The concept of a carceral archipelago was first used by the French historian and philosopher Michel Foucault in his 1975 publication, Surveiller et Punir, to describe the modern penal system of the 1970s, embodied by the well-known penal institution at Mettray in France. The phrase combines the adjective "carceral", which means that which is related to jail or prison, with archipelago—a group of islands. Foucault referred to the "island" units of the "archipelago" as a metaphor for the mechanisms, technologies, knowledge systems and networks related to a carceral continuum. The 1973 English publication of the book by Solzhenitsyn called The Gulag Archipelago referred to the forced labor camps and prisons that composed the sprawling carceral network of the Soviet Gulag.

Parole is a form of early release of a prison inmate where the prisoner agrees to abide by certain behavioral conditions, including checking-in with their designated parole officers, or else they may be rearrested and returned to prison.

San Quentin State Prison (SQ) is a California Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation state prison for men, located north of San Francisco in the unincorporated place of San Quentin in Marin County.

Incarceration in the United States is one of the primary means of punishment for crime in the United States. In 2023, over five million people are under supervision by the criminal justice system, with nearly two million people incarcerated in state or federal prisons and local jails. The United States has the largest known prison population in the world. Prison populations grew dramatically beginning in the 1970s, but began a decline around 2009, dropping 25% by year-end 2021.

The prison abolition movement is a network of groups and activists that seek to reduce or eliminate prisons and the prison system, and replace them with systems of rehabilitation and education that do not place a focus on punishment and government institutionalization. The prison abolitionist movement is distinct from conventional prison reform, which is the attempt to improve conditions inside prisons.

Recidivism is the act of a person repeating an undesirable behavior after they have experienced negative consequences of that behavior, or have been trained to extinguish. It is also used to refer to the percentage of former prisoners who are rearrested for a similar offense.

Prison reform is the attempt to improve conditions inside prisons, improve the effectiveness of a penal system, or implement alternatives to incarceration. It also focuses on ensuring the reinstatement of those whose lives are impacted by crimes.

Penal labour is a term for various kinds of forced labour which prisoners are required to perform, typically manual labour. The work may be light or hard, depending on the context. Forms of sentence involving penal labour have included involuntary servitude, penal servitude, and imprisonment with hard labour. The term may refer to several related scenarios: labour as a form of punishment, the prison system used as a means to secure labour, and labour as providing occupation for convicts. These scenarios can be applied to those imprisoned for political, religious, war, or other reasons as well as to criminal convicts.

The crack epidemic was a surge of crack cocaine use in major cities across the United States throughout the entirety of the 1980s and the early 1990s. This resulted in a number of social consequences, such as increasing crime and violence in American inner city neighborhoods, a resulting backlash in the form of tough on crime policies, and a massive spike in incarceration rates.

The United States Medical Center for Federal Prisoners is a United States federal prison in Springfield, Missouri which provides medical, mental health, and dental services to male offenders. It is operated by the Federal Bureau of Prisons, a division of the United States Department of Justice.
In the United States, life imprisonment is amongst the most severe punishments provided by law, depending on the state, and second only to the death penalty. According to a 2013 study, 1 of every 20,000 inhabitants of the U.S. were imprisoned for life as of 2012. Many U.S. states can release a convict on parole after a decade or more has passed, but in California, people sentenced to life imprisonment can normally apply for parole after seven years. Florida leads the country with nearly one quarter of its LWOP prisoners, more than California, New York and Texas combined. The laws in the United States categorize life sentences as "determinate life sentences" or "indeterminate life sentences," the latter indicating the possibility of an abridged sentence, usually through the process of parole. For example, sentences of "15 years to life," "25 years to life," or "life with mercy" are called "indeterminate life sentences", while a sentence of "life without the possibility of parole" or "life with no mercy" is called a "determinate life sentence". The potential for parole is not assured but discretionary, making it an indeterminate sentence. Even if a sentence explicitly denies the possibility of parole, government officials may have the power to grant an amnesty to reprieve, or to commute a sentence to time served.
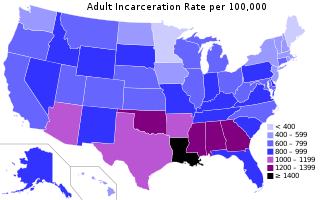
According to the latest available data at the World Prison Brief on May 7, 2023, the United States has the sixth highest incarceration rate in the world, at 531 people per 100,000. Between 2019 and 2020, the United States saw a significant drop in the total number of incarcerations. State and federal prison and local jail incarcerations dropped by 14% from 2.1 million in 2019 to 1.8 million in mid-2020. In 2018, the United States had the highest incarceration rate in the world.

A prison, also known as a jail, gaol, penitentiary, detention center, correction center, correctional facility, lock-up, hoosegow or remand center, is a facility in which convicted criminals are confined involuntarily and denied a variety of freedoms under the authority of the state as punishment for various crimes. Authorities most commonly use prisons within a criminal-justice system: people charged with crimes may be imprisoned until their trial; those who have pled or been found guilty of crimes at trial may be sentenced to a specified period of imprisonment.

Prison healthcare is the medical specialty in which healthcare providers care for people in prisons and jails. Prison healthcare is a relatively new specialty that developed alongside the adaption of prisons into modern disciplinary institutions. Enclosed prison populations are particularly vulnerable to infectious diseases, including arthritis, asthma, hypertension, cervical cancer, hepatitis, tuberculosis, AIDS, and HIV, and mental health issues, such as Depression, mania, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder. These conditions link prison healthcare to issues of public health, preventive healthcare, and hygiene. Prisoner dependency on provided healthcare raises unique problems in medical ethics.

A prisoner is a person who is deprived of liberty against their will. This can be by confinement or captivity in a prison, or forcible restraint. The term usually applies to one serving a sentence in a prison.

Imprisonment began to replace other forms of criminal punishment in the United States just before the American Revolution, though penal incarceration efforts had been ongoing in England since as early as the 1500s, and prisons in the form of dungeons and various detention facilities had existed as early as the first sovereign states. In colonial times, courts and magistrates would impose punishments including fines, forced labor, public restraint, flogging, maiming, and death, with sheriffs detaining some defendants awaiting trial. The use of confinement as a punishment in itself was originally seen as a more humane alternative to capital and corporal punishment, especially among Quakers in Pennsylvania. Prison building efforts in the United States came in three major waves. The first began during the Jacksonian Era and led to the widespread use of imprisonment and rehabilitative labor as the primary penalty for most crimes in nearly all states by the time of the American Civil War. The second began after the Civil War and gained momentum during the Progressive Era, bringing a number of new mechanisms—such as parole, probation, and indeterminate sentencing—into the mainstream of American penal practice. Finally, since the early 1970s, the United States has engaged in a historically unprecedented expansion of its imprisonment systems at both the federal and state level. Since 1973, the number of incarcerated persons in the United States has increased five-fold. Now, about 2,200,000 people, or 3.2 percent of the adult population, are imprisoned in the United States, and about 7,000,000 are under supervision of some form in the correctional system, including parole and probation. Periods of prison construction and reform produced major changes in the structure of prison systems and their missions, the responsibilities of federal and state agencies for administering and supervising them, as well as the legal and political status of prisoners themselves.

The incarceration of women in the United States refers to the imprisonment of women in both prisons and jails in the United States. There are approximately 219,000 incarcerated women in the US according to a November 2018 report by the Prison Policy Initiative, and the rate of incarceration of women in the United States is at a historic and global high, with 133 women in correctional facilities per every 100,000 female citizens. The United States is home to just 4% of the world's female population, yet the US is responsible for 33% of the entire world's incarcerated female population. The steep rise in the population of incarcerated women in the US is linked to the complex history of the war on drugs and the US's prison–industrial complex, which lead to mass incarceration among many demographics, but had particularly dramatic impacts on women and especially women of color. However, women made up only 10.4% of the US prison and jail population, as of 2015.
Marie Gottschalk is an American political scientist and professor of political science at the University of Pennsylvania, known for her work on mass incarceration in the United States. Gottschalk is the author of The Prison and the Gallows: The Politics of Mass Incarceration in America (2006) and Caught: the Prison State and the Lockdown of American Politics (2016). Her research investigates the origins of the carceral state in the United States, the critiques of the scope and size of the carceral network, and the intersections of the carceral state with race and economic inequality.

Decarceration in the United States involves government policies and community campaigns aimed at reducing the number of people held in custody or custodial supervision. Decarceration, the opposite of incarceration, also entails reducing the rate of imprisonment at the federal, state and municipal level. As of 2019, the US was home to 5% of the global population but 25% of its prisoners. Until the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. possessed the world's highest incarceration rate: 655 inmates for every 100,000 people, enough inmates to equal the populations of Philadelphia or Houston. The COVID-19 pandemic has reinvigorated the discussion surrounding decarceration as the spread of the virus poses a threat to the health of those incarcerated in prisons and detention centers where the ability to properly socially distance is limited. As a result of the push for decarceration in the wake of the pandemic, as of 2022, the incarceration rate in the United States declined to 505 per 100,000; meaning that the United States no longer has the highest incarceration rate in the world, but remains in the top 5.

Pinto or Pinta is a member of a Chicano subculture of people who are or have been incarcerated. It is an in-group moniker used to distinguish oneself from the general prison population or from "model inmates." It is a term which embraces the oppositional elements of being a Convicto. The term came from a bilingual play on the Spanish word for penitencia (penitence), since pintos and pintas are people who have spent time in penitentiaries. The term has also been traced to the Spanish word Pintao.












