosigmoidectomy, Hartmann's operation or Hartmann's procedure is the surgical resection of the rectosigmoid colon with closure of the anorectal stump and formation of an end colostomy. It was used to treat colon cancer or inflammation. Currently, its use is limited to emergency surgery when immediate anastomosis is not possible, or more rarely it is used palliatively in patients with colorectal tumours.
Total mesorectal excision (TME) is a standard surgical technique for treatment of rectal cancer, first described in 1982 by Professor Bill Heald at the UK's Basingstoke District Hospital. It is a precise dissection of the mesorectal envelope comprising rectum containing the tumour together with all the surrounding fatty tissue and the sheet of tissue that contains lymph nodes and blood vessels. Dissection is along the avascular alveolar plane between the presacral and mesorectal fascia, described as holy plane. Dissection along this plane facilitates a straightforward dissection and preserves the sacral vessels and hypogastric nerves and is a sphincter-sparing resection and decreases permanent stoma rates. It is possible to rejoin the two ends of the colon; however, most patients require a temporary ileostomy pouch to bypass the colon, allowing it to heal with less risk of infection, perforation or leakage.
A lower anterior resection, formally known as anterior resection of the rectum and colon and anterior excision of the rectum or simply anterior resection, is a common surgery for rectal cancer and occasionally is performed to remove a diseased or ruptured portion of the intestine in cases of diverticulitis. It is commonly abbreviated as LAR.

The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about 12 centimetres (4.7 in) long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal, which is about 4 centimetres (1.6 in) long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin rectumintestinum, meaning straight intestine.
Pouchoscopy is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure to examine an ileo-anal pouch, a replacement for the colon / rectum which is surgically created from the small intestine (ileum) as treatment for ulcerative colitis, a preventive measure in certain genetic illnesses such as FAP or HNPCC or as a procedure in the treatment of colon cancer. Typically, a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube is passed through the anus. Pouchoscopy is the first line test to evaluate pouch dysfunction, and is used for surveillance in individuals with genetic cancer syndromes (FAP). While pouchoscopy may help assess the integrity of the J-pouch, this evaluation is more commonly completed using a pouchogram. A pouchoscopy is normally part of a routine follow up and is used to confirm the diagnosis of pouchitis and cuffitis.
Rectal discharge is intermittent or continuous expression of liquid from the anus. Normal rectal mucus is needed for proper excretion of waste. Otherwise, this is closely related to types of fecal incontinence but the term rectal discharge does not necessarily imply degrees of incontinence. Types of fecal incontinence that produce a liquid leakage could be thought of as a type of rectal discharge.
A rectovestibular fistula, also referred to simply as a vestibular fistula, is an anorectal congenital disorder where an abnormal connection (fistula) exists between the rectum and the vulval vestibule of the female genitalia.
Warren operation is a surgery performed to correct anal incontinence. It is done by disrupting the anterior segment of the anal sphincter, perineal body and rectovaginal septum.

The National Accreditation Program for Rectal Cancer (NAPRC) was formed to address the differences between patient outcomes in the United States as compared to Europe. According to the American College of Surgeons, outcomes for rectal cancer patients in Europe have for years been significantly better than for those in the U.S. Characterized by the use of multidisciplinary teams to make treatment decisions, the NAPRC standards aim to decrease the average circumferential resection margins, decrease the overall colostomy rate, and increase quality of life as reported by recovering patients.

William Harrison Cripps was a prominent British surgeon. He was particularly noted for his expertise on cancer of the rectum.
References
- ↑ Schmelzer, T. M.; Hope, W. W.; Iannitti, D. A.; Kercher, K. W.; Heniford, B. T. (December 2006). "Laparoscopic colostomy takedown offers advantages over traditional surgery". J Minim Access Surg. 2 (4): 201–2. doi: 10.4103/0972-9941.28179 . PMC 3016479 . PMID 21234145.