
AWK is a domain-specific language designed for text processing and typically used as a data extraction and reporting tool. Like sed and grep, it is a filter, and it is a standard feature of most Unix-like operating systems.

In computing, Bash is an interactive command interpreter and command programming language developed for UNIX-like operating systems. Created in 1989 by Brian Fox for the GNU Project, it is supported by the Free Software Foundation and designed as a 100% free alternative for the Bourne shell (sh) and other proprietary Unix shells.
In computing, the utility diff is a data comparison tool that computes and displays the differences between the contents of files. Unlike edit distance notions used for other purposes, diff is line-oriented rather than character-oriented, but it is like Levenshtein distance in that it tries to determine the smallest set of deletions and insertions to create one file from the other. The utility displays the changes in one of several standard formats, such that both humans or computers can parse the changes, and use them for patching.
In software development, Make is a command-line interface software tool that performs actions ordered by configured dependencies as defined in a configuration file called a makefile. It is commonly used for build automation to build executable code from source code. But, not limited to building, Make can perform any operation available via the operating system shell.
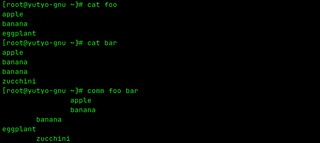
The comm command in the Unix family of computer operating systems is a utility that is used to compare two files for common and distinct lines. comm is specified in the POSIX standard. It has been widely available on Unix-like operating systems since the mid to late 1980s.

A newline is a control character or sequence of control characters in character encoding specifications such as ASCII, EBCDIC, Unicode, etc. This character, or a sequence of characters, is used to signify the end of a line of text and the start of a new one.
The archiver, also known simply as ar, is a Unix utility that maintains groups of files as a single archive file. Today, ar is generally used only to create and update static library files that the link editor or linker uses and for generating .deb packages for the Debian family; it can be used to create archives for any purpose, but has been largely replaced by tar for purposes other than static libraries. An implementation of ar is included as one of the GNU Binutils.
xargs is a command on Unix and most Unix-like operating systems used to build and execute commands from standard input. It converts input from standard input into arguments to a command.
dd is a command-line utility for Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems and beyond, the primary purpose of which is to convert and copy files. On Unix, device drivers for hardware and special device files appear in the file system just like normal files; dd can also read and/or write from/to these files, provided that function is implemented in their respective driver. As a result, dd can be used for tasks such as backing up the boot sector of a hard drive, and obtaining a fixed amount of random data. The dd program can also perform conversions on the data as it is copied, including byte order swapping and conversion to and from the ASCII and EBCDIC text encodings.

tr is a command in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems. It is an abbreviation of translate or transliterate, indicating its operation of replacing or removing specific characters in its input data set.

wc is a command in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems. The program reads either standard input or a list of computer files and generates one or more of the following statistics: newline count, word count, and byte count. If a list of files is provided, both individual file and total statistics follow.
In computing, echo is a command that outputs the strings that are passed to it as arguments. It is a command available in various operating system shells and typically used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to the screen or a computer file, or as a source part of a pipeline.
nl is a Unix utility for numbering lines, either from a file or from standard input, reproducing output on standard output.

The file command is a standard program of Unix and Unix-like operating systems for recognizing the type of data contained in a computer file.
In Unix-like operating systems, find is a command-line utility that locates files based on some user-specified criteria and either prints the pathname of each matched object or, if another action is requested, performs that action on each matched object.
In computing, tee is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) using standard streams which reads standard input and writes it to both standard output and one or more files, effectively duplicating its input. It is primarily used in conjunction with pipes and filters. The command is named after the T-splitter used in plumbing.

In computing, sort is a standard command line program of Unix and Unix-like operating systems, that prints the lines of its input or concatenation of all files listed in its argument list in sorted order. Sorting is done based on one or more sort keys extracted from each line of input. By default, the entire input is taken as sort key. Blank space is the default field separator. The command supports a number of command-line options that can vary by implementation. For instance the "-r" flag will reverse the sort order.
In Unix, Plan 9, and Unix-like operating systems, the strip program is a command-line utility used to remove non-essential information from executable binary programs and object files. This information, which is not required for execution, typically includes debugging data, symbol tables, relocation information, and other metadata. Its primary purpose is to reduce the file size of the binary executable and potentially increase performance. The output of this process is known as a stripped binary.

In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, printf is a shell builtin that formats and outputs text like the same-named C function.

cat is a standard Unix utility that reads files sequentially, writing them to standard output. The name is derived from its function to (con)catenate files . It has been ported to a number of operating systems.










