
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek caeno- (recent), rhabditis (rod-like) and Latin elegans (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it Rhabditides elegans. Osche placed it in the subgenus Caenorhabditis in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised Caenorhabditis to the status of genus.

Ophisops elegans, commonly known as the snake-eyed lizard, is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is endemic to the Mediterranean region and Central Asia. There are nine recognized subspecies.

Oxyloma elegans is a species of small European land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk belonging to the family Succineidae, the amber snails.

Ceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish. It has been described as a "catch all", and a "form genus" used to refer to the remains of a variety of lungfish belonging to the extinct family Ceratodontidae. Fossil evidence dates back to the Early Triassic. A wide range of fossil species from different time periods have been found around the world in places such as the United States, Argentina, Greenland, England, Germany, Egypt, Madagascar, China, and Australia. Ceratodus is believed to have become extinct sometime around the beginning of the Eocene Epoch.

Tritoniopsis elegans is a species of dendronotid nudibranch. It is a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Tritoniidae and is found in the western Indo-Pacific. It was first described by the French naturalist Jean Victoire Audouin in 1826, the type specimen being found in the Red Sea.

François Émile Maupas was a French librarian, protozoologist, cytologist, and botanist. Maupas contributed to ideas on the life cycle and reproduction of the ciliates. He founded the idea, known as the Maupasian life cycle, that some protists had a definite death following sexual reproduction, contrary to contemporary ideas on protists being immortal. He also identified the existence of mating types in ciliates. He developed culture techniques for a number of organisms and described the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, which has since become a widely used model organism in biological studies.
The elegant coral snake is a species of elapid snake, native to southern Mexico and Guatemala. There are two recognized subspecies.

Dismorphia crisia, the crisia mimic white or cloud forest mimic-white, is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1782. It is found from northern Central America to Bolivia and the Amazon basin.
Mionochroma elegans is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Olivier in 1790. It is known from Guadeloupe, Grenada, Dominica, and St. Lucia.
Chrysis elegans is a species of cuckoo wasps found in Southern Europe.

Chromidina elegans is a species of parasitic ciliates. It is a parasite of the cuttlefish Sepia elegans.
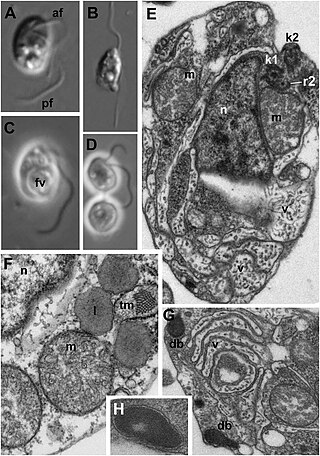
Bigyromonadea is a recently described non-photosynthetic lineage of Heterokonts that at present contains only one species.
Cavilucina is a genus of bivalves in the family Lucinidae.

Catenipora is an extinct genus of tabulate corals in the family Halysitidae, known from the Ordovician to the Silurian.
Tetracus is an extinct genus of gymnures. Species are from the Oligocene of Belgium and France. Fossils can also be found in the Bouldnor Formation in the Hampshire Basin of southern England.

Cattleya × elegans is a hybrid orchid in the subtribe Laeliinae. It is a pseudobulb epiphyte. Its formula hybridae is Cattleya purpurata Van den Berg (2008) × Cattleya tigrina A.Rich. (1848). It is found in South and South-East Brazil.

Cosmacanthus is an extinct genus of placoderms in the extinct family Groenlandaspididae that lived during the Late Devonian in Ireland, the UK, Russia and North America. It was named by Louis Agassiz in 1845.
Crisia is a genus of bryozoans in the family Crisiidae. Some species are known from the fossil record.
Crisia acuta is an extinct species of marine bryozoan within the family Crisiidae. It lived in the Paleogene period in southeastern Australia, with the locality being from Cape Otway. The species is distinguished by the convexity and smoothness of the zoarium in its front surface.











