
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by animals and people, by natural forces such as wind and water, and by chemical, thermal, or electrical power, and include a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems.
Kinematics is a subfield of physics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies without considering the forces that cause them to move. Kinematics, as a field of study, is often referred to as the "geometry of motion" and is occasionally seen as a branch of mathematics. A kinematics problem begins by describing the geometry of the system and declaring the initial conditions of any known values of position, velocity and/or acceleration of points within the system. Then, using arguments from geometry, the position, velocity and acceleration of any unknown parts of the system can be determined. The study of how forces act on bodies falls within kinetics, not kinematics. For further details, see analytical dynamics.

A cylinder has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.

A trunnion is a cylindrical protrusion used as a mounting or pivoting point. First associated with cannons, they are an important military development.

In the study of mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed-chain movable linkage. It consists of four bodies, called bars or links, connected in a loop by four joints. Generally, the joints are configured so the links move in parallel planes, and the assembly is called a planar four-bar linkage. Spherical and spatial four-bar linkages also exist and are used in practice.
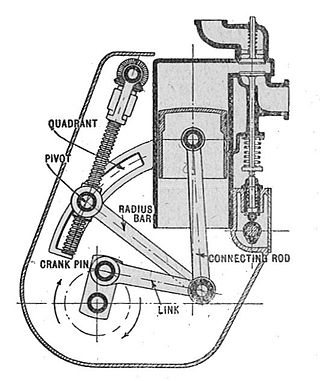
A mechanical linkage is an assembly of systems connected to manage forces and movement. The movement of a body, or link, is studied using geometry so the link is considered to be rigid. The connections between links are modeled as providing ideal movement, pure rotation or sliding for example, and are called joints. A linkage modeled as a network of rigid links and ideal joints is called a kinematic chain.
In fluid dynamics, the Taylor number (Ta) is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes the importance of centrifugal "forces" or so-called inertial forces due to rotation of a fluid about an axis, relative to viscous forces.

A mirror mount is a device that holds a mirror. In optics research, these can be quite sophisticated devices, due to the need to be able to tip and tilt the mirror by controlled amounts, while still holding it in a precise position when it is not being adjusted.

A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or end-effector. Perhaps, the best known parallel manipulator is formed from six linear actuators that support a movable base for devices such as flight simulators. This device is called a Stewart platform or the Gough-Stewart platform in recognition of the engineers who first designed and used them.
Multibody system is the study of the dynamic behavior of interconnected rigid or flexible bodies, each of which may undergo large translational and rotational displacements.
In classical mechanics, a kinematic pair is a connection between two physical objects that imposes constraints on their relative movement (kinematics). German engineer Franz Reuleaux introduced the kinematic pair as a new approach to the study of machines that provided an advance over the motion of elements consisting of simple machines.

Nikolai Aleksandrovich Bernstein was a Soviet neurophysiologist who has pioneered motion-tracking devices and formal processing of information obtained from the use of these devices. He was also one of first psychologists to suggest that behaviour is generative, constructive and not reactive. He was born and died in Moscow.

In engineering, a mechanism is a device that transforms input forces and movement into a desired set of output forces and movement. Mechanisms generally consist of moving components which may include:
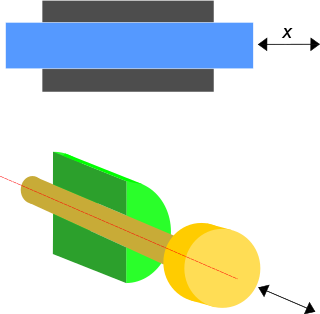
A prismatic joint is a one-degree-of-freedom kinematic pair which constrains the motion of two bodies to sliding along a common axis, without rotation; for this reason it is often called a slider or a sliding pair. They are often utilized in hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders.

A revolute joint is a one-degree-of-freedom kinematic pair used frequently in mechanisms and machines. The joint constrains the motion of two bodies to pure rotation along a common axis. The joint does not allow translation, or sliding linear motion, a constraint not shown in the diagram. Almost all assemblies of multiple moving bodies include revolute joints in their designs. Revolute joints are used in numerous applications such as door hinges, mechanisms, and other uni-axial rotation devices.
A screw joint is a one-degree-of-freedom kinematic pair used in mechanisms. Screw joints provide single-axis translation by utilizing the threads of a lead screw to provide such translation. This type of joint is used primarily on most types of linear actuators and certain types of cartesian robots.

A mechanical joint is a section of a machine which is used to connect one or more mechanical part to another. Mechanical joints may be temporary or permanent; most types are designed to be disassembled. Most mechanical joints are designed to allow relative movement of these mechanical parts of the machine in one degree of freedom, and restrict movement in one or more others.
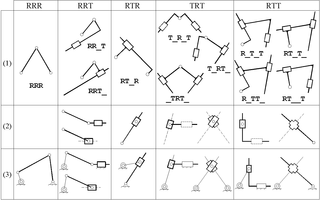
In kinematics, an Assur group is a kinematic chain with zero degree of mobility, which added or subtracted from a mechanism do not alter its original number of degrees of freedom. They have been first described by the Russian engineer Leonid Assur (1878–1920) in 1914.
In robotics, Cartesian parallel manipulators are manipulators that move a platform using parallel-connected kinematic linkages ('limbs') lined up with a Cartesian coordinate system. Multiple limbs connect the moving platform to a base. Each limb is driven by a linear actuator and the linear actuators are mutually perpendicular. The term 'parallel' here refers to the way that the kinematic linkages are put together, it does not connote geometrically parallel; i.e., equidistant lines.

The Jackson cross cylinder (JCC) is an instrument used by ophthalmologists, orthoptists and optometrists in their routine eye examination, particularly in determination of corrective lens power in patients with astigmatism. It is also used for testing near point of the eye.














