
Bash, short for Bourne-Again SHell, is a shell program and command language supported by the Free Software Foundation and first developed for the GNU Project by Brian Fox. Designed as a 100% free software alternative for the Bourne shell, it was initially released in 1989. Its moniker is a play on words, referencing both its predecessor, the Bourne shell, and the concept of renewal.

A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be scripting languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manipulation, program execution, and printing text. A script which sets up the environment, runs the program, and does any necessary cleanup or logging, is called a wrapper.
grep is a command-line utility for searching plaintext datasets for lines that match a regular expression. Its name comes from the ed command g/re/p, which has the same effect. grep was originally developed for the Unix operating system, but later available for all Unix-like systems and some others such as OS-9.

The cd command, also known as chdir, is a command-line shell command used to change the current working directory in various operating systems. It can be used in shell scripts and batch files.

The mkdir command in the Unix, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems is used to make a new directory. It is also available in the EFI shell and in the PHP scripting language. In DOS, OS/2, Windows and ReactOS, the command is often abbreviated to md.

In Unix-like and some other operating systems, the pwd command writes the full pathname of the current working directory to the standard output.
A background process is a computer process that runs behind the scenes and without user intervention. Typical tasks for these processes include logging, system monitoring, scheduling, and user notification.
xargs is a command on Unix and most Unix-like operating systems used to build and execute commands from standard input. It converts input from standard input into arguments to a command.
In computing, echo is a command that outputs the strings that are passed to it as arguments. It is a command available in various operating system shells and typically used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to the screen or a computer file, or as a source part of a pipeline.
In computing, kill is a command that is used in several popular operating systems to send signals to running processes.

rm is a basic command on Unix and Unix-like operating systems used to remove objects such as computer files, directories and symbolic links from file systems and also special files such as device nodes, pipes and sockets, similar to the del command in MS-DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows. The command is also available in the EFI shell.
The proc filesystem (procfs) is a special filesystem in Unix-like operating systems that presents information about processes and other system information in a hierarchical file-like structure, providing a more convenient and standardized method for dynamically accessing process data held in the kernel than traditional tracing methods or direct access to kernel memory. Typically, it is mapped to a mount point named /proc at boot time. The proc file system acts as an interface to internal data structures about running processes in the kernel. In Linux, it can also be used to obtain information about the kernel and to change certain kernel parameters at runtime (sysctl).
In computing, tee is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) using standard streams which reads standard input and writes it to both standard output and one or more files, effectively duplicating its input. It is primarily used in conjunction with pipes and filters. The command is named after the T-splitter used in plumbing.
In computing, sleep is a command in Unix, Unix-like and other operating systems that suspends program execution for a specified time.
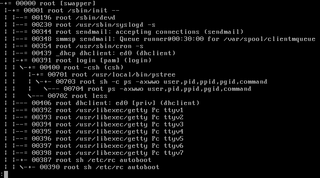
pstree is a Linux command that shows the running processes as a tree. It is used as a more visual alternative to the ps command. The root of the tree is either init or the process with the given pid. It can also be installed in other Unix systems.
pgrep is a command-line utility initially written for use with the Solaris 7 operating system by Mike Shapiro. It has since been available in illumos and reimplemented for the Linux and BSDs. It searches for all the named processes that can be specified as extended regular expression patterns, and—by default—returns their process ID. Alternatives include pidof and ps.
chsh is a command on Unix-like operating systems that is used to change a login shell. Users can either supply the pathname of the shell that they wish to change to on the command line, or supply no arguments, in which case chsh allows the user to change the shell interactively.
The Unix command fuser is used to show which processes are using a specified computer file, file system, or Unix socket.
Toybox is a free and open-source software implementation of over 200 Unix command line utilities such as ls, cp, and mv. The Toybox project was started in 2006, and became a 0BSD licensed BusyBox alternative. Toybox is used for most of Android's command-line tools in all currently supported Android versions, and is also used to build Android on Linux and macOS. All of the tools are tested on Linux, and many of them also work on BSD and macOS.

A Unix-like operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-like application is one that behaves like the corresponding Unix command or shell. Although there are general philosophies for Unix design, there is no technical standard defining the term, and opinions can differ about the degree to which a particular operating system or application is Unix-like.








