
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions. These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word frons.

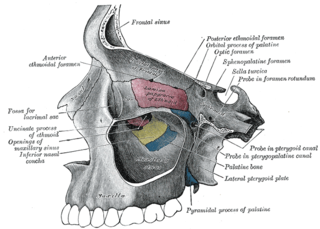
The lacrimal bone is a small and fragile bone of the facial skeleton; it is roughly the size of the little fingernail. It is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. It has two surfaces and four borders. Several bony landmarks of the lacrimal bone function in the process of lacrimation or crying. Specifically, the lacrimal bone helps form the nasolacrimal canal necessary for tear translocation. A depression on the anterior inferior portion of the bone, the lacrimal fossa, houses the membranous lacrimal sac. Tears or lacrimal fluid, from the lacrimal glands, collect in this sac during excessive lacrimation. The fluid then flows through the nasolacrimal duct and into the nasopharynx. This drainage results in what is commonly referred to a runny nose during excessive crying or tear production. Injury or fracture of the lacrimal bone can result in posttraumatic obstruction of the lacrimal pathways.
The inferior nasal concha is one of the three paired nasal conchae in the nose. It extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and consists of a lamina of spongy bone, curled upon itself like a scroll,. The inferior nasal conchae are considered a pair of facial bones. As the air passes through the turbinates, the air is churned against these mucosa-lined bones in order to receive warmth, moisture and cleansing. Superior to inferior nasal concha are the middle nasal concha and superior nasal concha which arise from the cranial portion of the skull. Hence, these two are considered as a part of the cranial bones.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, check ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.

The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film. In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone. Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose.
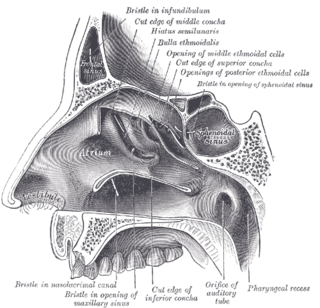
The agger nasi is a small ridge on the lateral side of the nasal cavity. It is located midway at the anterior edge of the middle nasal concha, directly above the atrium of the middle meatus. It is formed by a mucous membrane that is covering the ethmoidal crest of the maxilla.

Auroraceratops, meaning "dawn horned face", is a genus of bipedal basal neoceratopsian dinosaur, from the Early Cretaceous of north central China and South Korea. The etymology of the generic name refers to its status as an early ceratopsian and also to Dawn Dodson, wife of Peter Dodson, one of the palaeontologists who described it.

Monolophosaurus is a genus of tetanuran theropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Shishugou Formation in what is now Xinjiang, China. It was named for the single crest on top of its skull. Monolophosaurus was a mid-sized theropod at about 5 metres long.

Zupaysaurus is a genus of early theropod dinosaur living during the Norian stage of the Late Triassic in what is now Argentina. Fossils of the dinosaur were found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina. Although a full skeleton has not yet been discovered, Zupaysaurus can be considered a bipedal predator, up to 4 metres (13 ft) long. It may have had two parallel crests running the length of its snout.

The lacrimal sac or lachrymal sac is the upper dilated end of the nasolacrimal duct, and is lodged in a deep groove formed by the lacrimal bone and frontal process of the maxilla. It connects the lacrimal canaliculi, which drain tears from the eye's surface, and the nasolacrimal duct, which conveys this fluid into the nasal cavity. Lacrimal sac occlusion leads to dacryocystitis.

The lateral or orbital surface of the lacrimal bone is divided by a vertical ridge, the posterior lacrimal crest, into two parts.
The anterior lacrimal crest is a bony projection on the frontal process of maxilla in the skull. It creates the lateral margin of the lacrimal sac fossa and is continuous with the orbital margin. At its junction with the orbital surface is a small tubercle, the lacrimal tubercle, which serves as a guide to the position of the lacrimal sac. The medial palpebral ligament is attached to anterior lacrimal crest.

The medial palpebral ligament is about 4 mm in length and 2 mm in breadth. Its anterior attachment is to the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and its posterior attachment is the lacrimal bone. Laterally, it is attached to the tarsus of the upper and lower eyelids.

The frontal process of maxilla is a strong plate, which projects upward, medialward, and backward from the maxilla, forming part of the lateral boundary of the nose.

Anatosuchus is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorph discovered in Gadoufaoua, Niger, and described by a team of palaeontologists led by the American Paul Sereno in 2003, in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Its duck-like snout coincidentally makes it resemble a crocoduck, an imagined hybrid animal with the head of a crocodile and the body of a duck.

The surface ectoderm forms the following structures:
The posterior lacrimal crest, with a part of the orbital surface immediately behind it, gives origin to the lacrimal part of the orbicularis oculi and ends below in a small, hook-like projection, the lacrimal hamulus, which articulates with the lacrimal tubercle of the maxilla, and completes the upper orifice of the lacrimal canal; it sometimes exists as a separate piece, and is then called the lesser lacrimal bone.
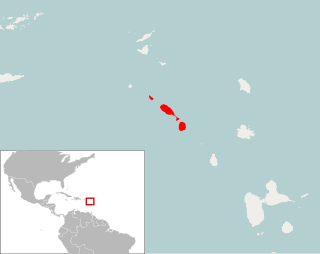
Pennatomys nivalis is an extinct oryzomyine rodent from the islands of Sint Eustatius, Saint Kitts, and Nevis in the Lesser Antilles. The only species in the genus Pennatomys, it is known from skeletal remains found in Amerindian archeological sites on all three islands, with dates ranging from 790–520 BCE to 900–1200 CE. No live specimens are known, but there are several historical records of rodents from Saint Kitts and Nevis that could conceivably refer to Pennatomys. The animal apparently belongs to a group within the tribe Oryzomyini that includes many other island-dwelling species.

Hamipterus is an extinct genus of pteranodontoid pterosaurs from the Early Cretaceous of northwestern China. It is known from a single species, the type species, H. tianshanensis.

Krause's glands, Wolfring's glands and Popov's gland are the accessory lacrimal glands of the lacrimal system of human eye. These glands are structurally and histologically similar to the main lacrimal gland. Glands of Krause are located in the stroma of the conjunctival fornix, and the glands of Wolfring are located along the orbital border of the tarsal plate. These glands are oval and display numerous acini. The acini are surrounded, sometimes incompletely, by a row of myoepithelial cells. Animal studies suggest that the ducts of Wolfring glands have a tortuous course and open onto the palpebral conjunctiva. Like the main lacrimal gland, the accessory lacrimal glands are also densely innervated, but they lack parasympathetic innervation. These glands are exocrine glands, responsible for the basal (unstimulated) secretion of the middle aqueous layer of the tear film. 20 to 40 glands of Krause are found in the upper fornix, and 6-8 glands appear in the lower fornix. There are usually 2 to 5 Ciaccio's glands, and are found along the superior tarsal border of the upper eye lid. Popov’s glands are located within the substance of the caruncle.

















