Related Research Articles

In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR).

Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airspace. The primary purpose of ATC is to prevent collisions, organize and expedite the flow of traffic in the air, and provide information and other support for pilots.
Aviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Articles related to aviation include:
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as outer space which is the expanse or space outside the Earth and aerospace which is the general term for Earth's atmosphere and the outer space within the planet's vicinity.
Automatic terminal information service, or ATIS, is a continuous broadcast of recorded aeronautical information in busier terminal areas. ATIS broadcasts contain essential information, such as current weather information, active runways, available approaches, and any other information required by the pilots, such as important NOTAMs. Pilots usually listen to an available ATIS broadcast before contacting the local control unit, which reduces the controllers' workload and relieves frequency congestion. ATIS was developed and adopted by the FAA in the mid-1960s and internationally beginning in 1974. Before the adoption of ATIS, this information was routinely disseminated to each aircraft separately, increasing controller workload during periods of high traffic density.
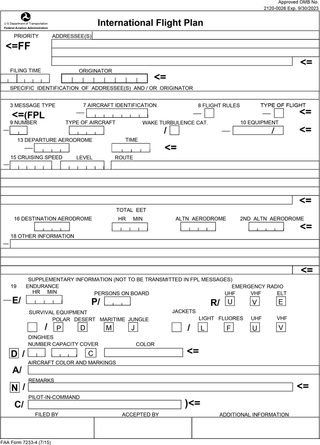
Flight plans are documents filed by a pilot or flight dispatcher with the local Air Navigation Service Provider prior to departure which indicate the plane's planned route or flight path. Flight plan format is specified in ICAO Doc 4444. They generally include basic information such as departure and arrival points, estimated time en route, alternate airports in case of bad weather, type of flight, the pilot's information, number of people on board, and information about the aircraft itself. In most countries, flight plans are required for flights under IFR, but may be optional for flying VFR unless crossing international borders. Flight plans are highly recommended, especially when flying over inhospitable areas such as water, as they provide a way of alerting rescuers if the flight is overdue. In the United States and Canada, when an aircraft is crossing the Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ), either an IFR or a special type of VFR flight plan called a DVFR flight plan must be filed. For IFR flights, flight plans are used by air traffic control to initiate tracking and routing services. For VFR flights, their only purpose is to provide needed information should search and rescue operations be required, or for use by air traffic control when flying in a "Special Flight Rules Area."
A NOTAM is a notice filed with an aviation authority to alert aircraft pilots of potential hazards along a flight route or at a location that could affect the flight. NOTAMs are notices or advisories that contain information concerning the establishment, conditions or change in any aeronautical facility, service, procedure or hazard, the timely knowledge of which may be essential to personnel and systems concerned with flight operations.

A flight service station (FSS) is an air traffic facility that provides information and services to aircraft pilots before, during, and after flights, but unlike air traffic control (ATC), is not responsible for giving instructions or clearances or providing separation. They do, however, relay clearances from ATC for departure or approaches. The people who communicate with pilots from an FSS are referred to as flight service specialists.

Flight planning is the process of producing a flight plan to describe a proposed aircraft flight. It involves two safety-critical aspects: fuel calculation, to ensure that the aircraft can safely reach the destination, and compliance with air traffic control requirements, to minimise the risk of midair collision. In addition, flight planners normally wish to minimise flight cost through the appropriate choice of route, height, and speed, and by loading the minimum necessary fuel on board. Air Traffic Services (ATS) use the completed flight plan for separation of aircraft in air traffic management services, including tracking and finding lost aircraft, during search and rescue (SAR) missions.

The Canada Flight Supplement (CFS) is a joint civil/military publication and is a supplement of the Aeronautical Information Publication. It is the nation's official airport directory. It contains information on all registered Canadian and certain Atlantic aerodromes and certified airports.
In aviation, a standard terminal arrival route (STAR) is a published flight procedure followed by aircraft on an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan just before reaching a destination airport.

Special use airspace (SUA) is a type of special airspaces in the United States designated for operations of a nature such that limitations may be imposed on aircraft not participating in those operations. Often these operations are of a military nature. The designation of SUAs identifies for other users the areas where such activity occurs, provides for segregation of that activity from other users, and allows charting to keep airspace users informed of potential hazards.
An aeronautical chart is a map designed to assist in the navigation of aircraft, much as nautical charts do for watercraft, or a roadmap does for drivers. Using these charts and other tools, pilots are able to determine their position, safe altitude, best route to a destination, navigation aids along the way, alternative landing areas in case of an in-flight emergency, and other useful information such as radio frequencies and airspace boundaries. There are charts for all land masses on Earth, and long-distance charts for trans-oceanic travel.

In United States aviation, a sectional aeronautical chart, often called a sectional chart or a sectional for short, is a type of aeronautical chart designed for air navigation under visual flight rules (VFR).
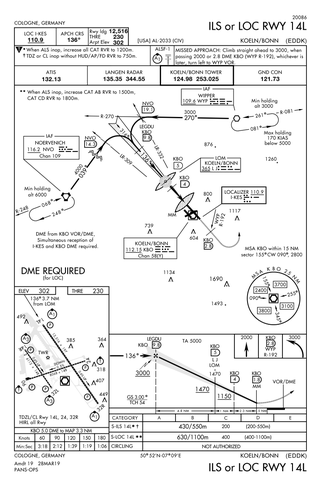
Approach plates are the printed or digital charts of instrument approach procedures that pilots use to fly instrument approaches during instrument flight rules (IFR) operations. Each country maintains its own instrument approach procedures according to International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards.
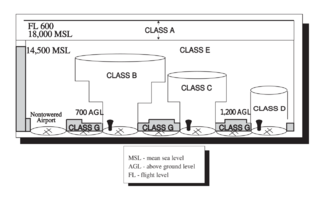
The United States airspace system's classification scheme is intended to maximize pilot flexibility within acceptable levels of risk appropriate to the type of operation and traffic density within that class of airspace – in particular to provide separation and active control in areas of dense or high-speed flight operations.
The Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen) is an ongoing United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) project to modernize the National Airspace System (NAS). The FAA began work on NextGen improvements in 2007 and plans to finish the final implementation segment by 2030. The goals of the modernization include using new technologies and procedures to increase the safety, efficiency, capacity, access, flexibility, predictability, and resilience of the NAS while reducing the environmental impact of aviation.
L-3 SmartDeck - is a fully integrated cockpit system originally developed by L-3 Avionics Systems. and acquired in 2010 by Esterline CMC Electronics through an exclusive licensing agreement.

Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast (ADS-B) is an aviation surveillance technology and form of electronic conspicuity in which an aircraft determines its position via satellite navigation or other sensors and periodically broadcasts its position and other related data, enabling it to be tracked. The information can be received by air traffic control ground-based or satellite-based receivers as a replacement for secondary surveillance radar (SSR). Unlike SSR, ADS-B does not require an interrogation signal from the ground or from other aircraft to activate its transmissions. ADS-B can also receive point-to-point by other nearby equipped ADS-B equipped aircraft to provide traffic situational awareness and support self-separation.

ForeFlight is an electronic flight bag for iOS and iPadOS devices designed to assist pilots and corporate flight departments with flight planning. It includes information about facilities such as airports, NAVAIDs, and air traffic control facilities. It also aids pilots in tasks including flight planning, weather monitoring, and document management, as well as an electronic logbook to help pilots record flight time. The United States, Canada, and Europe are supported regions. The company was founded in 2007 and has since been purchased by Boeing.
References
- ↑ Namowitz, Dan (14 March 2018). "FAA to end DUATS service May 16". Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ↑ "Flight Service Transitions to Leidos Pilot Web Portal". FAASafety. Federal Aviation Administration. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ↑ "Aeronautical Information Manual". Federal Aviation Administration. Retrieved 1 July 2024.