
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms (kg) and height in metres (m).

The cat, commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Recent advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a house pet and farm cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. Valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin, the cat's retractable claws are adapted to killing small prey like mice and rats. It has a strong, flexible body, quick reflexes, and sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat communication includes vocalizations like meowing, purring, trilling, hissing, growling, and grunting as well as cat body language. It can hear sounds too faint or too high in frequency for human ears, such as those made by small mammals. It secretes and perceives pheromones.

3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly known as ecstasy, and molly or mandy, is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant and minor psychedelic properties. Investigational indications include as an adjunct to psychotherapy in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and social anxiety in autism spectrum disorder. The purported pharmacological effects that may be prosocial include altered sensations, increased energy, empathy, and pleasure. When taken by mouth, effects begin in 30 to 45 minutes and last three to six hours.

A mammal is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia. Mammals are characterized by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 29 orders.

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the largest country in the world by area, extending across eleven time zones and sharing land borders with fourteen countries. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country. Russia is a highly urbanised country including 16 population centres with over a million inhabitants. Its capital as well as its largest city is Moscow. Saint Petersburg is Russia's second-largest city and its cultural capital.

Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.

Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined, or libre open access, barriers to copying or reuse are also reduced or removed by applying an open license for copyright.

A digital object identifier (DOI) is a persistent identifier or handle used to uniquely identify various objects, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). DOIs are an implementation of the Handle System; they also fit within the URI system. They are widely used to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports, data sets, and official publications.

Narendra Damodardas Modi is an Indian politician serving as the current Prime Minister of India since 26 May 2014. Modi was the chief minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the Member of Parliament (MP) for Varanasi. He is a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a right wing Hindu nationalist paramilitary volunteer organisation. He is the longest-serving prime minister outside the Indian National Congress.

Fellowship of the Royal Society is an award granted by the Fellows of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science".

Humans or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus Homo. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligence. Humans have large brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that enable them to thrive and adapt in varied environments, develop highly complex tools, and form complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a multi-layered network of cooperating, distinct, or even competing social groups – from families and peer groups to corporations and political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, languages, and traditions, each of which bolsters human society. Humans are also highly curious, with the desire to understand and influence phenomena having motivated humanity's development of science, technology, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other frameworks of knowledge; humans also study themselves through such domains as anthropology, social science, history, psychology, and medicine. There are estimated to be more than eight billion humans alive.
A suicide method is any means by which a person may choose to end their life. Suicide attempts do not always result in death, and a non-fatal suicide attempt can leave the person with serious physical injuries, long-term health problems, and brain damage.

Ceres is a dwarf planet in the middle main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It was the first known asteroid, discovered on 1 January 1801 by Giuseppe Piazzi at Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Sicily, and announced as a new planet. Ceres was later classified as an asteroid and then a dwarf planet, the only one not beyond Neptune's orbit.

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neurone disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease in the United States, is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as limb-onset or bulbar-onset.
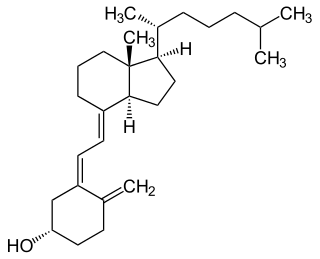
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and for many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).

Cattle are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus Bos. Mature female cattle are called cows and mature male cattle are bulls. Young female cattle are called heifers, young male cattle are oxen or bullocks, and castrated male cattle are known as steers.

Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics, including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies".
Autism, also called autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by symptoms of deficient reciprocal social communication and the presence of restricted, repetitive, and inflexible patterns of behavior that are impairing in multiple contexts and excessive or atypical to be developmentally and socioculturally inappropriate. Other common signs include difficulty with social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, along with perseverative interests, stereotypic body movements, rigid routines, and hyper- or hypo-reactivity to sensory input. Autism is clinically regarded as a spectrum disorder, meaning that it can manifest very differently in each person. For example, some are nonspeaking, while others have proficient spoken language. Because of this, there is wide variation in the support needs of people across the autism spectrum.
The dark web is the World Wide Web content that exists on darknets: overlay networks that use the Internet but require specific software, configurations, or authorization to access. Through the dark web, private computer networks can communicate and conduct business anonymously without divulging identifying information, such as a user's location. The dark web forms a small part of the deep web, the part of the web not indexed by web search engines, although sometimes the term deep web is mistakenly used to refer specifically to the dark web.
A uniform resource locator (URL), colloquially known as an address on the Web, is a reference to a resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. URLs occur most commonly to reference web pages (HTTP/HTTPS) but are also used for file transfer (FTP), email (mailto), database access (JDBC), and many other applications.















