
A fossil is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the fossil record.

Stromatolites or stromatoliths are layered sedimentary formations (microbialite) that are created mainly by photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota. These microorganisms produce adhesive compounds that cement sand and other rocky materials to form mineral "microbial mats". In turn, these mats build up layer by layer, growing gradually over time.
Hans J. Hofmann was a paleontologist, specializing in the study of Precambrian fossils using computer modelling and image analysis to quantify morphologic attributes.
Elso Sterrenberg Barghoorn was an American paleobotanist, called by his student Andrew Knoll, the present Fisher Professor of Natural History at Harvard, "the father of Pre-Cambrian palaeontology."

Collenia is genus of fossil cyanobacteria that form a particular type of stromatolites.

The Bitter Springs Group, also known as the Bitter Springs Formation is a Precambrian fossil locality in Australia, which preserves stromatolites and microorganisms in silica. Its preservational mode ceased in the late Neoproterozoic with the advent of silicifying organisms.
Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of palaeontology and its ramifications into the Earth and biological sciences, especially the disciplines of taxonomy, biostratigraphy, micropalaeontology, vertebrate palaeontology, palaeobotany, palynology, palaeobiology, palaeoanatomy, palaeoecology, biostratinomy, biogeography, chronobiology, biogeochemistry and palichnology. It is the official journal of the Association of Australasian Palaeontologists and is published by Taylor & Francis.
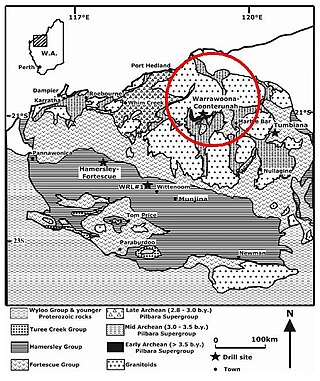
The Warrawoona Group is a geological unit in Western Australia containing putative fossils of cyanobacteria cells. Dated 3.465 Ga, these microstructures, found in Archean chert, are considered to be the oldest known geological record of life on Earth.

The Barberton Greenstone Belt of eastern South Africa contains some of the most widely accepted fossil evidence for Archean life. These cell-sized prokaryote fossils are seen in the Barberton fossil record in rocks as old as 3.5 billion years. The Barberton Greenstone Belt is an excellent place to study the Archean Earth due to exposed sedimentary and metasedimentary rocks.
James William Schopf is an American paleobiologist and professor of earth sciences at the University of California Los Angeles. He is also Director of the Center for the Study of Evolution and the Origin of Life, and a member of the Department of Earth and Space Sciences, the Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, and the Molecular Biology Institute at UCLA. He is most well known for his study of Precambrian prokaryotic life in Australia's Apex chert. Schopf has published extensively in the peer reviewed literature about the origins of life on Earth. He is the first to discover Precambrian microfossils in stromatolitic sediments of Australia (1965), South Africa (1966), Russia (1977), India (1978), and China (1984). He served as NASA's principal investigator of lunar samples during 1969–1974.
Stanley Awramik is an American biogeologist and paleontologist. He is best known for his work related to the Precambrian. In 2013, he was inducted as a fellow of the Geological Society of America.

Kulpara is a rural town in South Australia, situated on the Copper Coast Highway and Upper Yorke Road in the Hummocks Range at the northern end of Yorke Peninsula.

The earliest known life forms on Earth may be as old as 4.1 billion years old according to biologically fractionated graphite inside a single zircon grain in the Jack Hills range of Australia. The earliest evidence of life found in a stratigraphic unit, not just a single mineral grain, is the 3.7 Ga metasedimentary rocks containing graphite from the Isua Supracrustal Belt in Greenland. The earliest direct known life on land may be stromatolites which have been found in 3.480-billion-year-old geyserite uncovered in the Dresser Formation of the Pilbara Craton of Western Australia. Various microfossils of microorganisms have been found in 3.4 Ga rocks, including 3.465-billion-year-old Apex chert rocks from the same Australian craton region, and in 3.42 Ga hydrothermal vent precipitates from Barberton, South Africa. Much later in the geologic record, likely starting in 1.73 Ga, preserved molecular compounds of biologic origin are indicative of aerobic life. Therefore, the earliest time for the origin of life on Earth is at least 3.5 billion years ago, possibly as early as 4.1 billion years ago — not long after the oceans formed 4.5 billion years ago and after the formation of the Earth 4.54 billion years ago.

Inzeria is a genus of fossil stromatolite-forming cyanobacteria from the late Riphean stage of the Neoproterozoic era. There are currently 9 accepted species.
Pilbaria is a genus of fossil stromatolite-forming cyanobacteria from the Paleoproterozoic era 2.3 to 1.7 billion years ago. It is named after the Pilbara region of Western Australia where the type specimen was found.
Kulparia is a genus of fossil stromatolite-forming cyanobacteria from the late Neoproterozoic era. It is named after the town of Kulpara in South Australia, where the type specimen was found.
Linella is a genus of fossil stromatolite-forming cyanobacteria from the late Neoproterozoic era. There are currently 6 accepted species.
Jurusania is a genus of fossil stromatolite-forming cyanobacteria from the late Riphean to Vendian stages of the Neoproterozoic era.









