
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploration, and managing fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the US exclusive economic zone. The agency is part of the United States Department of Commerce and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland.

Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the varying conditions within the Solar System and its heliosphere. This includes the effects of the solar wind, especially on the Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Though physically distinct, space weather is analogous to the terrestrial weather of Earth's atmosphere. The term "space weather" was first used in the 1950s and popularized in the 1990s. Later, it prompted research into "space climate", the large-scale and long-term patterns of space weather.

The Brazilian Space Agency is the civilian authority in Brazil responsible for the country's space program. It operates a spaceport at Alcântara, and a rocket launch site at Barreira do Inferno. It is the largest and most prominent space agency in Latin America.

The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C., in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959, as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs about 10,000 civil servants and contractors. Named for American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard, it is one of ten major NASA field centers. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.
The Earth Observing System (EOS) is a program of NASA comprising a series of artificial satellite missions and scientific instruments in Earth orbit designed for long-term global observations of the land surface, biosphere, atmosphere, and oceans. Since the early 1970s, NASA has been developing its Earth Observing System, launching a series of Landsat satellites in the decade. Some of the first included passive microwave imaging in 1972 through the Nimbus 5 satellite. Following the launch of various satellite missions, the conception of the program began in the late 1980s and expanded rapidly through the 1990s. Since the inception of the program, it has continued to develop, including; land, sea, radiation and atmosphere. Collected in a system known as EOSDIS, NASA uses this data in order to study the progression and changes in the biosphere of Earth. The main focus of this data collection surrounds climatic science. The program is the centrepiece of NASA's Earth Science Enterprise.
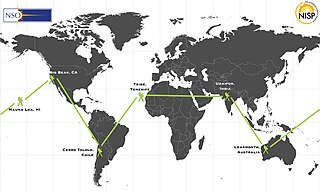
The Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) is a worldwide network of six identical telescopes, designed to have 24/7 observations of the Sun. The network serves multiple purposes, including the provision of operation data for use in space weather prediction, and the study of solar internal structure and dynamics using helioseismology.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the U.S. space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program, and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the lunar Artemis program.

NASA Research Park is a research facility under the auspices of NASA located in San Jose, California. It is focused on fostering collaboration among government entities and academic institutions.
The Solar System Exploration Research Virtual Institute (SSERVI), originally the NASA Lunar Science Institute, is an organization, established by NASA in 2008, that supplemented and extended existing NASA lunar science programs. Supported by the NASA Science Mission Directorate (SMD) and the Exploration Systems Mission Directorate (ESMD), SSERVI is a NASA program office located at the NASA Ames Research Center and was modeled on the NASA Astrobiology Institute (NAI) with dispersed teams across the nation working together to help lead the agency's research activities related to NASA's human exploration goals. Competitively selected team investigations focused on one or more aspects of lunar science investigations of the Moon, from the Moon, and on the Moon.

SAC-D, also known as Aquarius after its primary instrument, is an Argentine Earth science satellite built by INVAP and operated by CONAE. SAC-D was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on 10 June 2011, with a planned mission life of five years. Due to a power system failure, the mission was ended on 8 June 2015.

45th Weather Squadron, 45th Operations Group, Space Launch Delta 45, at Patrick Space Force Base, Florida performs weather assessments for air and space operations; specifically, weather observations, forecasts, advisories, and warnings. It specialized in the weather assessments for the Space Shuttle launches at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.

The South African National Space Agency (SANSA) is South Africa's government agency responsible for the promotion and development of aeronautics and aerospace space research. It fosters cooperation in space-related activities and research in space science, seeks to advance scientific engineering through human capital, as well as the peaceful use of outer space, and supports the creation of an environment conducive to the industrial development of space technologies within the framework of national government.

Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) is a joint mission between JAXA and NASA as well as other international space agencies to make frequent observations of Earth's precipitation. It is part of NASA's Earth Systematic Missions program and works with a satellite constellation to provide full global coverage. The project provides global precipitation maps to assist researchers in improving the forecasting of extreme events, studying global climate, and adding to current capabilities for using such satellite data to benefit society. GPM builds on the notable successes of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), which was also a joint NASA-JAXA activity.

The Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) is the latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites. JPSS will provide the global environmental data used in numerical weather prediction models for forecasts, and scientific data used for climate monitoring. JPSS will aid in fulfilling the mission of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an agency of the Department of Commerce. Data and imagery obtained from the JPSS will increase timeliness and accuracy of public warnings and forecasts of climate and weather events, thus reducing the potential loss of human life and property and advancing the national economy. The JPSS is developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), who is responsible for operation of JPSS. Three to five satellites are planned for the JPSS constellation of satellites. JPSS satellites will be flown, and the scientific data from JPSS will be processed, by the JPSS – Common Ground System (JPSS-CGS).

The NASA Launch Services Program (LSP) is responsible for procurement of launch services for NASA uncrewed missions and oversight of launch integration and launch preparation activity, providing added quality and mission assurance to meet program objectives. LSP operates under the NASA Space Operations Mission Directorate (SOMD).

The Heliophysics Science Division of the Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA) conducts research on the Sun, its extended Solar System environment, and interactions of Earth, other planets, small bodies, and interstellar gas with the heliosphere. Division research also encompasses geospace—Earth's uppermost atmosphere, the ionosphere, and the magnetosphere—and the changing environmental conditions throughout the coupled heliosphere.

The NASA International Space Apps Challenge is the largest global annual hackathon. This two-day event provides an opportunity for participants to utilize NASA's free and open data and its Space Agency Partners' space-based data to address real-world problems on Earth and in space.
The Space Safety Programme, formerly the Space Situational Awareness (SSA) programme, is the European Space Agency's (ESA) initiative to monitor hazards from space, determine their risk, make this data available to the appropriate authorities and where possible, mitigate the threat.

Capella Space is an American space company with satellite and unclassified SAR data solutions for government and commercial use. It offers space-based radar Earth observation satellites equipped with synthetic-aperture radar that can collect imagery through clouds and at night. The company is based in San Francisco, California with offices in Washington, D.C., and Louisville, Colorado. It was founded by Payam Banazadeh, a former engineer at Jet Propulsion Laboratory of NASA, and William Walter Woods.

While the United States Space Force gained its independence on 20 December 2019, the history of the United States Space Force can be traced back to the beginnings of the military space program following the conclusion of the Second World War in 1945. Early military space development was begun within the United States Army Air Forces by General Henry H. Arnold, who identified space as a crucial military arena decades before the first spaceflight. Gaining its independence from the Army on 18 September 1947, the United States Air Force began development of military space and ballistic missile programs, while also competing with the United States Army and United States Navy for the space mission.

















