The Columbia University Indo-Iranian Series is a 13-volume book series edited by A. V. Williams Jackson and published by the Columbia University Press between 1901 and 1932. [1]
The Columbia University Indo-Iranian Series is a 13-volume book series edited by A. V. Williams Jackson and published by the Columbia University Press between 1901 and 1932. [1]
| Volume | Year | Author | Title | Reviews | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1914 | A. V. Williams Jackson ; Abraham Yohannan | A Catalogue of the Collection of Persian Manuscripts | [2] | [3] |
| 2 | 1902 | Louis H. Gray | Indo-Iranian Phonology | [4] | [5] |
| 3 | 1906 | Montgomery Schuyler, Jr. | A Bibliography of the Sanskrit Drama | [6] | [7] |
| 4 | 1901 | Montgomery Schuyler, Jr. | Index Verborum of the Fragments of the Avesta | [8] | |
| 5 | 1908 | Justin Hartley Moore | Sayings of Buddha: The Iti-vuttaka | [9] | |
| 6 | 1908 | Maneckji Nusservanji Dhalla | The Nyaishes, or Zoroastrian Litanies | [10] | |
| 7 | 1912 | George C. O. Haas | The Daśarūpa, a Treatise on Hindu Dramaturgy by Dhanamjaya | [11] | [12] |
| 8 | 1913 | Louis H. Gray | Vāsavadattā, A Sanskrit Romance by Subandhu | [13] | [14] |
| 9 | 1917 | George Payn Quackenbos | The Sanskrit Poems of Mayura by Mayura | [15] | [16] |
| 10 | 1923 | G. K. Nariman; A. V. Williams Jackson; Charles J. Ogden | Priyadarsika, a Sanskrit Drama by Harsha | [17] [18] | [19] |
| 11 | 1926 | Jal Dastur Cursetji Pavry | The Zoroastrian Doctrine of a Future Life | [20] [21] [22] | |
| 12 | 1928 | A. V. Williams Jackson | Zoroastrian Studies: The Iranian Religion and Various Monographs | [23] [24] | |
| 13 | 1932 | A. V. Williams Jackson | Researches in Manichaeism, with Special Reference to the Turfan Fragments | [25] | [26] |

The Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, commonly known as the Royal Asiatic Society, was established, according to its royal charter of 11 August 1824, to further "the investigation of subjects connected with and for the encouragement of science, literature and the arts in relation to Asia." From its incorporation the society has been a forum, through lectures, its journal, and other publications, for scholarship relating to Asian culture and society of the highest level. It is the United Kingdom's senior learned society in the field of Asian studies. Fellows of the society are elected regularly and include highly accomplished and notable scholars of Asian studies; they use the post-nominal letters FRAS.
Kuchean was a Western member of the Tocharian branch of Indo-European languages, extinct from the ninth century. Once spoken in the Tarim Basin in Central Asia, Tocharian B shows an internal chronological development; three linguistic stages have been detected. The oldest stage is attested only in Kucha. There is also the middle ('classicalʼ), and the late stage.
Indology, also known as South Asian studies, is the academic study of the history and cultures, languages, and literature of the Indian subcontinent, and as such is a subset of Asian studies.

Abraham Valentine Williams Jackson, L.H.D., Ph.D., LL.D. was an American specialist on Indo-European languages.

Anga was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of eastern India whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The members of the Aṅga tribe were called the Āṅgeyas.
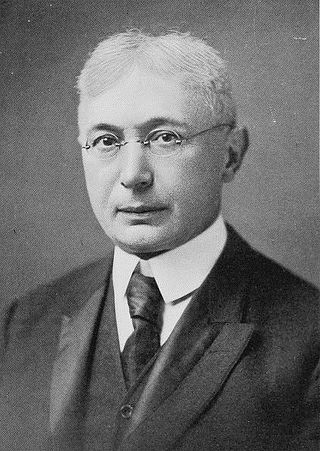
Maurice Bloomfield, Ph.D., LL.D. was an Austrian Empire-born American philologist and Sanskrit scholar.

Louis Herbert Gray (1875–1955) was an American Orientalist, born at Newark, New Jersey. He graduated from Princeton University in 1896 and from Columbia University.

The Origins of The Koran: Classic Essays on Islam’s Holy Book is a 1998 book edited by Ibn Warraq. It contains a collection of 13 critical studies of the Qur'an written over the past two centuries by historians and scholars of the Middle East: Ibn Warraq, Theodor Nöldeke, Leone Caetani, Alphonse Mingana, Arthur Jeffery, David Samuel Margoliouth, Abraham Geiger, William St. Clair Tisdall, Charles Cutler Torrey and Andrew Rippin. Most of these authors wrote their essays on the Qur'an before World War II (1939–1945).
Priyadarsika is a Sanskrit play attributed to king Harsha. It was first translated into English by G. K. Nariman, A. V. Williams Jackson, and Charles J. Ogden and published by the Columbia University Press in 1923 as the tenth volume of the 13 volume Columbia University Indo-Iranian Series (1901–32).

Sir George Abraham Grierson was an Irish administrator and linguist in British India. He worked in the Indian Civil Service but an interest in philology and linguistics led him to pursue studies in the languages and folklore of India during his postings in Bengal and Bihar. He published numerous studies in the journals of learned societies and wrote several books during his administrative career but proposed a formal linguistic survey at the Oriental Congress in 1886 at Vienna. The Congress recommended the idea to the British Government and he was appointed superintendent of the newly created Linguistic Survey of India in 1898. He continued the work until 1928, surveying people across the British Indian territory, documenting spoken languages, recording voices, written forms and was responsible in documenting information on 179 languages, defined by him through a test of mutual unintelligibility, and 544 dialects which he placed in five language families. He published the findings of the Linguistic Survey in a series that consisted of 19 volumes.
Robert J. Zydenbos is a Dutch-Canadian scholar who has doctorate degrees in Indian philosophy and Dravidian studies. He also has a doctorate of literature from the University of Utrecht in the Netherlands. Zydenbos also studied Indian religions and languages at the South Asia Institute and at the University of Heidelberg in Germany. He taught Sanskrit at the University of Heidelberg and later taught Jain philosophy at the University of Madras in India. Zydenbos later taught Sanskrit, Buddhism, and South Asian religions at the University of Toronto in Canada. He was the first western scholar to write a doctoral thesis on contemporary Kannada fiction.

The Harshacharita is the biography of Indian emperor Harsha by Banabhatta, also known as Bana, who was a Sanskrit writer of seventh-century CE India. He was the Asthana Kavi, meaning Court Poet, of Harsha. The Harshacharita was the first composition of Bana and is considered to be the beginning of writing of historical poetic works in the Sanskrit language.
John Mildenhall or John Midnall was a British explorer and adventurer and one of the first to make an overland journey to India. He was the self-styled ambassador of the British East India Company in India. His is the first recorded burial of an Englishman in India.

Vasavadatta is a classical Sanskrit romantic tale (akhyayika) written in an ornate style by Subandhu, whose time period isn't precisely known. He is generally taken to have written the work in the second quarter of the seventh century. However, scholar Maan Singh has stated that he was a courtier of the Gupta emperors Kumaragupta I (414-455) and Skandagupta (455-467), dating him between 385 and 465 AD.
Walter Eugene Clark, was an American philologist. He was the second Wales Professor of Sanskrit at Harvard University and editor of the volumes 38-44 of the Harvard Oriental Series. He translated the Aryabhatiya of Aryabhata with critical notes which was published in 1930, by the University of Chicago Press.
Franklin Edgerton was an American linguistic scholar. He was Salisbury Professor of Sanskrit and Comparative Philology at Yale University (1926) and visiting professor at Benares Hindu University (1953–4). Between 1913 and 1926, he was the Professor of Sanskrit at the University of Pennsylvania. He is well known for his exceptionally literal translation of the Bhagavad Gita which was published as volume 38-39 of the Harvard Oriental Series in 1944. He also edited the parallel edition of four recensions of the Simhāsana Dvātrṃśika, and a reconstruction of the (lost) original Sanskrit text of the Panchatantra. Edgerton was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1920, the American Philosophical Society in 1935.

Vasantavilas is a fagu poem by unknown author written in old Gujarati language, believed to be written in first half of the 14th-century. Its theme is the depiction of Shringara, an erotic sentiments. The poem has a significant historical value as it provides linguistic evidence of Old Gujarati.
The Lekhapaddhati, also known as Lekhapañcāśikā, is a collection of Sanskrit documents written between the 8th and 15th centuries during the Chaulukya rule in Gujarat, India. It was later also composed in Prakrit and it contained rules for drafting variety of documents like documents related to land grants, treaties between the rulers and rule of administration.

Darab Dastur Peshotan Sanjana was an Indian scholar and Zoroastrian head-priest (Dastur). He is known for his translations of works from Central Asia, in languages including Bactrian, Pahlavi, and Avestan. He became a member of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland in 1893.