
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international treaty that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of October 2024, 169 States and the European Union are parties.

The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, and is its legal successor. It covers an area of 20,368,759 km2 (7,864,422 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political, and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security, including cross-border crime prevention.

The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian political, economic, international security and defence organization established by China and Russia in 2001. It is the world's largest regional organization in terms of geographic scope and population, covering approximately 80% of the area of Eurasia and 40% of the world population. As of 2023, its combined GDP based on PPP was around 32% of the world's total.

The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands.

Territorial waters are informally an area of water where a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potentially the extended continental shelf. In a narrower sense, the term is often used as a synonym for the territorial sea.

Law of the sea is a body of international law governing the rights and duties of states in maritime environments. It concerns matters such as navigational rights, sea mineral claims, and coastal waters jurisdiction. The connotation of ocean law is somewhat broader, but the law of the sea is so comprehensive that it covers all areas of ocean law as well.

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind.

The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline is a proposed subsea pipeline between Türkmenbaşy in Turkmenistan, and Baku in Azerbaijan. According to some proposals it would also include a connection between the Tengiz Field in Kazakhstan, the Sangachal Terminal in Baku, and Türkmenbaşy. The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline project would transport natural gas from Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan to European Union member countries, circumventing both Russia and Iran. It would do this by feeding the Southern Gas Corridor. This project attracts significant interest since it would connect vast Turkmen gas resources to major consumers Turkey and Europe.

Iran and Turkmenistan share a common border of more than 1000 km. Since Turkmenistan's independence from the Soviet Union in 1991, the two countries have enjoyed good relations and have cooperated in economic, transportation, infrastructure development, and energy sectors. The two nations have strong historic ties.
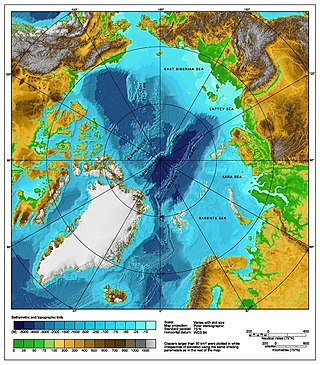
The Arctic consists of land, internal waters, territorial seas, exclusive economic zones (EEZs) and international waters above the Arctic Circle. All land, internal waters, territorial seas and EEZs in the Arctic are under the jurisdiction of one of the eight Arctic coastal states: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States. International law regulates this area as with other portions of Earth.

The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake and sometimes referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of 371,000 km2 (143,000 sq mi), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of 78,200 km3 (19,000 cu mi). It has a salinity of approximately 1.2%, about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.

The Australia–Indonesia border is a maritime boundary running west from the two countries' tripoint maritime boundary with Papua New Guinea in the western entrance to the Torres Straits, through the Arafura Sea and Timor Sea, and terminating in the Indian Ocean. The boundary is, however, broken by the Timor Gap, where Australian and East Timorese territorial waters meet and where the two countries have overlapping claims to the seabed.

The International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) is a 7,200-km long multi-mode network of ship, rail, and road route for moving freight between India, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia and Europe. The route primarily involves moving freight from India, Iran, Azerbaijan and the Russian Federation via ship, rail and road. The objective of the corridor is to increase trade connectivity between major cities such as Mumbai, Moscow, Tehran, Baku, Bandar Abbas, Astrakhan, Bandar Anzali, etc. Dry runs of two routes were conducted in 2014, the first was Mumbai to Baku via Bandar Abbas and the second was Mumbai to Astrakhan via Bandar Abbas, Tehran and Bandar Anzali. The objective of the study was to identify and address key bottlenecks. The results showed transport costs were reduced by "$2,500 per 15 tons of cargo". Other routes under consideration include via Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan.
Framework Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Caspian Sea is a regional convention signed by the official representatives of the five littoral Caspian states: Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Russian Federation and Turkmenistan in Tehran (Iran) on 4 November 2003. The Framework Convention, also called Tehran Convention, entered into force on 12 August 2006.
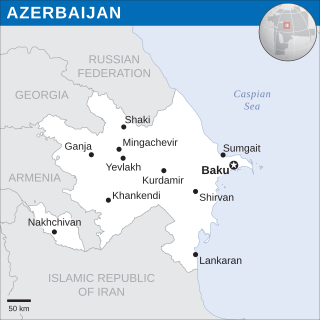
The Borders of Azerbaijan define the land and maritime borders of Azerbaijan. Azerbaijan has international land borders with 5 states.

Relations between Turkic Council and Azerbaijan started from the year of 2009 until present. Taking into account of the establishment date of the organization, Azerbaijan continues relations as a member of the founding country.

In the Soviet period, the Caspian Sea was practically an inland water basin within the Soviet Union's borders and washed off the coast of Iran only to the south. Until 1992, the status of the Caspian was regulated by the Soviet-Iranian treaties. After the collapse of the USSR, the emergence of the independent states of Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan raised the issue of dividing the Caspian Sea.
The borders of Indonesia include land and maritime borders with Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and East Timor, as well as shared maritime boundaries with Australia, India, Palau, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.

Several states in the Caspian region, including the five littoral states of the Caspian Sea, namely the Islamic Republic of Iran, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, the Russian Federation, and the Republic of Azerbaijan use ad hoc diplomatic relations to build trust and goodwill as well as to boost the bargaining power of their governments.

















