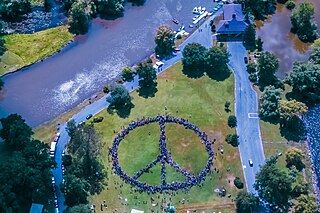Team building is a collective term for various types of activities used to enhance social relations and define roles within teams, often involving collaborative tasks. It is distinct from team training, which is designed by a combination of business managers, learning and development/OD and an HR Business Partner to improve the efficiency, rather than interpersonal relations.
In philosophy of mind and cognitive science, folk psychology, or commonsense psychology or naïve psychology, is a human capacity to explain and predict the behavior and mental state of other people. Processes and items encountered in daily life such as pain, pleasure, excitement, and anxiety use common linguistic terms as opposed to technical or scientific jargon. Folk psychology allows for an insight into social interactions and communication, thus stretching the importance of connection and how it is experienced.
Conflict resolution is conceptualized as the methods and processes involved in facilitating the peaceful ending of conflict and retribution. Committed group members attempt to resolve group conflicts by actively communicating information about their conflicting motives or ideologies to the rest of group and by engaging in collective negotiation. Dimensions of resolution typically parallel the dimensions of conflict in the way the conflict is processed. Cognitive resolution is the way disputants understand and view the conflict, with beliefs, perspectives, understandings and attitudes. Emotional resolution is in the way disputants feel about a conflict, the emotional energy. Behavioral resolution is reflective of how the disputants act, their behavior. Ultimately a wide range of methods and procedures for addressing conflict exist, including negotiation, mediation, mediation-arbitration, diplomacy, and creative peacebuilding.
In computer science, resource starvation is a problem encountered in concurrent computing where a process is perpetually denied necessary resources to process its work. Starvation may be caused by errors in a scheduling or mutual exclusion algorithm, but can also be caused by resource leaks, and can be intentionally caused via a denial-of-service attack such as a fork bomb.
The forming–storming–norming–performing model of group development was first proposed by Bruce Tuckman in 1965, who said that these phases are all necessary and inevitable in order for a team to grow, face up to challenges, tackle problems, find solutions, plan work, and deliver results. He suggested that these inevitable phases were critical to team growth and development. This series of developmental stages has become known as the Tuckman Ladder.
Tortious interference, also known as intentional interference with contractual relations, in the common law of torts, occurs when one person intentionally damages someone else's contractual or business relationships with a third party, causing economic harm. As an example, someone could use blackmail to induce a contractor into breaking a contract; they could threaten a supplier to prevent them from supplying goods or services to another party; or they could obstruct someone's ability to honor a contract with a client by deliberately refusing to deliver necessary goods.
Formal consensus refers to a specific organizational structure which formalizes both the relationships between members of an organization and the processes through which they interact to create an environment in which consensus decision-making can occur in a specific, consistent, and efficient manner. While many diverse consensus decision-making techniques exist, formal consensus emphasizes the concept that the particular process by which a decision is made is equally significant to gaining consensus as the content of any proposal or discussion.
Goal-oriented Requirements Language (GRL), an i*-based modeling language used in systems development, is designed to support goal-oriented modeling and reasoning about requirements especially the non-functional requirements
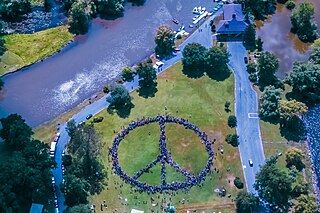
Peacebuilding is an activity that aims to resolve injustice in nonviolent ways and to transform the cultural and structural conditions that generate deadly or destructive conflict. It revolves around developing constructive personal, group, and political relationships across ethnic, religious, class, national, and racial boundaries. The process includes violence prevention; conflict management, resolution, or transformation; and post-conflict reconciliation or trauma healing before, during, and after any given case of violence.

Temptation is a desire to engage in short-term urges for enjoyment that threatens long-term goals. In the context of some religions, temptation is the inclination to sin. Temptation also describes the coaxing or inducing a person into committing such an act, by manipulation or otherwise of curiosity, desire or fear of loss something important to a person.
Organizational conflict, or workplace conflict, is a state of discord caused by the actual or perceived opposition of needs, values and interests between people working together. Conflict takes many forms in organizations. There is the inevitable clash between formal authority and power and those individuals and groups affected. There are disputes over how revenues should be divided, how the work should be done, and how long and hard people should work. There are jurisdictional disagreements among individuals, departments, and between unions and management. There are subtler forms of conflict involving rivalries, jealousies, personality clashes, role definitions, and struggles for power and favor. There is also conflict within individuals – between competing needs and demands – to which individuals respond in different ways.
Non-possession is a religious tenet followed in Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain traditions in South Asia. In Jainism, aparigraha is the virtue of non-possessiveness, non-grasping, or non-greediness.

Protracted social conflict is a technical term that generally refers to conflicts which are complex, severe, enduring, and often violent. The term was first presented in a theory developed by Edward Azar and contemporary researchers and conflict scholars continue to use it.
MIBE architecture is a behavior-based robot architecture developed at Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Lab of Politecnico di Milano by Fabio La Daga and Andrea Bonarini in 1998. MIBE architecture is based on the idea of animat and derived from subsumption architecture, formerly developed by Rodney Brooks and colleagues at MIT in 1986.
In business, operational objectives are short-term goals whose achievement brings an organization closer to its long-term goals. It is slightly different from strategic objectives, which are longer term goals of a business, but they are closely related, as a business will only be able to achieve strategic objectives when operational objectives have been met. Operational objectives are usually set by middle managers for the next six to twelve months based on an organisation's aim. They should be attainable and specific so that they can provide a clear guidance for daily functioning of certain operations. This business term is typically used in the context of strategic management and operational planning.
Motivated forgetting is a theorized psychological behavior in which people may forget unwanted memories, either consciously or unconsciously. It is an example of a defence mechanism, since these are unconscious or conscious coping techniques used to reduce anxiety arising from unacceptable or potentially harmful impulses thus it can be a defence mechanism in some ways. Defence mechanisms are not to be confused with conscious coping strategies.

An enemy or a foe is an individual or a group that is considered as forcefully adverse or threatening. The concept of an enemy has been observed to be "basic for both individuals and communities". The term "enemy" serves the social function of designating a particular entity as a threat, thereby invoking an intense emotional response to that entity. The state of being or having an enemy is enmity, foehood or foeship.

A conflict is a situation in which unacceptable differences in interests, expectations, values, and opinions occur in or between individuals or groups.

In the philosophy of mind, collective intentionality characterizes the intentionality that occurs when two or more individuals undertake a task together. Examples include two individuals carrying a heavy table up a flight of stairs or dancing a tango.
An intention is a mental state in which a person commits themselves to a course of action. Having the plan to visit the zoo tomorrow is an example of an intention. The action plan is the content of the intention while the commitment is the attitude towards this content. Other mental states can have action plans as their content, as when one admires a plan, but differ from intentions since they do not involve a practical commitment to realizing this plan. Successful intentions bring about the intended course of action while unsuccessful intentions fail to do so. Intentions, like many other mental states, have intentionality: they represent possible states of affairs.