Related Research Articles

A condyle is the round prominence at the end of a bone, most often part of a joint – an articulation with another bone. It is one of the markings or features of bones, and can refer to:

Cubitus valgus is a medical deformity in which the forearm is angled away from the body to a greater degree than normal when fully extended. A small degree of cubitus valgus is acceptable and occurs in the general population.

Akidolestes is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Spalacotheriidae, a group of mammals related to therians.
Brachypodosaurus is a dubious genus of dinosaur, possibly an ornithischian, from the Late Cretaceous Lameta Formation (Maastrichtian) in India.
Lateral condyle can refer to:

The medial epicondyle of the femur is an epicondyle, a bony protrusion, located on the medial side of the femur at its distal end.
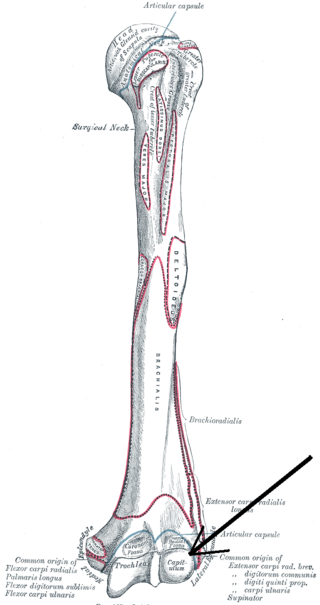
In human anatomy of the arm, the capitulum of the humerus is a smooth, rounded eminence on the lateral portion of the distal articular surface of the humerus. It articulates with the cup-shaped depression on the head of the radius, and is limited to the front and lower part of the bone.

A humerus fracture is a break of the humerus bone in the upper arm. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and bruising. There may be a decreased ability to move the arm and the person may present holding their elbow. Complications may include injury to an artery or nerve, and compartment syndrome.

A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. In children, many of these fractures are non-displaced and can be treated with casting. Some are angulated or displaced and are best treated with surgery. In children, most of these fractures can be treated effectively with expectation for full recovery. Some of these injuries can be complicated by poor healing or by associated blood vessel or nerve injuries with serious complications.
Brasilodon is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of Brasilodon has been estimated at 12 centimetres (4.7 in). Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species B. quadrangularis. Brasilodon belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, Brasilitherium and Minicynodon, are now considered to be junior synonyms of Brasilodon.
Pelecanoides miokuaka is an extinct species of diving petrel of New Zealand. Described in 2007, it is known only from a single humerus bone that was discovered from early Miocene sediments of the Manuherikia Group.

Many anatomical terms descriptive of bone are defined in anatomical terminology, and are often derived from Greek and Latin. Bone in the human body is categorized into long bone, short bone, flat bone, irregular bone and sesamoid bone.
Arcticodactylus is a genus of basal pterosaur living during the Late Triassic in the area of present Greenland. Its only species was previously attributed to Eudimorphodon, and its closest relatives may have been Eudimorphodon or Austriadraco.

Tingmiatornis is a genus of flighted and possibly diving ornithurine bird from the High Arctic of Canada. The genus contains a single species, T. arctica, described in 2016, which lived during the Turonian epoch of the Cretaceous.

Distal humeral fractures are a group of humerus fracture which includes supracondylar fractures, single condyle fractures, bi-column fractures and coronal shear fractures.
Zhuchengtitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Shandong, China. It contains a single species, Z. zangjiazhuangensis, named by Mo Jinyou and colleagues in 2017 from a single humerus. Zhuchengtitan can be identified by the extreme width of the top end of its humerus, as well as the expansion of the deltopectoral crest on its humerus; both of these characteristics indicate that it was likely closely related to Opisthocoelicaudia. However, it differs from the latter by the flatter bottom articulating surface of its humerus. Zhuchengtitan lived in a floodplain environment alongside Shantungosaurus, Zhuchengtyrannus, and Sinoceratops.

Tethydraco is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period of what is now the area of present Morocco, about 66 million years ago. Tethydraco was originally assigned to the family Pteranodontidae. Some researchers argued that subsequently described material suggests that it may have been an azhdarchid, and possibly synonymous with Phosphatodraco, though this has been disputed. The type and only species is T. regalis.

Anhuilong is a genus of mamenchisaurid dinosaur known from the Hongqin Formation of Anhui province, China. The genus contains a single species, Anhuilong diboensis.
Melanerpes shawi is an extinct species of woodpecker from the Pleistocene of California. It was found in the La Brea tar pits. It's part of the genus Melanerpes, which includes twenty-four extant species found across North and South America.
Aurorarctos is an extinct North American genus of bears. It contains a single species, Aurorarctos tirawa, which lived in the Middle Miocene. Its fossils were discovered in the Valentine formation and Myers Farm of Nebraska, and represent the earliest known member of the Ursinae, showcasing that basal members of this subfamily were small, but already showed adaptions towards increasing herbivory as well as an arboreal lifestyle The genus name combines the Latin words aurora (dawn) and Greek arctos (bear); the specific epithet references the creator god Tirawa in Pawnee mythology.
References
- ↑ xiphoid.biostr.washington.edu/fma/fmabrowser-hierarchy.html?search=Condyle of humerus