Related Research Articles

In statistics, cluster sampling is a sampling plan used when mutually homogeneous yet internally heterogeneous groupings are evident in a statistical population. It is often used in marketing research.
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste.
Cost estimation models are mathematical algorithms or parametric equations used to estimate the costs of a product or project. The results of the models are typically necessary to obtain approval to proceed, and are factored into business plans, budgets, and other financial planning and tracking mechanisms.
Design–bid–build, also known as Design–tender, traditional method, or hardbid, is a project delivery method in which the agency or owner contracts with separate entities for the design and construction of a project.
Comparables is a real estate appraisal term referring to properties with characteristics that are similar to a subject property whose value is being sought. This can be accomplished either by a real estate agent who attempts to establish the value of a potential client's home or property through market analysis or, by a licensed or certified appraiser or surveyor using more defined methods, when performing a real estate appraisal.
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time.

In earthmoving, cut and fill is the process of constructing a railway, road or canal whereby the amount of material from cuts roughly matches the amount of fill needed to make nearby embankments to minimize the amount of construction labor.
Integrated logistics support (ILS) is a technology in the system engineering to lower a product life cycle cost and decrease demand for logistics by the maintenance system optimization to ease the product support. Although originally developed for military purposes, it is also widely used in commercial customer service organisations.
A bill of quantities is a document used in tendering in the construction industry in which materials, parts, and labor are itemized. It also (ideally) details the terms and conditions of the construction or repair contract and itemizes all work to enable a contractor to price the work for which he or she is bidding. The quantities may be measured in number, area, volume, weight or time. Preparing a bill of quantities requires that the design is complete and a specification has been prepared.
A cost estimate is the approximation of the cost of a program, project, or operation. The cost estimate is the product of the cost estimating process. The cost estimate has a single total value and may have identifiable component values.
A building estimator or cost estimator is an individual that quantifies the materials, labor, and equipment needed to complete a construction project. Building cost estimating can concern diverse forms of construction from residential properties to hi-rise and civil works. Both estimators and quantity surveyors must have a background education in the construction industry. Representative professional bodies which regulate property professionals:
Construction cost estimating software is computer software designed for contractors to estimate construction costs for a specific project. A cost estimator will typically use estimating software to estimate their bid price for a project, which will ultimately become part of a resulting construction contract. Some architects, engineers, construction managers, and others may also use cost estimating software to prepare cost estimates for purposes other than bidding such as budgeting and insurance claims.
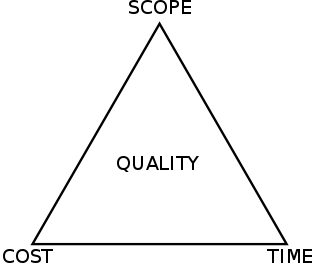
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.
The value of work done (VOWD) is a project management technique for measuring and estimating the project cost at a point in time. It is mainly used in project environments of the Petroleum industry and is defined as the value of goods and services progressed, regardless of whether or not they have been paid for or received. The primary purpose of determining VOWD is to get an accurate and comprehensive as possible estimate of cost for a project at a point in time. This is used in overall project management including reporting and cost control.
Tool management is needed in metalworking so that the information regarding the tools on hand can be uniformly organized and integrated. The information is stored in a database and is registered and applied using tool management. Tool data management consists of specific data fields, graphics and parameters that are essential in production, as opposed to managing general production equipment.
Pre-construction services are services that are offered to support owners, architects, and engineers in making decisions. They are used in planning a construction project before the actual construction begins. The stage where these services are offered is called pre-construction or "pre-con".
Chemical plant cost indexes are dimensionless numbers employed to updating capital cost required to erect a chemical plant from a past date to a later time, following changes in the value of money due to inflation and deflation. Since, at any given time, the number of chemical plants is insufficient to use in a preliminary or predesign estimate, cost indexes are handy for a series of management purposes, like long-range planning, budgeting and escalating or de-escalating contract costs.

Estimation is the process of finding an estimate or approximation, which is a value that is usable for some purpose even if input data may be incomplete, uncertain, or unstable. The value is nonetheless usable because it is derived from the best information available. Typically, estimation involves "using the value of a statistic derived from a sample to estimate the value of a corresponding population parameter". The sample provides information that can be projected, through various formal or informal processes, to determine a range most likely to describe the missing information. An estimate that turns out to be incorrect will be an overestimate if the estimate exceeds the actual result and an underestimate if the estimate falls short of the actual result.
The following is a glossary of terms relating to construction cost estimating.
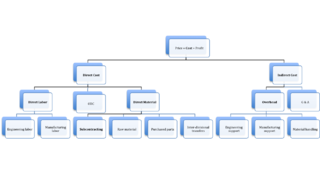
In business economics cost breakdown analysis is a method of cost analysis, which itemizes the cost of a certain product or service into its various components, the so-called cost drivers. The cost breakdown analysis is a popular cost reduction strategy and a viable opportunity for businesses.
References
- ↑ J. David Nardon, Bridge and Structure Estimating, McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1995, Page 5
- ↑ "A Visual Approach to Construction Cost Estimating", Phuwadol Samphaongoen, Marquette University, e-Publications@Marquette, Page 47
- ↑ "A Visual Approach to Construction Cost Estimating", Phuwadol Samphaongoen, e-Publications@Marquette, Page 7
- ↑ MasterFormat Numbers & Titles, April 2012, The Construction Specifications Institute and Construction Specifications Canada
- ↑ "Uniformat," Construction Specifications Institute, http://www.csinet.org/uniformat