Related Research Articles

In computing, the Executable and Linkable Format, is a common standard file format for executable files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps. First published in the specification for the application binary interface (ABI) of the Unix operating system version named System V Release 4 (SVR4), and later in the Tool Interface Standard, it was quickly accepted among different vendors of Unix systems. In 1999, it was chosen as the standard binary file format for Unix and Unix-like systems on x86 processors by the 86open project.
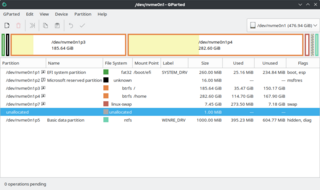
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
The Open Sound System (OSS) is an interface for making and capturing sound in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is based on standard Unix devices system calls. The term also sometimes refers to the software in a Unix kernel that provides the OSS interface; it can be thought of as a device driver for sound controller hardware. The goal of OSS is to allow the writing of sound-based applications that are agnostic of the underlying sound hardware.
The Unix file system (UFS) is a family of file systems supported by many Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is a distant descendant of the original filesystem used by Version 7 Unix.

Unix System V is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. System V Release 4 (SVR4) was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as Unix System Unification, which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV.

cksum is a command in Unix and Unix-like operating systems that generates a checksum value for a file or stream of data. The cksum command reads each file given in its arguments, or standard input if no arguments are provided, and outputs the file's 32-bit cyclic redundancy check (CRC) checksum and byte count. The CRC output by cksum is different from the CRC-32 used in zip, PNG and zlib.

In computing, netstat is a command-line network utility that displays network connections for Transmission Control Protocol, routing tables, and a number of network interface and network protocol statistics. It is available on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems including macOS, Linux, Solaris and BSD. It is also available on IBM OS/2 and on Microsoft Windows NT-based operating systems including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 10.

pkgsrc is a package management system for Unix-like operating systems. It was forked from the FreeBSD ports collection in 1997 as the primary package management system for NetBSD. Since then it has evolved independently; in 1999, support for Solaris was added, followed by support for other operating systems.
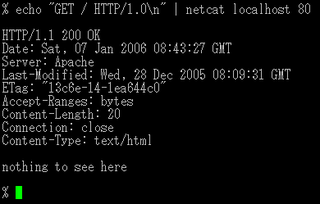
netcat is a computer networking utility for reading from and writing to network connections using TCP or UDP. The command is designed to be a dependable back-end that can be used directly or easily driven by other programs and scripts. At the same time, it is a feature-rich network debugging and investigation tool, since it can produce almost any kind of connection its user could need and has a number of built-in capabilities.

ifconfig is a system administration utility in Unix-like operating systems for network interface configuration.

DTrace is a comprehensive dynamic tracing framework originally created by Sun Microsystems for troubleshooting kernel and application problems on production systems in real time. Originally developed for Solaris, it has since been released under the free Common Development and Distribution License (CDDL) in OpenSolaris and its descendant illumos, and has been ported to several other Unix-like systems.
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1.
OS-level virtualization is an operating system (OS) virtualization paradigm in which the kernel allows the existence of multiple isolated user space instances, called containers, zones, virtual private servers (OpenVZ), partitions, virtual environments (VEs), virtual kernels, or jails. Such instances may look like real computers from the point of view of programs running in them. A computer program running on an ordinary operating system can see all resources of that computer. However, programs running inside of a container can only see the container's contents and devices assigned to the container.
tip is a Unix utility for establishing a terminal connection to a remote system via a modem. It is commonly associated with BSD Unix, as well as other UNIX operating systems such as Sun's Solaris. It was originally included with 4.2BSD. The name may refer to ARPANET's Terminal Interface Processor (TIP), a variant of the IMP, used to connect serial terminals directly with ARPANET.

On Linux, network block device (NBD) is a network protocol that can be used to forward a block device from one machine to a second machine. As an example, a local machine can access a hard disk drive that is attached to another computer.
In Unix-like operating systems, a device file or special file is an interface to a device driver that appears in a file system as if it were an ordinary file. There are also special files in DOS, OS/2, and Windows. These special files allow an application program to interact with a device by using its device driver via standard input/output system calls. Using standard system calls simplifies many programming tasks, and leads to consistent user-space I/O mechanisms regardless of device features and functions.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.

Illumos is a partly free and open-source Unix operating system. It is based on OpenSolaris, which was based on System V Release 4 (SVR4) and the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Illumos comprises a kernel, device drivers, system libraries, and utility software for system administration. This core is now the base for many different open-sourced Illumos distributions, in a similar way in which the Linux kernel is used in different Linux distributions.
References
- ↑ "cu(1)". FreeBSD Manual Pages. The FreeBSD Project. 2017-04-22. Retrieved 2019-05-09.
- ↑ The Insider's Guide To The Universe (PDF). Charles River Data Systems, Inc. 1983. p. 13.
- ↑ "cu - call another UNIX system". Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library. Oracle Corporation. 2013. Retrieved 2019-05-09.
- ↑ "cu(1) - Linux man page". die.net. Retrieved 2019-05-09.