Related Research Articles

Southern California Edison, the largest subsidiary of Edison International, is the primary electricity supply company for much of Southern California. It provides 14 million people with electricity across a service territory of approximately 50,000 square miles. However, the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, San Diego Gas & Electric (SDG&E), Imperial Irrigation District, and some smaller municipal utilities serve substantial portions of the southern California territory. The northern part of the state is generally served by the Pacific Gas & Electric Company of San Francisco. Other investor-owned utilities (IOUs) in California include SDG&E, PacifiCorp, Bear Valley Electric, and Liberty Utilities.
Blue Oak Energy is an American full-service photovoltaic system design, engineering and construction firm. The company engineers and constructs commercial and utility solar photovoltaic (PV) energy systems in the United States and abroad.

Community Choice Aggregation (CCA), also known as Community Choice Energy, municipal aggregation, governmental aggregation, electricity aggregation, and community aggregation, is an alternative to the investor owned utility energy supply system in which local entities in the United States aggregate the buying power of individual customers within a defined jurisdiction in order to secure alternative energy supply contracts. The CCA chooses the power generation source on behalf of the consumers.
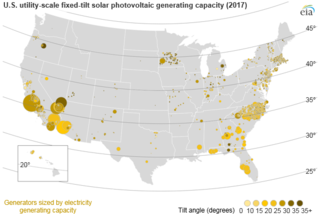
Solar power in the United States includes utility-scale solar power plants as well as local distributed generation, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics. As of the end of 2019, the United States had over 71.3 gigawatts (GW) of installed photovoltaic capacity. In 2018, utility scale solar power generated 66.6 terawatt-hours (TWh), 1.66% of total U.S. electricity. During the same time period total solar generation, including estimated small scale photovoltaic generation, was 96.1 TWh, 2.30% of total U.S. electricity. In terms of total cumulative installed capacity, by year end 2017 the United States ranked 2nd in the world behind China. In 2016, 39% of all new electricity generation capacity in the country came from solar, more than any other source and ahead of natural gas (29%). By 2015, solar employment had overtaken oil and gas as well as coal employment in the United States. In 2016, more than 260,000 Americans were employed in the solar industry.

Topaz Solar Farm is a 550 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station in San Luis Obispo County, California. Construction on the project began in November 2011 and ended in November 2014. It is one of the world's largest solar farms. The $2.5 billion project includes 9 million CdTe photovoltaic modules based on thin-film technology, manufactured by U.S. company First Solar. The company also built, operates and maintains the project for MidAmerican Renewables, a Berkshire Hathaway company. Pacific Gas and Electric will buy the electricity under a 25-year power purchase agreement. According to First Solar, it created about 400 construction jobs.

The California Valley Solar Ranch (CVSR) is a 250 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power plant in the Carrizo Plain, northeast of California Valley. The project is owned by NRG Energy, and SunPower is the EPC contractor and technology provider. The project constructed on 1,966 acres (796 ha) of a 4,365-acre (1,766 ha) site of former grazing land. It is utilizing high-efficiency, crystalline PV panels designed and manufactured by SunPower. The project includes up to 88,000 SunPower solar tracking devices to hold PV panels that track the sun across the sky.

eSolar is a privately held company that develops concentrating solar power (CSP) plant technology. The company was founded by the Pasadena-based business incubator Idealab in 2007 as a developer of CSP plant technology. The company aims to develop a low cost alternative to fossil fuels through a combination of small heliostats, modular architecture, and a high-precision sun-tracking system. In October 2017, an article in GreenTech Media suggested that eSolar ceased business in late 2016.
Martin Next Generation Solar Energy Center is the solar parabolic-trough component of an integrated solar combined cycle (ISCC) 1150 MW plant, in western Martin County, Florida, United States, just north of Indiantown. The project was built by Florida Power & Light Company (FPL). Lauren Engineers & Constructors (Abilene, TX) was the EPC contractor for the project. Its construction began in 2008 and was completed by the end of 2010.

Solar power in California includes utility-scale solar power plants as well as local distributed generation, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics. It has been growing rapidly because of high insolation, community support, declining solar costs, and a Renewable Portfolio Standard which requires that 33% of California's electricity come from renewable resources by 2020, and 60% by 2030. Much of this is expected to come from solar power via photovoltaic facilities or concentrated solar power facilities.

Solar power in New Jersey has grown significantly, increasing from less than 50 megawatts (MW) in 2007 to over 2,800 MW in 2018, such that solar power provided 4.17% of the state's electricity consumption. This is aided by a Renewable Portfolio Standard which requires that 22.5% of New Jersey's electricity come from renewable resources by 2021, and by one of the most favorable net metering standards in the country, along with Arizona, allowing unlimited customers of any size array to use net metering, although generation may not exceed annual demand. Best practices recommend limiting net metering only to the size of the customer’s service entrance capacity. As of 2018, New Jersey has the sixth-largest installed solar capacity of all U.S. states and the largest installed solar capacity of the Northeastern States.

Solar power in Arizona has the potential to, according to then-Governor Janet Napolitano, make Arizona "the Persian Gulf of solar energy". In 2012, Arizona had 1,106 MW of photovoltaic (PV) solar power systems, and 6 MW of concentrated solar power (CSP), bringing the total to over 1,112 megawatts (MW) of solar power. The Solana Generating Station is a 280 MW parabolic trough solar plant which is the largest plant of its type in the world. Solana includes 6 hours of power storage by molten salt. The plant will provide 5% of the power from Arizona Public Service, the state's largest utility.
REC Solar is a solar energy contractor specializing in commercial solar and storage systems, including the installation of commercial solar electric systems in the United States. The company is focused on providing products and services to support commercial, government and utility scale solar photovoltaic (PV) installations.

The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System is a concentrated solar thermal plant in the Mojave Desert. It is located at the base of Clark Mountain in California, across the state line from Primm, Nevada. The plant has a gross capacity of 392 megawatts (MW). It deploys 173,500 heliostats, each with two mirrors focusing solar energy on boilers located on three 459 ft tall solar power towers. The first unit of the system was connected to the electrical grid in September 2013 for an initial synchronisation test. The facility formally opened on February 13, 2014. In 2014, it was the world's largest solar thermal power station.
CleanPowerSF is the City and County of San Francisco's Community Choice Aggregation (CCA) program, whose purpose is to significantly increase the proportion of electrical energy supplied to the San Francisco electrical grid from local renewable sources, decrease San Francisco's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and help combat global climate change, while meeting or exceeding California's Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS). The RPS requires that 33% of energy supplied by "investor-owned utilities, electric service providers, and community choice aggregators" should be from eligible renewable sources by 2020.

The San Luis Valley Solar Ranch is a 30 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station in the San Luis Valley, located near the town of Mosca, Colorado. It was the largest solar facility in the state when it came online at the end of 2011. The electricity is being sold to Public Service of Colorado, a subsidiary of Xcel Energy, under a 20-year power purchase agreement.
Mastec, Inc. is an American multinational infrastructure engineering and construction company based in Coral Gables, Florida. Limited to the engineering, building, installation, maintenance and upgrade of energy, utility and communications infrastructure, including electrical utility transmission and distribution, power generation, natural gas and petroleum pipelines, wireless, wireline and satellite communications, wind farms, solar farms and other renewable energy, industrial infrastructure and water and sewer systems. Its customers are primarily in the utility, communications and government industries. The company's core services are the engineering, building, installing, maintaining and upgrading of infrastructures.

Solar power in Vermont provides almost 11% of the state's electricity as of 2018. A 2009 study indicated that distributed solar on rooftops can provide 18% of all electricity used in Vermont. A 2012 estimate suggests that a typical 5 kW system costing $25,000 before credits and utility savings will pay for itself in 10 years, and generate a profit of $34,956 over the rest of its 25-year life.

Apple Park is the corporate headquarters of Apple Inc., located at One Apple Park Way in Cupertino, California, United States. It was opened to employees in April 2017, while construction was still underway, and has superseded the original headquarters at 1 Infinite Loop, which opened in 1993.

The San Isabel Solar Energy Center is a 30 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station in Las Animas County, Colorado located about 20 miles north of the city of Trinidad. The electricity is being sold to Tri-State Generation and Transmission under a 25-year power purchase agreement. It is the second solar project, following the Cimarron Solar Facility in year 2010, to be added to the utility cooperative's renewables portfolio.
References
- 1 2 Chronos Interactive. "History - Cupertino Electric, Inc" . Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- ↑ Chronos Interactive. "Values" . Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- 1 2 "Cupertino Electric, Inc.: Private Company Information - Businessweek". Businessweek.com. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- ↑ "IBEW Local 332 - Contractor Information" . Retrieved 15 December 2015.
| This article about a United States company or corporation involved in the energy industry is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |