
Stromatolites or stromatoliths are layered sedimentary formations (microbialite) that are created mainly by photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota. These microorganisms produce adhesive compounds that cement sand and other rocky materials to form mineral "microbial mats". In turn, these mats build up layer by layer, growing gradually over time. A stromatolite may grow to a meter or more. Although they are rare today, fossilized stromatolites provide records of ancient life on Earth.

The geology of Great Britain is renowned for its diversity. As a result of its eventful geological history, Great Britain shows a rich variety of landscapes across the constituent countries of England, Wales and Scotland. Rocks of almost all geological ages are represented at outcrop, from the Archaean onwards.
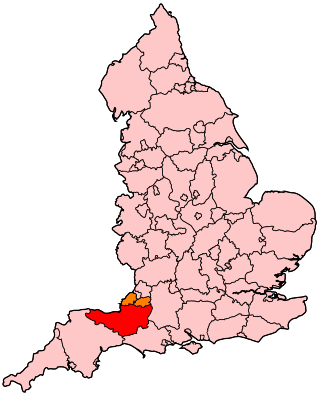
Dorset is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. Covering an area of 2,653 square kilometres (1,024 sq mi); it borders Devon to the west, Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north-east, and Hampshire to the east. The great variation in its landscape owes much to the underlying geology, which includes an almost unbroken sequence of rocks from 200 to 40 million years ago (Mya) and superficial deposits from 2 Mya to the present. In general, the oldest rocks appear in the far west of the county, with the most recent (Eocene) in the far east. Jurassic rocks also underlie the Blackmore Vale and comprise much of the coastal cliff in the west and south of the county; although younger Cretaceous rocks crown some of the highpoints in the west, they are mainly to be found in the centre and east of the county.
The Early Jurassic Epoch is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma, and ends at the start of the Middle Jurassic 174.1 Ma.
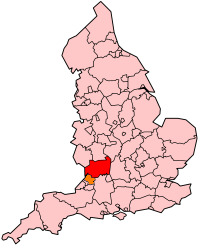
Somerset is a rural county in the southwest of England, covering 4,171 square kilometres (1,610 sq mi). It is bounded on the north-west by the Bristol Channel, on the north by Bristol and Gloucestershire, on the north-east by Wiltshire, on the south-east by Dorset, and on the south west and west by Devon. It has broad central plains with several ranges of low hills. The landscape divides into four main geological sections from the Silurian through the Devonian and Carboniferous to the Permian which influence the landscape, together with water-related features.

The New Red Sandstone, chiefly in British geology, is composed of beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian to the end of the Triassic, that underlie the Jurassic-Triassic age Penarth Group. The name distinguishes it from the Old Red Sandstone which is largely Devonian in age, and with which it was originally confused due to their similar composition.

The geology of England is mainly sedimentary. The youngest rocks are in the south east around London, progressing in age in a north westerly direction. The Tees–Exe line marks the division between younger, softer and low-lying rocks in the south east and the generally older and harder rocks of the north and west which give rise to higher relief in those regions. The geology of England is recognisable in the landscape of its counties, the building materials of its towns and its regional extractive industries.

The geology of Wales is complex and varied; its study has been of considerable historical significance in the development of geology as a science. All geological periods from the Cryogenian to the Jurassic are represented at outcrop, whilst younger sedimentary rocks occur beneath the seas immediately off the Welsh coast. The effects of two mountain-building episodes have left their mark in the faulting and folding of much of the Palaeozoic rock sequence. Superficial deposits and landforms created during the present Quaternary period by water and ice are also plentiful and contribute to a remarkably diverse landscape of mountains, hills and coastal plains.
Gloucestershire is one of the most geologically and scenically diverse counties in England, with rocks from the Precambrian through to the Jurassic represented. These varying rock-types are responsible for the three major areas of the county, each with its own distinctive scenery and land-use - the Forest of Dean in the west, bordering Wales, the Cotswolds in the east, and in between, the Severn Vale.

Monte San Giorgio is a mountain and UNESCO World Heritage Site on the border between Switzerland and Italy. It is part of the Lugano Prealps, overlooking Lake Lugano in the Swiss Canton of Ticino.

The Blue Lias is a geological formation in southern, eastern and western England and parts of South Wales, part of the Lias Group. The Blue Lias consists of a sequence of limestone and shale layers, laid down in latest Triassic and early Jurassic times, between 195 and 200 million years ago. The Blue Lias is famous for its fossils, especially ammonites.
The Penarth Group is a Rhaetian age (Triassic) lithostratigraphic group which is widespread in Britain. It is named from the seaside town of Penarth near Cardiff in south Wales where strata of this age are exposed in coastal cliffs southwards to Lavernock Point. This sequence of rocks was previously known as the Rhaetic or Rhaetic Beds.

The Surprise Canyon Formation is a geologic formation that consists of clastic and calcareous sedimentary rocks that fill paleovalleys and paleokarst of Late Mississippian (Serpukhovian) age in Grand Canyon. These strata outcrop as isolated, lens-shaped exposures of rocks that fill erosional valleys and locally karsted topography and caves developed in the top of the Redwall Limestone. The Surprise Canyon Formation and associated unconformities represent a significant period of geologic time between the deposition of the Redwall Limestone and the overlying Supai Group.

The Bass Formation, also known as the Bass Limestone, is a Mesoproterozoic rock formation that outcrops in the eastern Grand Canyon, Coconino County, Arizona. The Bass Formation erodes as either cliffs or stair-stepped cliffs. In the case of the stair-stepped topography, resistant dolomite layers form risers and argillite layers form steep treads. In general, the Bass Formation in the Grand Canyon region and associated strata of the Unkar Group-rocks dip northeast (10°–30°) toward normal faults that dip 60+° toward the southwest. This can be seen at the Palisades fault in the eastern part of the main Unkar Group outcrop area. In addition, thick, prominent, and dark-colored basaltic sills intrude across the Bass Formation.

The Americus Limestone is a member of the Foraker Limestone Formation in eastern Kansas, where it is quarried as a distinctive ornamental stone. In outcrop, it is typically recognized as two relatively thin but persistent beds of hard limestone separated by shale that forms the lowest prominent bench of the many benches of the Flint Hills. The recognizable facie of the member in excavated or eroded exposures is two thin limestone beds separated a bed of shale and adjacent shales above and below having a particular gray or bluish color darker than higher limestones. A third, lower, highly variable algal limestone is often present and included as the base of the member. The unit is not particularly massive, the limestone pair totaling 3 to 4 feet in places, more in other locations but less to the North, and up to nearly to 9 feet at the type location of Americus, Kansas. The addition of the lower algal limestone as a base for the unit increases the thickness to over 18 feet. Initially thought to be the lowest of the Permian rock of Kansas and as such classified as the lowest unit of the Council Grove Group, the unit is now dated within the uppermost Late Carboniferous.

Fossil Beach, at Sedbury, Gloucestershire, England, is beneath the Sedbury Cliffs by the River Severn and is known as a rich source of easily discovered fossils. It is within the Severn Estuary Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI).
The geology of South Dakota began to form more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Archean eon of the Precambrian. Igneous crystalline basement rock continued to emplace through the Proterozoic, interspersed with sediments and volcanic materials. Large limestone and shale deposits formed during the Paleozoic, during prevalent shallow marine conditions, followed by red beds during terrestrial conditions in the Triassic. The Western Interior Seaway flooded the region, creating vast shale, chalk and coal beds in the Cretaceous as the Laramide orogeny began to form the Rocky Mountains. The Black Hills were uplifted in the early Cenozoic, followed by long-running periods of erosion, sediment deposition and volcanic ash fall, forming the Badlands and storing marine and mammal fossils. Much of the state's landscape was reworked during several phases of glaciation in the Pleistocene. South Dakota has extensive mineral resources in the Black Hills and some oil and gas extraction in the Williston Basin. The Homestake Mine, active until 2002, was a major gold mine that reached up to 8000 feet underground and is now used for dark matter and neutrino research.

The geology of Slovakia is structurally complex, with a highly varied array of mountain ranges and belts largely formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras.
The geology of Exmoor National Park in south-west England contributes significantly to the character of Exmoor, a landscape which was designated as a national park in 1954. The bedrock of the area consists almost wholly of a suite of sedimentary rocks deposited during the Devonian, a period named for the English county of Devon in which the western half of the park sits. The eastern part lies within Somerset and it is within this part of the park that limited outcrops of Triassic and Jurassic age rocks are to be found.

The San Salvatore Dolomite, sometimes known as the Salvatore Dolomite or San Salvatore Formation, is a Middle Triassic geological formation in Switzerland and Italy. The primarily lithology is micritic dolomite with a high proportion of algal mounds (stromatolites). It corresponds to a thick warm-water carbonate platform on the northern edge of an island in what is now the Po Plain. This formation and its local equivalents are common in the hills around Lake Maggiore, Varese, and Lugano, preserving fossils of marine invertebrates such as ammonoids, gastropods, and bivalves. At its southernmost extent on Monte San Giorgio, only the lower part of the San Salvatore Dolomite is preserved. The middle and upper parts are replaced by the Besano Formation, San Giorgio Dolomite, and Meride Limestone, which were deposited in a deeper and more anoxic basin between carbonate platforms.

















