Related Research Articles

High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device. HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards.

1080p is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes referred to as 2K resolution, other sources differentiate between 1080p and (true) 2K resolution.
Digital Cinema Initiatives, LLC (DCI) is a consortium of major motion picture studios, formed to establish specifications for a common systems architecture for digital cinema systems.
Avid DNxHD is a lossy high-definition video post-production codec developed by Avid for multi-generation compositing with reduced storage and bandwidth requirements. It is an implementation of SMPTE VC-3 standard.

Avid Media Composer is a non-linear editing (NLE) software application developed by Avid Technology. First introduced in the late 1980s and widely adopted in the 1990s, it has become a prominent tool in the professional editing landscape, particularly in the film, television, and broadcast industries. Media Composer is used in a variety of production environments, including feature films, television shows, documentaries, and streaming service content.
Blackbird is an integrated internet video platform, video editing software, covering non-linear editing and publishing for broadcast, web and mobile.
AVC-Intra is a type of video coding developed by Panasonic, and then supported in products made by other companies. AVC-Intra is available in Panasonic's high definition broadcast products, such as, for example, their P2 card equipped broadcast cameras.
Uncompressed video is digital video that either has never been compressed or was generated by decompressing previously compressed digital video. It is commonly used by video cameras, video monitors, video recording devices, and in video processors that perform functions such as image resizing, image rotation, deinterlacing, and text and graphics overlay. It is conveyed over various types of baseband digital video interfaces, such as HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort and SDI. Standards also exist for the carriage of uncompressed video over computer networks.
Ingex is an open-source (GPL) suite of software for the digital capture of audio and video data, without the need for traditional audio or video tape or cassettes. Serial digital interface (SDI) capture is supported, as well as real-time transcoding. Portions of the software suite also act as a network file server for media files, as well as archiving to LTO-3 data tape. Audio and video media files can also be stored on USB hard drives or Network Attached Storage. The software is heavily used by the BBC, and was developed by the BBC Research Laboratory.

4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 3840 × 2160 with a 16:9 aspect ratio is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 4096 × 2160.
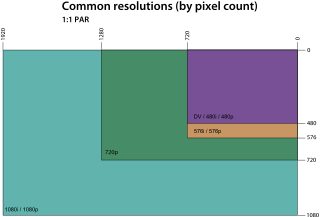
A display resolution standard is a commonly used width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism which is descriptive of its dimensions.

x265 is an encoder for creating digital video streams in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format developed by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). It is available as a command-line app or a software library, under the terms of GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2 or later; however, customers may request a commercial license.

ITU-R Recommendation BT.2020, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2020 or BT.2020, defines various aspects of ultra-high-definition television (UHDTV) with standard dynamic range (SDR) and wide color gamut (WCG), including picture resolutions, frame rates with progressive scan, bit depths, color primaries, RGB and luma-chroma color representations, chroma subsamplings, and an opto-electronic transfer function. The first version of Rec. 2020 was posted on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) website on August 23, 2012, and two further editions have been published since then.
XAVC is a recording format that was introduced by Sony on October 30, 2012. XAVC is a format that will be licensed to companies that want to make XAVC products.

CineAsset was a complete mastering software suite by Doremi Labs that could create and playback encrypted and unencrypted DCI compliant packages from virtually any source. CineAsset included a separate "Editor" application for generating Digital Cinema Packages (DCPs). CineAsset Pro added the ability to generate encrypted DCPs and Key Delivery Messages (KDMs) for any encrypted content in the database. It has since been discontinued, along with CineAsset Player.
Apple ProRes is a high quality, "visually lossless" lossy video compression format developed by Apple Inc. for use in post-production that supports video resolution up to 8K. It is the successor of the Apple Intermediate Codec and was introduced in 2007 with Final Cut Studio 2. Much like the H.26x and MPEG standards, the ProRes family of codecs use compression algorithms based on the discrete cosine transform (DCT). ProRes is widely used as a final format delivery method for HD broadcast files in commercials, features, Blu-ray and streaming.

CinePlayer is a software based media player used to review Digital Cinema Packages (DCP) without the need for a digital cinema server by Doremi Labs. CinePlayer can play back any DCP, not just those created by Doremi Mastering products. In addition to playing DCPs, CinePlayer can also playback JPEG2000 image sequences and many popular multimedia file types.
High Efficiency Video Coding implementations and products covers the implementations and products of High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).

Ultra-high-definition television today includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD, which are two digital video formats with an aspect ratio of 16:9. These were first proposed by NHK Science & Technology Research Laboratories and later defined and approved by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
The TICO codec, an abbreviation for "Tiny Codec," is a video compression technology created to facilitate the transmission of high-resolution video over existing network infrastructures, including both IP networks and SDI infrastructures, the result appears visually lossless. TICO codec was represented in 2013 by the Belgian company intoPIX.
References
- 1 2 "Avid Introduces DNxHR Codec for 2K, 4K, and UHD Editing". Archived from the original on 6 November 2014. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
- 1 2 3 "Avid High-Resolution Workflows Guide - December 2014" (PDF). Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- 1 2 "DNxHR Codec Bandwidth Specifications". avid.force.com. Retrieved 2015-10-09.