Related Research Articles

Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a transmission network. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the electrical grid.

A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems.

The Baltic Cable is a monopolar HVDC power line running beneath the Baltic Sea that interconnects the electric power grids of Germany and Sweden. Its maximum transmission power is 600 megawatts (MW).

The HVDC Cross-Channel is the 73 km long high-voltage direct current (HVDC) interconnector that operates since 1986 under the English Channel between the continental European grid at Bonningues-lès-Calais and the British electricity grid at Sellindge. The cable is also known as IFA, and should not be confused with the new IFA-2, another interconnect with France that is three times as long but only half as powerful.
The HVDC Inter-Island link is a 610 km (380 mi) long, 1200 MW high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system connecting the electricity networks of the North Island and South Island of New Zealand together. It is commonly referred to as the Cook Strait cable in the media and in press releases, although the link is much longer than its Cook Strait section. The link is owned and operated by state-owned transmission company Transpower New Zealand.

The National Grid is the high-voltage electric power transmission network serving Great Britain, connecting power stations and major substations, and ensuring that electricity generated anywhere on the grid can be used to satisfy demand elsewhere. The network serves the majority of Great Britain and some of the surrounding islands. It does not cover Northern Ireland, which is part of the Irish single electricity market.
Directlink (Terranora)Interconnector is a mixed buried and above ground 59 kilometre (37 mi) High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) electricity transmission cable route from near Lavertys Gap (28°34′15″S153°27′8″E), 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) Southwest of Mullumbimby, New South Wales and Bungalora (28°15′20″S153°28′20″E) & connected via a 3.5km (2.2mi) AC Overhead Transmission Line to the NorthEast to the Terranora Electrical Substation (28°14′28.3″S153°30′12.7″E) @ Terranora, New South Wales New South Wales in Eastern Australia. The DC cables alternate between above ground in a galvanised steel trough and below ground with depths up to 1m.

A submarine power cable is a transmission cable for carrying electric power below the surface of the water. These are called "submarine" because they usually carry electric power beneath salt water but it is also possible to use submarine power cables beneath fresh water. Examples of the latter exist that connect the mainland with large islands in the St. Lawrence River.

The Shoreham Nuclear Power Plant was a completed General Electric nuclear boiling water reactor located adjacent to Long Island Sound in East Shoreham, New York.

Hydro-Québec's electricity transmission system is an international electric power transmission system centred in Quebec, Canada. The system pioneered the use of very high voltage 735-kilovolt (kV) alternating current (AC) power lines that link the population centres of Montreal and Quebec City to distant hydroelectric power stations like the Daniel-Johnson Dam and the James Bay Project in northwestern Quebec and the Churchill Falls Generating Station in Labrador.
TenneT is a transmission system operator in the Netherlands and in a large part of Germany.
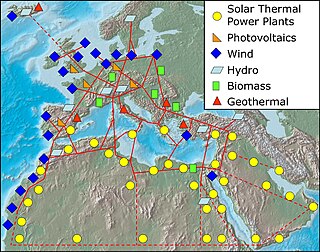
A super grid or supergrid is a wide-area transmission network, generally trans-continental or multinational, that is intended to make possible the trade of high volumes of electricity across great distances. It is sometimes also referred to as a "mega grid". Super grids typically are proposed to use high-voltage direct current (HVDC) to transmit electricity long distances. The latest generation of HVDC power lines can transmit energy with losses of only 1.6% per 1,000 km.
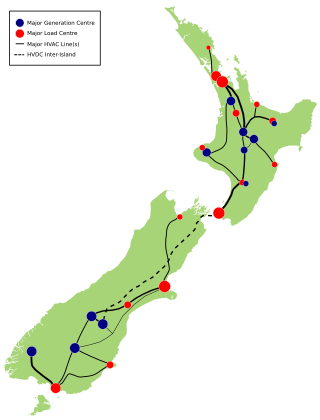
The National Grid is the nationwide system of electric power transmission in New Zealand. The grid is owned, operated and maintained by Transpower New Zealand, a state-owned enterprise, although some lines are owned by local distribution companies and leased to Transpower. In total, the national grid contains 11,803 kilometres (7,334 mi) of high-voltage lines and 178 substations.
BritNed is a 1,000 MW high-voltage direct-current (HVDC) submarine power cable between the Isle of Grain in Kent, the United Kingdom; and Maasvlakte in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
The Neptune Cable is a 500kV and 660 MW high-voltage direct current submarine power cable between Sayreville, New Jersey and Levittown, New York on Long Island. It carries 22 percent of Long Island's electricity. It was developed by Anbaric Development Partners.
The Trans Bay Cable is a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) underwater transmission cable interconnection between San Francisco, California and Pittsburg, California. The 53 mi (85 km) cable under San Francisco Bay and through the Carquinez Strait can transmit 400 megawatts of power at a DC voltage of ±200 kV, enough to provide 40% of San Francisco's peak power needs.
The Champlain Hudson Power Express (CHPE) is a proposed high-voltage direct current (HVDC) underwater and underground power cable project project linking the Quebec area to the New York City neighborhood of Astoria, Queens. Following completion of a review by the New York State Public Service Commission, construction is set to begin in 2022. The line is permitted and expected to be operational in 2025.
COMETA is an undersea electric power transmission system between mainland Spain and the island of Majorca. It connects Morvedre near Valencia and Santa Ponsa near Palma de Mallorca. The project was developed by Red Electrica de España. The project aims were to connect the Balearic Islands with the Spanish peninsular grid, providing a better electrical supply to the two isolated Balearic grids.
An HVDC converter converts electric power from high voltage alternating current (AC) to high-voltage direct current (HVDC), or vice versa. HVDC is used as an alternative to AC for transmitting electrical energy over long distances or between AC power systems of different frequencies. HVDC converters capable of converting up to two gigawatts (GW) and with voltage ratings of up to 900 kilovolts (kV) have been built, and even higher ratings are technically feasible. A complete converter station may contain several such converters in series and/or parallel to achieve total system DC voltage ratings of up to 1,100 kV.
FAB Link is a proposed HVDC Interconnector, spanning the 220 kilometres (140 mi) between France and Great Britain, running close to the island of Alderney.
References
- ↑ Fairley, Peter (April 2005). "TransÉnergie : Playing Two Power Games". Technology Review. Retrieved 2009-03-21.
- ↑ Babcock & Brown Infrastructure (February 28, 2006). "Completion of Acquisition: New England - New York Cross Sound Cable" (PDF). Archived from the original (pdf) on April 1, 2010. Retrieved 2009-11-29.