
Lean manufacturing is a method of manufacturing goods aimed primarily at reducing times within the production system as well as response times from suppliers and customers. It is closely related to another concept called just-in-time manufacturing. Just-in-time manufacturing tries to match production to demand by only supplying goods that have been ordered and focus on efficiency, productivity, and reduction of "wastes" for the producer and supplier of goods. Lean manufacturing adopts the just-in-time approach and additionally focuses on reducing cycle, flow, and throughput times by further eliminating activities that do not add any value for the customer. Lean manufacturing also involves people who work outside of the manufacturing process, such as in marketing and customer service.
Software development is the process of designing and implementing a software solution to satisfy a user. The process is more encompassing than programming, writing code, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing requirements, design, testing and release. The process is part of software engineering which also includes organizational management, project management, configuration management and other aspects.

IDEF, initially an abbreviation of ICAM Definition and renamed in 1999 as Integration Definition, is a family of modeling languages in the field of systems and software engineering. They cover a wide range of uses from functional modeling to data, simulation, object-oriented analysis and design, and knowledge acquisition. These definition languages were developed under funding from U.S. Air Force and, although still most commonly used by them and other military and United States Department of Defense (DoD) agencies, are in the public domain.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises.

Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) is a domain of software tools used to design and implement applications. CASE tools are similar to and are partly inspired by computer-aided design (CAD) tools used for designing hardware products. CASE tools are intended to help develop high-quality, defect-free, and maintainable software. CASE software was often associated with methods for the development of information systems together with automated tools that could be used in the software development process.

Integrated Computer-Aided Manufacturing (ICAM) is a US Air Force program that develops tools, techniques, and processes to support manufacturing integration. It influenced the computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) project efforts of many companies. The ICAM program was founded in 1976 and initiative managed by the US Air Force at Wright-Patterson as a part of their technology modernization efforts. The program initiated the development a series of standards for modeling and analysis in management and business improvement, called Integrated Definitions, short IDEFs.
A functional software architecture (FSA) is an architectural model that identifies enterprise functions, interactions and corresponding IT needs. These functions can be used as a reference by different domain experts to develop IT-systems as part of a co-operative information-driven enterprise. In this way, both software engineers and enterprise architects can create an information-driven, integrated organizational environment.

Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments.

Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each part. Manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone by the integration of computers. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as flexible design and manufacturing.

IDEF0, a compound acronym, is a function modeling methodology for describing manufacturing functions, which offers a functional modeling language for the analysis, development, reengineering and integration of information systems, business processes or software engineering analysis.

Integration DEFinition for information modeling (IDEF1X) is a data modeling language for the development of semantic data models. IDEF1X is used to produce a graphical information model which represents the structure and semantics of information within an environment or system.
DELMIA, a brand within Dassault Systèmes, is a software platform designed for use in manufacturing and supply chain professionals. It offers various tools encompassing digital manufacturing, operations, and supply-chain management, including simulation, planning, scheduling, modeling, execution, and real-time operations management.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.
An integration competency center (ICC), sometimes referred to as an integration center of excellence (COE), is a shared service function providing methodical data integration, system integration, or enterprise application integration within organizations, particularly large corporations and public sector institutions.
Enterprise engineering is the body of knowledge, principles, and practices used to design all or part of an enterprise. An enterprise is a complex socio-technical system that comprises people, information, and technology that interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. One definition is: "an enterprise life-cycle oriented discipline for the identification, design, and implementation of enterprises and their continuous evolution", supported by enterprise modelling. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, material flows, and organizational structure. Enterprise engineering may focus on the design of the enterprise as a whole, or on the design and integration of certain business components.

IDEF3 or Integrated DEFinition for Process Description Capture Method is a business process modelling method complementary to IDEF0. The IDEF3 method is a scenario-driven process flow description capture method intended to capture the knowledge about how a particular system works.
Lean IT is the extension of lean manufacturing and lean services principles to the development and management of information technology (IT) products and services. Its central concern, applied in the context of IT, is the elimination of waste, where waste is work that adds no value to a product or service.
In software engineering, a software development process or software development life cycle (SDLC) is a process of planning and managing software development. It typically involves dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or sequential steps or sub-processes to improve design and/or product management. The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application.
Lean integration is a management system that emphasizes creating value for customers, continuous improvement, and eliminating waste as a sustainable data integration and system integration practice. Lean integration has parallels with other lean disciplines such as lean manufacturing, lean IT, and lean software development. It is a specialized collection of tools and techniques that address the unique challenges associated with seamlessly combining information and processes from systems that were independently developed, are based on incompatible data models, and remain independently managed, to achieve a cohesive holistic operation.
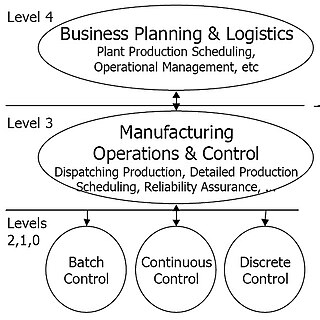
Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA), or the Purdue model, is a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture, developed by Theodore J. Williams and members of the Industry-Purdue University Consortium for Computer Integrated Manufacturing.











