
Tulu is a Dravidian language whose speakers are concentrated in Dakshina Kannada and in the southern part of Udupi of Karnataka in south-western India and also in the northern parts of the Kasaragod district of Kerala. The native speakers of Tulu are referred to as Tuluva or Tulu people and the geographical area is unofficially called Tulu Nadu.

The Kodava is an endangered Dravidian language and it is spoken in Kodagu district in Southern Karnataka, India. The term Kodava has two related usages. Firstly, it is the name of the Kodava language and culture followed by a number of communities from Kodagu. Secondly, within the Kodava-speaking communities and region (Kodagu), it is a demonym for the dominant Kodava people. Hence, the Kodava language is not only the primary language of the Kodavas but also of many other castes and tribes in Kodagu. The language has two dialects: Mendele and Kiggat.

Mangalore, officially known as Mangaluru, is a major industrial port city in the Indian state of Karnataka and on the west coast of India. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about 352 km (219 mi) west of Bangalore, the state capital, 14 km north of Karnataka–Kerala border and 297 km south of Goa. Mangalore is the state's only city to have all four modes of transport—air, road, rail and sea. The population of the urban agglomeration was 619,664 according to the 2011 national census of India. It is known for being one of the locations of the Indian strategic petroleum reserves.
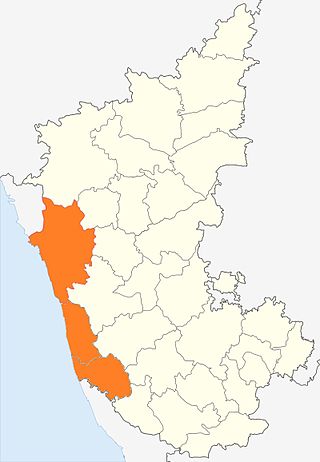
Kanara or Canara, also known as Karavali is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka. The subregion comprises three civil districts, namely: Uttara Kannada, Udupi, and Dakshina Kannada. Kassergode was included prior to the States Reorganisation Act.

Dakshina Kannada district is a district of Karnataka state in India, with its headquarters in the coastal city of Mangalore. It is part of the larger Tulu Nadu region. The district covers an area nestled in between the Western Ghats to its east and the Arabian Sea to its west. Dakshina Kannada receives abundant rainfall during the Indian monsoon. It is bordered by Udupi district to the north, Chikmagalur district to the northeast, Hassan district to the east, Kodagu to the southeast and Kasaragod district of Kerala to the south. According to the 2011 census of India, Dakshina Kannada district had a population of 2,083,625. It is the only district in Karnataka state to have all modes of transport like road, rail, water and air due to the presence of a major hub, Mangalore. This financial district is also known as the Cradle of Indian banking.

Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva', speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, are the preponderant ethnic group of this region. South Canara, an erstwhile district and a historical area, encompassing the undivided territory of the contemporary Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka State and Kasaragod district of Kerala state forms the cultural area of the Tuluver.

The Beary are a community concentrated along the southwest coast of India, mostly in the Mangalore district of the south Indian state of Karnataka.
Banakal is a Malnad town in Mudigere Taluk, Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India. This town is situated atop the Charmadi hills in the Western Ghats section. The Western Ghats is one amongst twenty-five identified hot spots for biodiversity conservation in the world. Banakal is surrounded by coffee estates and paddy fields and known for its pleasant weather throughout the year. Banakal town is the headquarters of Banakal Hobli.
Jeppu is a locality in Mangalore city, Karnataka, India. It is situated on the southern part of Mangalore. Jeppu is on the bank of Nethravathi River. The National Highway 17 (India) passes through this locality.

Rani Abbakka Chowta was the first Tuluva Queen of Ullal who fought the Portuguese in the latter half of the 16th century. She belonged to the Chowta dynasty who ruled over parts of coastal Karnataka, India. Their capital was Puttige. The port town of Ullal served as their subsidiary capital. The Portuguese made several attempts to capture Ullal as it was strategically placed. But Abbakka repulsed each of their attacks for over four decades. For her bravery, she came to be known as Abhaya Rani. She was also one of the earliest Indians to fight Eurochristian colonialism and is sometimes regarded as the 'first woman freedom fighter of India'. In the state of Karnataka, she is celebrated along with Rani Kittur Chennamma, Keladi Chennamma, Rani Chennabhairadevi and Onake Obavva, as the foremost women warriors and patriots.
Mangalore district that was partitioned from the erstwhile South Canara, has been multicultural and is a little different from the prevalent culture of the Carnataca state of India. A native of Mangalore is known as a Mangalorean in English, Kudladakulu in Tulu, Kodyaalkar in Konknni, Manglurnavaru in Kannada& Maikaaltanga in Byari.
Kinnya or Kinya is a village in Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka state, India. The ancient Kinya Jumma Masjid And Talapady Durga Parameshwari Temple is in this village. The village Kinnya lies near Arabian Sea Shared Border with Thalapady, Kotekar, Naringana And Manjanady Village. Total Population 6800, Native Language Beary, Malayalam And Tulu. It is located 23 km south of Mangalore city. In local Tulu language Kinya means small. The Durga Parameshwari Temple was recently renovated in the year 2015. Shree Durga Parameshwari temple is the family deity (Kuladevi) of many people who are the natives of undivided South Canara District. The village code is 02699400 as per Karnataka Administrative atlas 2001 published by DCO of Karnataka state. Pincode of Kinya village post office is 575023.
Daijiworld Media is an Indian company, headquartered in Mangalore, that provides news services, including the web portal, www.daijiworld.com. It was founded by Walter Nandalike, as www.daijidubai.com on 14 January 2001, primarily with the objective of relaying news from the Coastal Konkan region of India. It was later renamed as www.daijiworld.com, and established as a media company in 2007.
Mangaloreans are a collection of diverse ethnic groups that hail from the historical locales of South Canara (Tulunaad) on the south western coast of Karnataka, India, particularly the residents native to Mangaluru.
Bekoor is a village near Uppala town in Kasaragod district in the state of Kerala, India. This locality is located in eastern Uppala, in Uppala-Bayar road, which connects Uppala with Paivalike, Bayar, and leads to Kanyana, Vittal and Puttur in dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka. It is around 3 km from Kaikamba junction and 1 km from Sonkal.

Karkala, also known as Karla in Tulu language, is a town and the headquarters of Karkala taluk in the Udupi district of Karnataka, India. Located about 60 km from Mangalore in the Tulu Nadu region of the state, it lies near the foothills of the Western Ghats. Karkala has a number of natural and historical landmarks, and is a major tourist and transit destination due to its strategic location along the way to Hebri, Sringeri, Kalasa, Horanadu, Udupi, Kollur, Subrahmanya and Dharmasthala.

Tulu Nadu State movement is aimed at increasing Tulu Nadu's influence and political power through the formation of separate Tulu Nadu state from Karnataka and Kerala. Tulu Nadu is a region on the south-western coast of India. It consists of Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka, and Kasargod district up to the Chandragiri river in Kerala. The Chandragiri river is traditionally considered to be a boundary between Tulu Nadu and Kerala from the fourteenth century AD onwards. The first call for separate Tulu Nadu state was made just after the Quit India Movement in 1942 by Srinivas Updhyaya Paniyadi, a banker and a press owner from Udupi. Mangalore is the largest and the chief city of Tulu Nadu. Tulu activists have been demanding a separate Tulu Nadu state since the late 2000s, considering language and culture as the basis for their demand.
Karnataka is a state in the southern part of India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act. Karnataka is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, Goa to the north-west, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the south-east, and Kerala to the south-west. The state covers an area of 74,122 sq mi (191,976 km2), or 5.83% of the total geographical area of India. It comprises 30 districts. Kannada is the official language of Karnataka and as per the 2011 census is the mother tongue of 66.5% of the population. Various ethnic groups with origins in other parts of India have unique customs and use languages at home other than Kannada, adding to the cultural diversity of the state. Significant linguistic minorities in the state in 2011 included speakers of Urdu (10.8%), Telugu (5.8%), Tamil (3.5%), Marathi (3.4%), Hindi (3.2%), Tulu (2.6%), Konkani (1.3%) and Malayalam (1.3%).
Beary or Byari is a Dravidian language spoken by the Muslim communities mainly of Karnataka and extreme northern end of Kerala like Manjeshwaram, Kunjathur, Uppala, Hosangadi of Kasaragod district (Byaris). Bearys speak a language made of Malayalam idioms with Tulu phonology and grammar. This language is traditionally known as Mappila Bashe because of Bearys' close contact with Mappila, the Malayali Muslims. Due to the intensive influence of Tulu for centuries, it is today considered close to both Tulu and Malayalam.

Perla is an administrative capital of Enmakaje Panchayat, which is in Kasaragod district, Kerala, India.









